* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Product Management & Marketing Planning
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
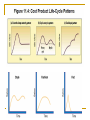
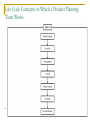
Introduction to Product Management & Marketing Planning Session 1 By: - Neeraj Gupta Product Concept It is anything that can be offered to a market that might satisfy a want or a need.-Marketing Products are purchased as raw materials and sold as finished goods. – Manufacturing Anything that is produced, whether as a result generation, growth, labor, or thought, or by the operation of involuntary causes, of seasons, or of farms, of manufacturers, or of brain. COMPONENTS OF THE MARKET OFFERING The customer will judge the offering by three basic elements : product features and quality, services mix and quality, and price appropriateness. Value based pricing Attractiveness of the market offering Product features and quality Services mix and quality Product Product: Five Levels of Meaning The core benefit level is the fundamental need or want that consumers satisfy by consuming the product or service. The generic product level is a basic version of the product containing only those attributes or characteristics absolutely necessary for its functioning but with no distinguishing features. This is basically a stripped-down, no-frills version of the product that adequately performs the product function. The expected product level is a set of attributes or characteristics that buyers normally expect and agree to when they purchase a product. The augmented product level includes additional product attributes, benefits, or related services that distinguish the product from competitors. The potential product level includes all the augmentations and transformations that a product might ultimately undergo in the future. 1.5 Classification Durable Non Durable Service Product Related Concepts Product Development: -Product development is the process of designing, building, operating, and maintaining a good or service. Product development adds things like pricing, marketing, and customer support to the technology to create a complete product. New Product: -A new product can be defined as a product that is new to the market. ---5 categories New- to-the-world – e.g. new inventions New category –products or services that are new to a firm Additions to product lines -- add products or services that are new to a firm Product Improvements – dettol soap Repositioning target products to new markets for new uses. Product Related Concepts Product Life Cycle: -Products need managing throughout their working lives. This requires deciding: – What products should be created. – The best time to launch them and introduce them to the public. – How to capitalise on a product’s strengths and iron out any weaknesses. – When an older product is past its prime and needs modification or withdrawal from the market Stages in PLC Life Cycle Concepts on Which a Product Planning Team Works Life Cycle Concepts on Which a Product Planning Team Works Initiation Phase:- Product management, Engineering, or Operations submits a request for a new product or service or modification to a existing product or service. Feasibility Phase: -Here idea is explored in more depth to determine the feasibility of requested product or service within scope of Business needs. Design and Plan Phase: -Cross functional team documents all detail pertaining to development of product or service based on their own assessments. Using this a design and plan checklist is presented to governing committee for final approval before moving into the development phase. Blue print is created. Life Cycle Concepts on Which a Product Planning Team Works Development Phase: -Actual engineering of product or service is completed. Then preparatory work for testing and introduction phases is taken care of side by side. Testing Phase: -It is spent certifying the hardware and software changes involved in the product or service. Readiness tests in lab are conducted. Then after this field trials are undertaken. The a go decision at the testing phase decision gate authorises the launch of product or service Product launch Phase: -Deployment of product or service in the market. Operation Phase: -Typically the longest of phases since development of product phase. It requires an organization that can manage the product, track problems and bugs, and respond to customer issues regarding the product in a timely and cost effective manner. Life Cycle Concepts on Which a Product Planning Team Works Decommissioning Phase: -It occurs at the end of Product life cycle. If a product is successful then it is continued otherwise it is taken out of market in such a way that company’s assets are managed properly. Product Upgrade: -After using the product it can be upgraded to a new product that meets their needs or is deprovisioned. Upgrade is desirable. Deprovisioning: -Planned departure of customers by the company who have stopped making further purchases of their products as otherwise they can prove to be unsuccessful. What is Product Mix ? Product Item A specific version of a product that can be designated as a distinct offering among an organization’s products. Product Line A group of closely-related product items. Product Mix All products that an organization sells. Product Line Decisions: Product Mix • Product mix: set of all product lines – Width: # of product lines – Length: # of products in lines Width Detergent Soap # product lines (3) Shampoo ABC – Depth: # of versions of each product carried – Consistency: how closely related the product lines are Adapted from Kotler, McDougall and Picard, p.360 Product Management Product management: -is an organizational lifecycle function within a company dealing with the planning or marketing of a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. Product management and product marketing: -complementary efforts with the objective of maximizing sales revenues, market share, and profit margins. Product Management starts with type of company one works for: Technology-driven Company driven Sales-driven Market-driven Role of a Product Manager Serving as the voice of customer. Indirect management and cooperation with other members of various groups . It has four main tasks: Developing the market requirements document. Managing the product features list. Coordinating activities of different functional groups. Participating in and/or running the launch and post-lunch marketing activities for a product. Goal of Product Management: Ensure market driven whole product offering, Establish competeitive and profitable pricing models. Ensure the existence and support of product distribution Create effective marketing promotions that generate revenue. Aspects of Product Management Product Management:- has a variety of functions and roles. P&L responsibility is used as a key metric for evaluating product managers performance. PRODUCT PLANNING: -is ongoing process of identifying and articulating market requirements that define a product’s feature sets. Defining new products: -ideas for new products can be obtained from SWOT or brainstorming. Gathering Market Requirements: -by analyzing market and consumer trends, competitors, focus groups, corporate spies, trade shows, or ethnographic discovery methods. Building Product Roadmaps, particularly technology roadmaps: used as a tool to predict future path a particular product’s in its lifecycle. Product Life Cycle Considerations: -designing and selling is just a part of story. Every product has to go through a series of steps between the time it is first concieved and the time the manufactured product is retired or discarded. Product Differentiation Product Marketing Product Marketing: - is based on identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer needs effectively and profitably. It encompasses market research, pricing, promotion, distribution, customer care, your brand image and much more. Product Positioning and outbound messaging Promoting the product externally with press, customers, and partners, packaging, trade shows, exhibitions, promotional videos etc. Monitoring the Competition:- Keep your friends close, and your enemies closer. Product Management: Scope Product managers are advocates for the customer's needs and desires. A product manager's responsibilities include the following: Defining and planning product lines and product enhancements Managing product contracts and saleso Setting strategic direction based on customer needs and business goals Interpreting strategic goals into operational tasks Making proposals to senior management regarding implications of proposed plan Serving as a representative to internal and external clients. Taking the leading establishing tactical plans and objectives Developing and implementing administrative and operational matters ensuring achievement of objectives Evaluating risks and trade-offs Proposing contingency plans Analyzing business processes and creating applications to improve or support those processes Branding Working with graphic designers to create look and feel Defining navigational flow and user experience Defining feature sets and scooping releases. Marketing Organization organization that markets one or more systems, applications, and/or components produced by a development organization to potential customer organizations. Responsibilities: Market applications to the customer organization(s). Provide change requests based on customer feedback to the development organization. Act as a source of requirements during the performance of the requirements identification task Marketing Organization Characteristics of Good Marketing Organization: flexible to allow the managers to use any type of marketing structure. It must give possible future growth and acceptable philosophy to the whole concern. Personnel in marketing department must be willing to take various job assignments. Connected with the problem of flexibility is the growth potential. So, the provisions are required for the growth of new products and segments in concern in future. There should be a central philosophy or tradition prevailing in the concern that should be intimated to all. In this way while policies and programmes change, the central philosophy remains guide to the future action. Types Of Marketing Organization Function Oriented (increased efficiency & elasticity) Market Oriented (Regional-for large territories) Product Oriented Customer Oriented:- Classes Of customers: Distributors Retailers Customers Combined Type:- such as Functional with territorial Functional with product oriented Market oriented with product Organizational Structure Functional Organizations: - products needing high level of specialized knowledge require a functionally organized structure e.g. a light weighted matrix organization with a product manager almost is functional. Project Organization- product oriented flows: projects and teams. (Persons leave functions and have to devote time to project tasks they have been assigned). Organizational Structure-another way for classification Product to be developed can be developed by one person. Development department small structured as functional ones. Product less complex with high workload. One whole functional department required for development. Product is most complex. Various disciplines do their own bit for it. Employees cannot work fulltime on one project. Cross-functional team creation in this situation is best alternative. Only problem being those persons in team are working on more than one project at a time. Product complex with high work. Employee participation full time so project organization best suited. Role of a Product Manager The key responsibilities of a product manger may include Managing the entire product line life cycle from strategic planning to tactical activities Specifying market requirements for current and future products by conducting market research Driving a solution set across development teams (primarily Development/Engineering, and Marketing Communications) through market requirements, product contract, and positioning. Developing and implementing a company-wide go-tomarket plan, working with all departments to execute. Analyzing potential partner relationships for the product. Marketing Planning/Strategic Planning Any plan to be formalized has to be in written form as a Marketing Plan. Plan should move from general to specific Output of each stage checked to see the impact it has on all other stages and is amended Mission-Objectives Components of a Marketing Plan Marketing plans vary by industry, by size of company and by stage of growth. The form isn't as important as the process of preparing it. Preparing a marketing plan is a process that makes you think about your business goals and what your marketing strategy will be to achieve those goals. This is an outline of a typical marketing plan: Executive Summary: The executive summary introduces your company and explains the major points of your plan Describes nature of your business States mission and company objectives Describes your team and organization structure Summarize the marketing objectives and strategies of the plan Components of a Marketing Plan Current Situation: -issues being faced, location, target market, competitive environment. Competitor and Issue analysis: Information about other individuals or companies offering similar products as you. Listing key business issues that can be challenges Marketing Objectives: -stating of your objectives along with time frame for achieving them Marketing Strategy: -Plan to achieve your marketing objectives using 4P’s of marketing mix. Action Plan: -what will be done, when it begins and is completed, and who will do what Components of a Marketing Plan Budget: -costs of marketing activities used in marketing plan Measurements: -Describes numerical targets that will measure the results of implementing your marketing plan, including time limits for achieving your goals Supporting Documents: -any document used in other sections to be included in this section as reference Defining the Competitive set Thorough study of your competitors essential for successful positioning of yourself. Choosing competitors is a step by step task. Data collection for each step necessary. Bases of competition Defining Competitors: First in terms of their primary and secondary importance. List basis of competition and key success factors for industry and then define competitive characteristics in terms of : Market Segments Products offered Price/Rates Advertising Programs Distribution channels Levels Of Market Competition Product: - Convincing customers that your brand is better Category: - Convincing customers that your product form is best in a particular category e.g. Cars Generic: -convince customers that particular category is best to satisfy his needs Budget: - convince customers that generic benefits are best use of income as compared to Bikes, scooters, jeeps etc. Factors Determining Competition Price ---Telecom Cost of Production ----because of factors of production Demand in the market Availability of Substitutes---less competitors will enter if more substitutes Number of existing players in the market Barriers to entry--- blocks potential entrants entry Patents Limit Pricing-lowering prices so much that new entrants are at loss Cost Advantage due to economies of scale Advertising and Marketing R&D expenditure Presence of Sunk Costs--- unrecoverable costs International trade Restrictions----tarriffs, quotas etc. Thank You