* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sales promotions
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
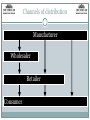
Marketing Marketing Marketing is... ‘The management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably’ Chartered Institute of Marketing Market segmentation Splitting up the market into groups of people with similar needs and characteristics Products and marketing activities can be tailored to the needs the segments Markets can be segmented by age, gender, lifestyle, income and geography Market research Market research is the process of collecting data about customers and competitors. There are two types of market research: Primary research – gathering first hand data e.g. through questionnaires and focus groups Secondary research – gathering existing data e.g. through trade journals and government statistics Marketing Mix The marketing mix The marketing mix is also known as the 4Ps: Product Price Place Promotion Product Product ‘Product’ refers to the functions and features of a good or service Should satisfy the needs of the customer May have a Unique Selling Proposition (USP) ‘Product’ also includes a range of factors such as packaging, quality, warranties, after-sales service and branding Products and brands may suggest certain images e.g. sporty, sophisticated, value Product lifecycle The product lifecycle looks at the sales of a product over time Stages of the product lifecycle Development – high costs but no sales Launch – high expenditure on promotion and product development, low sales Growth – sales increase and product should break even Maturity – sales stabilise, less expenditure on promotion needed, revenue & profit should be high Decline – sales decline, extension strategies can be adopted or the product withdrawn Extension strategies Extension strategies should maintain or increase sales. They include: Modifying the product Reducing the price Adding a feature Extension strategies Promoting to a different market sector Price Price The price of a product will depend on: The cost to make it The amount of profit desired The price competitors charge The objectives of the business The price customers are willing to pay Is there a high demand? Is demand sensitive to changes in price? Pricing strategies and tactics Skimming Launching with a high price when there is little competition, then reducing the price later. Often used with technology. Penetration A low price is charged initially to penetrate the market and build brand loyalty. The price is then increased e.g. introductory offers on magazines. Competitive A similar price is charged to that of competitors’ products. Loss leader Products may be sold at a price lower than the cost to produce it. Often used by supermarkets to encourage people into the store where it is hoped they will buy other products. Pricing strategies and tactics Psychological A price is set which customers perceive as lower than it is e.g. $39.99 instead of $40. Differential Different prices are charged for the same product e.g. bus fares for children are cheaper than adult prices. Cost plus pricing An additional ‘mark-up’ is added to the cost of producing a good or service. Strategic pricing Price is set to position an exclusive product or brand to make it more desirable for consumers, generate demand or demonstrate value Place Place Products should be conveniently available for customers to buy ‘Places’ include: Stores Mail order Telesales Internet The use of e-commerce (promoting and selling on the internet) has grown massively over the last few years Channels of distribution Manufacturer Wholesaler Retailer Consumer Promotion Promotion The aims of promotion are to: Raise awareness Encourage sales Create or change a brand image Maintain or increase market share Types of promotion Above-the-line promotion This uses mass media advertising over which a firm has no direct control e.g. television, radio and newspapers Below-the-line promotion This uses promotional media which the firm can control e.g. direct mail, sales promotions, sponsorship and social media Promotional activities Advertising e.g. TV, billboards and internet. Sales promotions e.g. loyalty cards, BOGOF, discounts & free gifts Sponsorship – a business pays to be associated with another firm, event or cause Direct mailing – promotional material is sent to potential customers by post/email Public relations – building the relationship between the firm and the public by enhancing its reputation Promotional mix Most businesses use a combination of different promotional activities. The chosen promotional mix will depend on: Cost Target market Product Competitors AIDA Promotional campaigns often take into account the AIDA model: Awareness - raising awareness of a product Interest – exciting interest in the product Desire – creating desire for the product Action – encouraging a purchase