* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Distribution
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
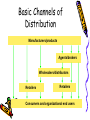
Distribution Strategy Introduction “Marketing channels are sets of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption” Philip Kotler Functions of a Distribution Channel • The main function of a distribution channel is to provide a link between production and consumption. Importance of Distribution Decision • Firms market share • Market penetration Decisions In Physical Distribution Systems • • • • Order processing Warehousing Inventory Transportation Distribution - types of distribution intermediary • • Distributors Distributors have a similar role to wholesalers – that of taking products from producers and selling them on. They also usually have a much narrower product range. Distributors are often involved in providing after-sales service. Wholesalers Wholesalers stock a range of products from several producers. The role of the wholesaler is to sell onto retailers. Wholesalers usually specialise in particular products. Franchises Franchises are independent businesses that operate a branded product (usually a service) in exchange for a licence fee and a share of sales. Agents Agents sell the products and services of producers in return for a commission (a percentage of the sales revenues) •Retailers •Retailers operate outlets that trade directly with household customers. Retailers can be classified in several ways: • Type of goods being sold( e.g. clothes, grocery, furniture) •Type of service (e.g. self-service, counter-service) • Size (e.g. corner shop; superstore) • Ownership (e.g. privately-owned independent; publicquoted retail group • Location (e.g. rural, city-centre, out-of-town) • Brand (e.g. nationwide retail brands; local one-shop name) Number of Channel Levels • • • • • Size of the market Service requirement Complexity of product Price Order lot size Basic Channels of Distribution Manufacturers/products Agents/brokers Wholesalers/distributors Retailers Retailers Consumers and organizational end users Transaction Cost by Channels As the value-added increases, the cost of transaction also increases • Direct marketing channels—low valueadded; low cost of transactions e.g. ecommerce, telemarketing • Indirect marketing channels—medium value-added; medium cost of transactions e.g. retail stores, distributors • Direct sales channels—high value-added; high cost of transactions e.g. own sales force Distribution Objectives • Minimize total distribution costs for a given service output • Determine the target segments and the best channels for each segment • Objectives may vary with product characteristics – e.g. perishables, bulky products, nonstandard items, products requiring installation & maintenance Role of Intermediaries • • • • • Information Price stability Promotion Financing Title Factors Influencing Distribution Decision • • • • Marketing Mix Strategy External Environmental Factors Market Characteristics Consumer Preference And Behaviour Marketing Mix Strategy • Long term strategic pricing plan determines distribution through high margin outlets or high volume outlets • Product characteristics • Image of the product • After sales service External Environmental Factors • Government policy • State of the economy • Infrastructure development Market Characteristics • No of customers • Average purchase • Type of customers Aligning Channels With How Customers Buy • • • • Identify customers’ channel preferences and buying behavior Tabulate channel selection to key buying criteria Provide flexible channel options Monitor (and respond to) changes in buying behavior Distribution-Scope Strategies • Exclusive Distribution – Limiting the distribution to only one intermediary in the territory • Intensive distribution – Distribute from as many outlets as possible to provide location convenience • Selective distribution – Appoint several but not all retailers Example of Exclusive Distribution • LEICA was officially appointed Jebsen & Jebsen Marketing as the exclusive distributor for Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia and Brunei • A main factor in choosing J&J was its expertise in “high-quality technical products on the consumer market.” Source: Smartinvestor, Singapore Ed. June 2000 Exclusive Distribution: Advantages • Maximize control over service level/output • Enhance product’s image & allow higher markups • Promotes dealers loyalty, better forecasting, better inventory and merchandising control • Restricts resellers from carrying competing brands Exclusive Distribution: Disadvantages • Betting on one dealer in each market • Only suitable for high price, high margin, and low volume products Example of Intensive Distribution • Newspapers • Most fast moving consumer goods you see in the newsstand • Photo processing shops Intensive Distribution • Advantages: – Increased sales, wider customer recognition, and impulse buying • Disadvantages: – Characteristically low price and lowmargin products that require a fast turnover – Difficult to control large number of retailers Example of Selective Distribution Daewoo have 2 distributors in Singapore • “Starsauto, part of a larger Indonesian group, represents Daewoo’s traditional line of sedans. • Homegrown family-owned JTA Motors market Daewoo’s offroad vehicles like the Musso and Korando, and an upmarket model called the Chairman. (Source: BT, Motoring, Feb4/1999) Selective Distribution • Advantages: – Better market coverage than exclusive distribution – More control and less cost than intensive distribution – Concentrate effort on few productive outlets – Selected firms capable of carrying full product line and provide the required service Selective Distribution (cont’d) • Disadvantages: – May not cover the market adequately – Difficult to select dealers (retailers) that can match your requirement and goals Multiple-Channel Strategy Using two or more different channels to distribute goods and services • Why? – Permits optimal access to each market segment – Increase market coverage, lower channel cost and provide more customized selling • What to look out for? – More channels usually means more conflict and control problems Complementary Channels Each channel handles a product or segment that is different or noncompeting e.g. • Toyota Lexus • Magazine distributions Competitive Channels The same product is sold through two different and competing channels e.g. – Non-prescriptive drugs – Electronic goods • Why? To increase sales • What to look out for? – Over extending yourself – Dealers’ resentment – Control problems Modifying Distribution Strategies Modify when the following changes occur: • Consumer markets and buying habits • Customer needs • Competitor’s perspectives • Relative importance of outlet types • Manufacturer’s financial strength • Sales volume level of existing products, and • The marketing mix Channel-Control Strategy • Vertical Marketing System (VMS) – Also known as centrally coordinated, professionally managed and centrally programmed network systems – The emerging trend in ASPAC replacing existing conventional marketing channels – Classified into corporate, administered and contractual VMS Channel-Control Strategy (cont’d) Horizontal Marketing System • One company putting together different resources to exploit a marketing opportunity. • Eg. ITC E-choupals • Aqua, Soya, Planters.net.com set up in A P. M P and Karnataka. Competitive Advantage of Channels • Traditional means of achieving competitive advantage is through products but can be easily copied • Low-cost as a competitive advantage – Also suffer from sustainability • Brands as competitive advantage – Only if you are a strong brand • Marketers are turning more and more to channels as a competitive advantage e.g. Dell Computer Source: The Channel Advantage by Friedman and Furey