* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of services
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Subscription box wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
E-governance wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
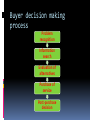
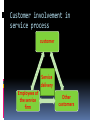
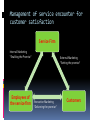
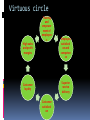
CLASSIFICATION OF SERVICES Classification based on the nature of service act Tangible actions towards customers Passenger transportation Health care Beauty saloon Restaurants Tangible actions towards customers’ possessions Freight transportation Industrial equipment repairs Laundry and dry cleaning Lawn care Veterinary care Classification based on the nature of service act (contd..) Intangible actions towards customers’ intellect Education Broadcasting Theaters Museum Intangible actions towards customers’ assets Banking Legal services Accounting Security insurance Classification based on the nature of service act (contd..) Key questions: Does the customer need to be present physically throughout the services? Does the customer have to be present only to initiate or terminate the transaction? Is customer’s presence not required at all? Is a customer changed as a result of the service? Classification based on the type of relationship the customer has with the service provider Continuous delivery/Membership related Insurance Telephone subscription College enrollment Banking Trade associations Continuous delivery/Without formal relationship Radio station Police protection Public highway Classification based on the type of relationship the customer has with the service provider (contd..) Discrete transaction/ Membership related Long distance phone calls Theater series subscriptions Commuter ticket or pass Discrete transaction/ without formal relationship Car rental Mail service Toll highway Pay phone Movie theater Public transportation Classification based on the type of relationship the customer has with the service provider (contd..) Key questions: Can anything be done to move informal to member relationship? Where can there be tradeoff between pricing and usage rates? Classification based on the scope for customization and judgment in service delivery High judgment/ High customization Professional services Surgery Beautician Plumber High judgment/Low customization Education Preventive health care programs College food services Classification based on the scope for customization and judgment in service delivery Low judgment/High customization Telephone services Hotel services Retail banking Low judgment/Low customization Public transportation Routine appliance repair Movie theater Spectator sports Classification based on the scope for customization and judgment in service delivery Key questions: Is it desirable to limit customization and get benefited by standardization and economies of scale? Should customization be increased to reach wide range of customers? Should service be simplified so that less judgment is required by the contact person? Should service be updated in order to capitalize on the expertise of the staff? Classification based on the nature of demand and supply for the service Peak demand met without major delay/Wide fluctuation Electricity Natural gas Telephone Hospital maternity services Police and fire emergencies Peak demand met without major delay/Narrow fluctuations Insurance Legal services Banking Laundry and dry cleaning Classification based on the nature of demand and supply for the service Peak demand met with delay/ wide fluctuations Accounting and tax preparations Passenger transport Hotel, Motel Restaurant Theater Peak demand met with delay/ narrow fluctuations Similar to without delay but where the scale of operations is very small comparitively Classification based on the nature of demand and supply for the Keyservice questions: What is the nature of demand fluctuation? Does it have a predictable cycle? What are the underlying causes for these fluctuations? Could marketing effect a change? What opportunities exists to change the level of supply? Should alternative strategies be adapted for adopting differential pricing? Should a new mix of strategies be experimented with, involving both capacity and price? Classification based on the method of service delivery Customer to organization/ Single site Theater Saloon Customer to organization/Multiple sites Bus services Fast food chain Organization to customers/Single site Lawn care service Pest control Taxi Classification based on the method of service delivery Organization to customers/Multiple site Mail delivery Emergency repairs At an arm distance/Single site Credit card company Local TV station At an arm distance/Multiple site Broadcast network Telephone company Classification based on the method of service delivery Key questions: Should the service be delivered at a single site or multiple sites? What is the most convenient type of transaction for the customers? Would the service quality improve or deteriorate with the type of change in interaction? Can suitable intermediaries be used in order to establish multiple outlets? MARKETING MIX Elements of the service marketing mix Product Price Promotion Place People Process Physical evidence Product ( Service package) Services are products. Even though intangible, they are things Consumer services: Shoe repair, dry cleaning and clothing alterations Shopping services: Insurance, banking, airline travel and automotive repairs Specialty services: Legal services, medical care, hair styling Conceptualization of the service concept Customer benefit concept: Customers are not buying goods. They are buying specific benefits and values Purchase bundle comprises of: Physical items- tangible elements that come with services Sensual benefits- those experiences which hits one or more of customer’s senses ex: aroma, taste, ambiance. Psychological benefits- which are determined by the customer subjectively. Service concept The general benefits the service provider will offer Core benefits Expected benefits Augmented services Potential services Service offer and service package It spells out in more detail those services to be provided, how they will be provided and to whom It is the elements that make up the total service package, including both the tangible and intangible components of the service. Service delivery system How the service is provided to the consumer. This speaks about the interaction between the customer and the service provider and the interaction between the customer and the service facility. It is a carefully designed blueprint that describes how the service is rendered to the customers. Analysis of the service Basic framework, services are classified into: Core services Secondary services But, the managerial perspective classifies it as: Core service: is the reason for being in the business Facilitating services: they are the support services which are used to add value to the core service. Reception, check-in service etc Supporting service: are used as a means of competition only. Without them, the core service can be used but the total service package may be less attractive. Price A customer pays for some product or service because of its ability to satisfy some specific need or want. Price is the value attached to the product by the service provider and it must compliment with the value attached by the consumer Managerial tasks in pricing involves Establishing pricing objectives Identifying the factors governing the price Determining the methods of pricing Formulation of pricing strategies and policies Price is service is also called as Professional service- fees or retention charges Transport- fare Insurance- premium Clubs- subscription, membership Hotel- tariff, rent etc Special issues to be considered Since service is intangible, many service firms portray their quality as the value for the customers’ money A service provider always uses price as a tool to manage the demand In certain cases, a customer may have to spend time, exert physical efforts or bear psychic cost. So the marketer has to include these intangible aspects of the cost related factors while fixing the price In some service industries especially public sector, price cannot be used as a tactical tool as the Govt. determines the price Pricing strategies Most marketers use competitive pricing Some firms who like to ration the supply would charge a higher price than the market price Higher price can also serve as an indication about the higher perceived quality Pricing strategies Flexible pricing is more prevalent in service sector than in other fields Some service firms either do not have a fixed price list or do not follow it in making price quotations Some firms mainly try to meet competition, some firms attempts to use tables of standard costs and a few even attempt to bargain with the customers. Most service marketers appear to have a definite profit margin in mind when quoting prices A Pricing decision maker should consider: Set annual profit and sales margin Target a definite price margin while quoting prices for each job Determine and understand their cost structure Review and update their price schedules regularly Work to secure higher rather than lower average price Strive for greater price flexibility Promotion It is a combination of strategies that an organization uses to communicate the service benefits to customers and influence them to buy their services They don’t sell any of their products. Instead, they sell the dreams and experience that the customer would want to have by availing a service McDonald’s, makemytrip.com, axis bank etc Promotion mix Advertising Personal selling Direst mails Sales promotion Publicity Word of mouth Corporate identity Advertising Experience Beliefs Values Policies Process Customer oriented aspects Personal selling The service provider has to be utmost knowledgeable Telephone orders Outbound tele-marketing Sales support staff Delivery personnel Direct mails Medicines Medical insurance These direct mails also play the role of follow- ups to track the response of the customers to the promotional activities of the company Sales promotion Sampling, display, demonstration becomes difficult Premiums Contests Sign-up rebates Publicity News release Stage activities Press conferences Sponsorship Word of mouth Customers are closely involved in service delivery and they tend to talk about their service experience to the potential customers An outsider promoting a company without any monetary gains can add more value and trust in the minds of the prospective customers Corporate identity Refers to the use of distinctive colours, symbols Lettering in prominent visible elements such as: Signage Vehicle Uniform Stationary To provide a unifying and recognizable theme linking all the firm’s operations Place Place no more means a geographical location where buyers and sellers meet. But in services, service being intangible, the service provider has to be present at the time of the delivery of services. At the same time, certain services like mail and ATM do not require the presence of the service provider Distribution is he provision of personal service and information to the customer. It adds value to the service The strategies involved in making the services available and accessible to the customer, will focus on two major factors: Where should he service be made available- the choice of location? Who should deliver the service- the choice of channel? Importance of location in pricing Who the target customers are? What is the degree of interaction required between the provider and customer in the delivery of the service? To what extent convenience of accessibility will affect customer decision making regarding use of the service? Is the service technology-based or people-based? How do competitors operate their service? Can new system and technology be used to improve existing location decision? Modes of selling Directly to the customers Use an intermediary who act on behalf of the buyer or seller- the intermediary may be an agent or a contracted franchise People The problem lies in the inseparability of the production consumption interface The satisfaction of not only the recipient of the service, that is the customer, but also the providers of the service, that is the company’s own personnel becomes extremely important Different roles of the service personnel Primary- where the service is actually carried out by the service provider Ex: Teachers, Consultants, Doctors, Lawyers etc Facilitating- where employees facilitate the service transaction and participate in it. Ex: Bank counter staff, Waiter at a hotel, Front office personnel, compounder etc Ancillary- where the employees helps to create the service exchange but is not part of it. Ex: travel agent, insurance agent etc Level of presence of the service personnel Customer contact employees These come in contact with the customers in the process of the service delivery They are also called as the frontline staff or “boundary spanners” These have a great influence on the customers’ perception about the service as the customers try to find tangibility of service in them As they influence the customers a lot, they are marketers too There might be either high contact or low contact Support personnel or non-contact personnel These do not come in contact with the customers Chefs in the hotel, laundry staff in the hotel etc They possess high technical skill and have high competency level They may be management support or technical support Without these people the customer contact employees cannot perform Human resource planning in service involves: Hire the right people Develop people to deliver service quality Provide needed support system Retain best people Internal marketing The key element of healthy business, is the individual contribution of every employee, both contact and support to the ultimate result of increase in company value Process It is concerned with the way in which the service is delivered How the personnel delivers the service Added value of the service becomes an important competitive weapon in differentiating the service Ex: Banks. Storing money is the basic activity but they introduced so many added services like ATMs, Debit Cards, Over drafts etc Many benefits from service occur not so much as a result of what is offered, but, in the way in which it is offered Designing a service process Location Facility design and layout for effective customer and work flow Procedure and job definitions for service providers Measures to ensure service quality Extent of customer involvement in the service delivery Equipment selection if it is equipment based service delivery Physical evidence Since the service is intangible, it is important for the client to search for tangible or physical clues which enable them to evaluate the service Physical evidence verifies either the existence or the completion of a service Categorization Peripheral evidence Is usually possessed as part of the purchase of a service It has little or no independent value Ex: a Cheque book, an ATM card, Napkins etc Essential evidence It cannot be possessed by the consumer It may be so dominant in its impact on service purchase and use that it must be considered virtually an element in its own right Ex: transport vehicle, office premise, staff uniform etc product place promotion Price people Process Physical evidence Physical attributes Channel type Promotion blend Flexibility Employee research Flow of activitiescustomized/standa rdized Facility design Quality level Outlet location Sales people: number, selection, training, incentives Price level Training No. of stepssimple/complex Aesthetics Product lines Intermediaries Advertising: targets, media types, types of ads Terms Motivation Level of customer involvement Functionality Branding Segmentation Sales promotion Differentiation Rewards Ambient conditions Positioning Franchising Publicity Discounts Teamwork Equipment New services Managing channels Direct marketing allowances Communicating culture and values Signage Motivating channel members Employee uniform and appearance Business card Statement guarentees CONSUMERS IN SERVICE INDUSTRY Introduction Consumer purchased goods/services based on their mental and economic forces. The mental forces creates desires and wants to satisfy pride, fear, love, fashion etc Economic forces included the purchasing power Fundamentals of marketing concept: The service provider should first determine the needs and expectations of the target group of customers Organize the input to deliver the service Achieve customer satisfaction to earn profits Managing customer relationship and building loyalty Service firms’ problems: How to create and deliver superior service? How to sustain service improvement effortsin short, how to build “customized” organization? Model of buyer behaviour marketing stimuli other stimuli product economic price technology place cultural promotion political buyer's black box buyer characteristics buyer's response product choice buyer's decision making process dealer choice purchase timing buyer's response Buyer characteristics Cultural factors Values, practices, customs, social class etc Social factors Family, friends, relatives, colleagues, reference groups etc Personal factors Age, life cycle stage, occupation, economic circumstances, life style etc Psychological factors Motive, perception, learning etc How do customers learn about the services offered for sale? How do they learn to recognize and recall these products and services? What process they develop in buying and consuming habits? Related needs at a hotel Self actualization The pride of being at the right place A place to feel wanted, loved a warm and friendly greeting Need for room or shelter (relieving concern & anxiety) Guests looking for restaurant, bar and room service Buyer decision making process Problem recognition Information search Evaluation of alternatives Purchase of service Post-purchase decision Problem recognition The need may be triggered by internal or external stimuli The intensity of the need will indicate the speed with which the buyer will try to fulfill the want The buyer should identify the stimuli, which induces interest in the service and develop marketing programs based on the stimuli This close knowledge of customers can be found through marketing research, in its various forms Information search When the consumers are not aware of the type of service that can best satisfy the need, how and where it an be secured, they will have to search for the relevant information The consumer gets these info from family, friends, reference groups, their past experience with the service firms etc and also from marketers in the form of advertisements, sales promotions etc This increases the awareness of the availability of the services and its attributes In services, the customer relies most on the personal sources Evaluation of alternatives The basic elements in the process of evaluation are Distinct service features Image of the service provider, Quality and price The major challenge of the service provider is to research customer expectations and demands in such a situations and offer more personalized services to these customers. Ex: Hotel:- food quality, menu variety, price, atmosphere and convenience etc Purchase of service The purchase of a service is an experience which, lead to the satisfaction of customer needs. The success of the service delivery depends on the service encounter The service encounter involves the interaction between the customer and the service provider Therefore, apart from motivating the staff, the service provider must also consider the moods and emotions of the customer and should attempt to influence those moods and emotions in a positive way Purchase of service (contd.) The service provider must anticipate, acknowledge and deal with the heterogeneous customers who have the potential to be incompatible. The service provider can also bring the homogeneous customers together and solidify relationship between them Post purchase evaluation Only after experiencing the service, the customer will be able to judge the service quality, in relation to his expectation and actual service delivered In some cases like medical diagnosis, legal services, the customers may find it difficult to judge the service rendered even after going through the service experience Customer complain less frequently about those services which requires their participation too Comparison of consumer and organizational buying behaviour Organizations buy services for profit maximization, reducing costs, meeting employee needs, and satisfying legal obligations. While, individuals buy services for their own need satisfaction. More people involved in organizational buying. There might be several influencers. The degree of influence is relatively less in case of individual buying even though there might be several influencers involved Organizational purchase in based on more formal routine like purchase policies, constraints and requirements by the organization. This does not apply to individual customers Comparison of consumer and organizational buying behaviour Poor service to individual may lead to dissatisfaction but, for the business, it may lead to losses To retain organizational customers, the service firms believe in long term relationship building, whereas, it prefers service bundling to retain individual customers Customer involvement in service process customer Service delivery Employees of the service firm Other customers Degree of customer involvement in service process Low level participation: only physical presence. Ex: Airline travel, entertainment concert. There are standardized services Medium level participation: customer needs to give information to customize the service. Ex: hair cut, full service restaurants, some consultancies. High level participation: here the customer has to participate in the generation of the service. Ex: personal training, weight loss programs. Effects of other customers in service process and delivery system The customer may sometimes interact with the other customers in the service delivery as they may receive the service simultaneously Or even as they may have wait at the service premise for their turn to come They may impact the service positively or negatively Positive: knowledgeable co-customer, health clubs, holiday resorts where they may support each other Negative: crying babies in the restaurant, smoking co-customers, noisy or unruly groups Role played by the customers in the service delivery Customer as co-producer Ex: Consultancy Customers as contributor to service quality, value and satisfaction Ex: Education Customers as competitors Ex: Child Care, Catering for staff, Business legal service etc. Management of service encounter for customer satisfaction Service Firm Internal Marketing “Enabling the Promise” Employees of the service firm External Marketing “Setting the promise” Interactive Marketing “Delivering the promise” Customers Customer evaluation of service delivery The customer perception of the service quality can be judged in two aspects: technical quality The service product, competence of the service provider in the form of skill, production facilities and equipment in the delivery of the service Refers to what the customers receive in heir interaction with the firm. These are quantifiable hence can be measured to some extent Hence more attention is given to this aspect Ex: food in the restaurant, transportation in the airlines But customers are not interested in what is just what is being delivered but also how it is delivered. This leads us to the next dimension of quality- functional quality Customer evaluation of service delivery The customer perception of the service quality can be judged in two aspects: Functional quality Relates to the behaviour of the employees and the manner in which the production facilities are used. It portrays the credibility of the service provider to serve the customer better. Thus, functional quality refers to how the service is delivered. It includes attitude, appearance of the personnel and approachability. Rude behaviour of receptionist, sloppy of the waiter can reverse the impression. Functional quality can be judged only on relative basis Both technical and functional qualities have a strong influence on the overall impression of the quality of the service Expected service quality Factors influencing: Personal needs External communication of the service provider Word of mouth Past experience Perceived service quality Five criteria: Tangibles Responsiveness Empathy (Human Touch) Assurance Reliability Responsiveness shows willingness to meet customer needs and empathy indicates willingness to go beyond customer needs. Customer satisfaction and service quality leads to: It is linked to customer loyalty and relationship commitment Highly satisfied customers promote positive word of mouth Hence, this lowers the cost of attracting new customers Satisfied customers are less susceptible to competitive offerings Market segmentation and targeting Basis for segmentation: Demographic Psychological Behavioural Criteria to evaluate choice of target market: Profit projection, size and growth options in the market The accessibility of the market for communication and service delivery Availability of substitute products and the strength of competitors Compatibility with the firm’s objectives and resources Alternative strategies Undifferentiated marketing: it ignores segmentation and attempts to appeal to the whole market with a single strategy and brand. Differentiated marketing: concentrating on multiple segments with tailor made strategies for each segment Concentrated marketing: it caters to the specific needs of one well defined market segment only Expanded service pyramid Platinum Loyal and Profitable Customers Gold Iron Lead Least Profitable Customers Relationship marketing and customer loyalty Transaction marketing Relationship marketing Focus is on a single Focus is on retention of transaction of sale Limited customer commitment Short term orientation Salesperson is the main interface between seller and customer Quality is the responsibility of the production team customers High customer commitment Long term orientation Multiple levels of relationship between seller and customer Quality is the responsibility o the departments Customer Relationship Management (CRM) With an effective CRM, a business can increase revenues by: Providing services and products that are exactly what customer wants Offering better customer service Cross selling products more effectively Helping sales staff close deals faster Retaining existing customers and discovering new ones Customer service can be improved by Providing online access to product information and technical assistance around the clock Identifying what customers value and devising appropriate service strategies for each customer Providing the mechanisms for managing and follow-up sales calls Tracking all contacts with a customer Customer service can be improved by Identifying potential problems before they occur Providing a user-friendly mechanism for registering customer complaints Providing a mechanism for handling problems and complaints Providing a mechanism for correcting service deficiency Storing customer interest in order to target customers selectively Providing mechanisms for managing and scheduling maintenance, repairs and on-going support The increased profitability associated with customer retention efforts occur because: The cost of acquisition occurs only at the beginning of a relationship Account maintenance costs decline as a percentage of total cost Long term customers may be less inclined to switch They may initiate free word of mouth They are more likely to purchase ancillary products They make it difficult for the competitors to enter the market and establish themselves Leads to ease in servicing as they are familiar with the service Makes the employees’ job easier Virtuous circle Training and empower ment of employee s High sales and profit margins Employee satisfacti on and competen ce Customer loyalty Superior service delivery Customer satisfacti on The various stages that take place before the relationship is developed It begins with buyers and sellers being aware of each other On entering into a relationship, the buyer and seller makes series of promises, which gives rise to expectations The information of the customers is usually recorded to assess future needs The firm would offer incentives to customers for maintaining relationship Retention strategies Financial bonds: These are monetary benefits Lower price for greater volume of purchase Lower price for loyal customers Volume and frequency rewards Non-Financial or social bonds: Customization. Continuous touch with customers These bonds may even be formed amongst the customers. Ex: Alumni meets Service firms may adopt different versions of the above retention programmes or move on to higher levels of customer intimacy. PLANNING AND MANAGING SERVICE DELIVERY Introduction Designing a service delivery process is a creative task The rapid growth of internet means that the service strategy must address issues like space, cyber space, and time paying at least as much attention to speed, scheduling and electronic access. Service design elements Structural Delivery system Front and back office, automation, customer participation Location Size, aesthetics, layout Capacity planning Managing queues, number of servers, accommodating average or peak demand Service design elements Managerial Service encounter Service culture, motivation, selection and training, employee empowerment Quality Measurement, monitoring, methods, expectations versus perceptions, service guarantee Managing capacity and demand Strategies for altering demand and controlling supply, queue management Information Competitive resources, data collection Considerations in the design of the service delivery system Nature of contract between the service provider and the customer Sequencing of the various steps in the service delivery process Where (location) and when (scheduling) should delivery take place? Imagery, atmosphere and experience to be created and delivered Nature of the service process Service protocol Generic approaches to service system delivery Production-line approach Limited discretionary action of personnel Division of labour Substitution of technology for people Service standardization Customer as co-producer Self service Smoothing service demand Generic approaches to service system delivery Customer contact approach Degree of customer contact Separation of High and Low-contact operations Delivery channel decision Factors to be considered: It should ensure easy accessibility and convenience for the customers to interact These distribution channel should add some value to the customers The channels chosen should not eat away the margins of the service provider The channel chosen should cover all the target markets The channels chosen should be reliable Types: without intermediaries Direct distribution: Advantages Control Healthy customer relationship Flexibility and confidentiality Disadvantages Financial risk Lack of knowledge Types of intermediaries for service delivery Franchising: Advantages Business expansion Improved revenues Reduced risk Consistency in service offering Local presence through global franchising Increased working capital and minimized financial risk Disadvantages Trouble in motivating franchisees Conflict between the two parties Quality maintenance Relationship with the customers Types of intermediaries for service delivery Agents and brokers Electronic channels Advantages Lower costs Increased customer convenience Increasing bargaining power of the customers Extensive distribution Ability to customize services and gain quick feedback Place decision in service delivery Multi-site strategy Ministores Locating in multipurpose facilities Multi-service strategy Multi-segment strategy Time decision in service delivery Economic pressure form consumers Economic incentives to improve asset utilization Availability of workers to work during unsocial hours Automated self service facilities Use of call centers Promoting and delivering services in cyberspace Development of smart mobile phones Voice recognition technology Creation of web sites Commercialization of smart cards Service productivity Efficiency Effectiveness Economy Production function Capacity utilization Reasons for low productivity Small size of most of the service firms Difficulty of using machine technology Improving service productivity methods Benefits Improve quality of labour force Higher service quality Fewer customer complaints Lower employee turnover Improvement in capital equipment Reduce labour cost Increased no. of customers can be served Improve consistency of services Automate tasks Reduce cost Improve consistence of service Increased no. of customers can be served Change customer/service interaction Speed up transactions Increased no. of customers can be served Separate the customer contact and support functions Increase quality of service Enhance quality of customer/employee interaction Increase self service options Reduces cost Increased no. of customers can be served Use outsourcing Reduce cost Increased no. of customers can be served Reduces the strain on service organization Consumer participation and productivity Consumer predisposition Consumer potential/commitment/ willingness to become involved Consumer knowledge and skills, how easily can they be developed if needed to be? Technology and service productivity Hard technology Soft technology Hybrid technology Role of technology and physical aids in service process Cost rationalization More effective quality Making higher quality possible Closer link up with the customers Technology as a factor affecting behaviour TOURISM & TRAVEL SERVICES Introduction Tourism is a very complicated operation due to its multiple activities, which satisfy the need of the tourist. Tourism embraces transportation, accommodation, food catering, tourist attraction, as well as organizers like tour operators and agents. The main problem lies in maintaining standards of these components The peculiarities of tourism: It cannot be provided by a single enterprise; each component of tourism- hotel, transport etc is highly specialized and together makes the final product The sales intermediaries play a dominant role Tourism has diverse motivation to travel The demand for tourism is highly unstable due to seasonal, economic and political factors Marketing of tourism is complicated dichotomy as supply is inelastic but demand is Changes in lifestyle The old sun, sea and sand mass market has fragmented. People want more specialized versions of it such as CLUBS, quieter resort with select hotels, self catering etc Changes in lifestyle People are taking second holiday in the form of in the form of short breaks/city breaks, ranging from British and European cities to country hotels Changes in lifestyle There has been a growth of niche markets catering for special interest or activities Development of technology ahs lead to The development of mass cruise holiday market The advent of affordable holidays to longhaul destinations such as New Zealand or Kenya The phenomenon of low budget airlines, utilizing private carriers and a new generation of small regional airports Forms and types of tourism Domestic/international Holiday/professional or business Individual/group Factors driving the growth of tourism Leisure and life style Business needs The rise of free independent travelers Expanding channels and networking Professional approach Leveraging technology Innovative partnership and promotions Market segmentation Eco, Cultural and spiritual for self discovery Pride of being at exotic location Provide excellent packages for fun, excitement and make new friends Need to reassure visitors safety, of their destination, travel comfort, etc Attraction of locations for recovery, rest and relaxation 7 Ps of tourism industry Tourism is a high-involvement, high-risk products to its consumers Involves committing large sum of money to something reasonably unknown Tourism is a product partly constituted by the dreams and fancies of its customers Unlike banking and car repair, tourism is not consumer for rational or functional purposes Tourism is a fragile industry susceptible to external forces which are beyond the control of its suppliers Tourism organizations sometimes have to make rapid responses to crisis in the form of product redesign, price reduction or promotional damage limitation 7Ps of tourism market Product Price Place promotion People Process Physical evidence Product Defining and communicating the distinguishing characteristics of the product to consumers is the key too successful marketing. A tourism product consists of two components: Attributes: Benefits: People Know who your target market is. Travelers or Tourists? What do they expect? People- (Employees) A tourism organization’s most valuable resource Physical appearance, behaviour, knowledge and attitude, has a powerful impact on customers’ perception of the tourism product Ensure uniform, grooming etc, conform to branding and target market People- (Employees) Ensure staff are trained to ensure the product is delivered in accordance with the marketing strategic plan Employees physically embody the product and are walking billboards from a promotional point of view Process Process is inseparable product If any part of the process is found to be unsuitable by the customer, it could result in the negative evaluation of the whole product Physical evidence Defined as the built environment owned and controlled by a tourist organization The tangible aspect of the tourism product May be used to facilitate the service delivery process. Ex: layout and signage Communicates message about quality, positioning and differentiation Marketing tourism Product and service Tangible and intangible People led and operated Market oriented