* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AGRI-BUSINESS ENVRIONMENT
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
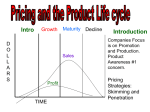
Developing marketing strategies Factors affecting marketing strategy (a) Product life cycle stage - marketing strategy must be adapted to the product stage in its life cycle (introduction, growth, maturity, or decline) (b) Company’s competitive position in the market - whether the company is a leader, challenger, follower, or nicher Stages of product life cycle Introduction - period of slow growth of sales as the product is introduced in the market - Profits are low because of heavy expenses of product introduction Growth - a period of rapid increase in sales - substantial profit Stages of product life cycle Maturity - a period of slowdown in sales growth because the product has achieved by most of the potential buyers - Profits stabilize or decline because of increased marketing outlays to defend the product against competition Decline - the period when sales show a strong downward drift - profits erode Marketing strategy in the introduction stage Rapid-skimming strategy - launching the new product at a high price and a high promotional level Market conditions - large part of the potential market is unaware of the product - those who become aware are eager to have the product and able to pay the asking price - the firm faces potential competition and wants to build up brand preference. Marketing strategy in the introduction stage Slow-skimming strategy - launching the new product at high price and low promotion Market conditions - the market is limited in size - most of the market is aware of the product - buyers are willing to pay a higher price - potential competition is not imminent Marketing strategy in the introduction stage Rapid-penetration strategy - launching the product at a low price and spending heavily on promotion Market conditions - the market is large - the market is unaware about the product - most buyers are price sensitive - strong potential competition Marketing strategy in the introduction stage Slow-penetration strategy - launching the new product at a low price and low level of promotion Market conditions - market is large - market is highly aware about the product - demand is price sensitive - there is some potential competition Marketing strategies in the growth stage The firm improves product quality and adds new product features It enters into new market segments It enters in new distribution channels Advertising focus shifts from building product awareness to bringing about product purchase Marketing strategies in the maturity stage Market modification - expand the market for its product by working with the two factors that make sales volume sales volume = number of users x usage rate per user Marketing strategies in the maturity stage The company can try to expand the number of product users through - convert nonusers - enter new market segment - win competitors’ customers Volume can also be increased by getting current users to increase their usage of the product - gap between recommended dose and present use - extension strategy Marketing strategies in the maturity stage Product modification - modifying the product characteristics in a way that will attract new users and/or more usage from current users - quality improvement to increase the functional performance of the product - feature improvement aims at adding new features (size, accessories) that expand product convenience Marketing strategies in the maturity stage Marketing-mix modifications (a) Prices - would a price cut attract new users? - if so, should the list price be lowered or should price be lowered through price specials, early purchase discount, volume related discounts or easier credit terms Marketing strategies in the maturity stage (b) Distribution - exploring new distribution channel (c) Advertising - changing advertising message, timing, frequency (d) Sales promotion - step up sales promotion through rebates, gifts, and contests Stages of product life cycle Characteristics Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Sales Low Rapidly rising Peak Declining Costs per customer High Average Low Low Profits Negative or low Rising High Declining Customers Innovators Early adopters Middle majority Laggards Competitors Few Growing Stable Decline Stages of product life cycle Marketing Objectives Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Product awareness Maximize market share Maximize profit while defending market share Reduce expenditure and milk the brand Stages of product life cycle Strategies Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Product Offer a basic product Offer product extensions Diversify brands Phase out weak items Price Use cost plus Price to penetrate market Price to match best competitor Cut price Distribution Selective Intensive More intensive Phase loss making outlets Advertising Build Product awareness among early adopters Build awareness among the mass market Stress brand Reduce differences and benefits Sales Promotion Use heavy sales promotion Reduce to take advantage of consumer demand Increase to encourage brand switching Reduce to minimum level