* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing Management
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
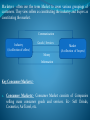
Example :1. Café Coffee Day 2. Kaun Banega Karorpati (Star Plus) Vs Sawal Dus Karor Ka (Zee TV) Vs Chappad Phad Ke (Sony TV) • • Good Marketing is no accident, but a result of Careful Planning & Execution. It is both Art & Science. – there is constant tension between its formulated side and creative side. Importance :- Financial success often depends upon marketing ability. Other business functions will not really matter if there isn’t sufficient demand for product & services. Hence now marketing has been given equal wait age. Example:- Xerox Nirma Washing Powder. The Scope of Marketing :- Marketing is about identifying and meeting human and social needs. Shortest definition of marketing can be “ Meeting Needs Profitably. Example :- eBay – Online auction clearing house. Formal Definition of Marketing:- Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating and delivering values to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. Thus we see Marketing management as the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping and growing customers through creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value. Social Definition of Marketing:- Marketing is a social process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. Managers sometimes think of marketing as “ the art of selling product” but selling is only the tip of the Marketing iceberg. Peter Drucker, a leading management theorist puts it as:There will always, one can assume, be need for some selling. But the aim of marketing is to make selling superfluous. The aim of Marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits him and sells itself. Ideally, marketing should result in a customer who is ready to buy. All that should be needed then is to make the product or service available. Example:- Sony’s Play station 3 game system, Apple’s iPod Nano digital music player. Tata Ace:- Breakthrough Marketing. What is Marketed? Marketing people market 10 types of entities:1. Goods:- cars, televisions etc. 2. Services:- Work of airlines, hotels, car rental firms, etc. 3. Events:- Time based events. Ex:- Major Trade shows, Artistic Performances, etc. 4. Experiences:- An amusement Park or a Water Park, Theme Restaurant that creates the ambience of a village of a state, etc. 5. Person:- Celebrity Marketing is a major business. Ex:- Artistes, Musicians, CEOs, Sportspersons etc. 6. Places:- Cities, States, Regions and even whole nations compete actively to attract tourists, factories, Company Head Quarters, etc. Ex:- Bangaluru:Silicon Valley of India. Tourism industry:- Kerela- Marketed as ‘God’s own country. Govt. of India – Incredible India. 7. Properties:- Properties are Intangible rights of ownership of either real property (Real Estate) or Financial property (Stocks & Bonds) 8. Organizations:- Organizations also market themselves to build their image in the market. Ex:- Philips:- ‘Sense the Simplicity’ campaign after research among the customers world – wide. 9. Information:- Information can be about anything and everything. Ex:- Schools, Colleges, Hospitals, Packaging. 10. Ideas:- Every market offering includes a basic idea. Ex:- Charles Revson of Revlon once observed– ‘ In the factory, we make cosmetics; in the store we sell hope’. Even social marketers are now busy promoting such idea by creating awareness about AIDS, encouraging family planning and discouraging smoking. Marketers & Prospects:- A marketer is someone who seeks a response – attention, a purchase, a vote, a donation – from another party called the prospect. If two parties are seeking to sell something to each other, we call them both Marketers. Marketing managers seek to influence the level, timing and composition of demand to meet the organization's objectives. Eight Demand states are possible:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Negative Demand:- Consumers dislike the product and may even pay a price to avoid it. Nonexistent Demand:- Consumers may be unaware of or uninterested in the product. Latent Demand:- Consumers may share a strong need that can not be satisfied with the existing product. Declining Demand:- Consumers begin to buy the product less frequently or not at all. Irregular Demand:- Consumer purchases vary on a Seasoned, monthly, weekly, daily or even hourly basis. Full Demand:- Adequately buying all products put in the market place. Over Full Demand:- More buyers than can be satisfied. Unwholesome Demand:- Consumers may be attracted to products that have undesirable social consequences. Market :- Traditionally, a ‘Market’ was a physical place where buyers and sellers gathered to buy and sell goods. Economists describe a market as a collection of buyers and sellers who transact over a particular product or product class. 5 Basic Markets and their connecting flow. Resources Resources Resource Markets Money Manufacturer Markets Services, Money Taxes, Goods Taxes, Goods Services, Money Government Markets Services, Money Money Taxes Consumer Markets Services Taxes, Goods Money Money Intermediary Markets Goods & Services Goods & Services Marketers often use the term Market to cover various groupings of customers. They view sellers as constituting the industry and buyers as constituting the market. Communication Industry (A collection of sellers) Goods / Services Market (A collection of buyers) Money Information Key Consumer Markets:1. Consumer Markets:- Consumer Market consists of Companies selling mass consumer goods and services. Ex:- Soft Drinks, Cosmetics, Air Travel, etc. 2. Business Markets:- Business Market consists of Companies selling business goods and services. This market often face well – trained and well – informed professional buyers, who are skilled at evaluating competitive offerings. Business buyers buy goods in order to make or resell a product to others at a profit. Hence, in this market, it is extremely important to show, how to maximize the profit. 3. Global Markets:- Companies selling goods and services in the global market place face additional decisions and challenges. They have to decide, which country, how to enter, how to adapt their product and service features to each country, the pricing strategies and the communication to be used to fit varying cultures, legal and political systems. 4. Non Profit & Government Markets:- Companies selling their products to non profit organizations such as churches, universities, charitable organizations and governmental agencies. Here the companies need to price carefully, as these buyers have limited purchasing power. Market Place:- Market place is physical, such as a store, you shop in. Market Space:- Market space is digital, as when we shop on the internet. Meta Market:- Meta Market is a cluster of complementary products and services that are closely related in the minds of consumers, but spread across a diverse set of industries. Ex:- marutitruevalue.com, MakeMyTrip.com, Yatra.com, etc. Marketing in Practice:- Marketing is not done only by the marketing department. Marketers must properly manage all possible touch points – Store layouts, package designs, product functions, employee training and shipping and logistics methods. Marketing must also be heavily involved in key general management activities, such as product innovation and new – business development. To create a strong marketing organization, marketers must think like executives in other departments, and executives in other departments must think like marketers. In practice, marketing follows a logical process. The marketing planning process consists of analyzing marketing opportunities, selecting target markets, designing marketing strategies, developing marketing programs and managing the marketing effort. However, in highly competitive marketplaces, marketing planning is more fluid and needs to be continually refreshed. There are 5 key functions for a CMO in leading marketing within the organization:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Strengthening the brands. Measuring marketing effectiveness. Driving new product development based on customer needs. Gathering meaningful customer insights. Utilizing new marketing technology. Core Marketing Concepts:- To understand the marketing function, we need to understand the following core set of concepts. 1. Needs, Wants & Demand:- Needs are the basic human requirements. People need air, food, water, clothing and shelter to survive. They also have a very strong needs for recreation, education and entertainment. These needs become wants, when they are directed to specific objects that might satisfy the need. Ex:- Food habit of USA and India. Demands are wants for specific products backed up by an ability to pay. Ex:- Mercedes, BMW etc. Companies must measure not only how many people want their product, but also how many would actually be willing and able to buy it. We can distinguish among five types of needs:a. Stated Needs:- Ex:- The Customer wants an inexpensive car. b. Real Needs:- Ex:- The Customer wants a car whose operating cost, not the initial price, is low. c. Unstated Needs:- Ex:- The Customer expects good service from the dealer. d. Delight Needs:- Ex:- The Customer would like the dealer to include an onboard navigation system. e. Secret Needs:- Ex:- The Customer wants his/her friends to see him as a savvy consumer. Simply giving customers what they want isn’t enough any more – to gain an edge, companies must help customers learn what they want. Ex:- Mobile manufacturing companies. 2. Target Markets, Positioning & Segmentation:- A marketer can rarely satisfy everyone in a market. Hence, marketers start by dividing the market into segments. They identify and profile distinct groups of buyers who might prefer or require varying product and service mixes by examining demographic, psychographic, and behavioral differences among buyers. After identifying market segments, the marketer then decides which are it’s target markets. For each market, the firm develops a market offering that it positions in the minds of the target buyers as delivering some central benefit(s). Ex:- Grameen Bank (Md. Yunus of Bangladesh) Volvo (Car Segment):- They focused on safety as the major concern and positioned as – The safest a customer can buy. Scorpio:- Designed for people who prefer a sturdy vehicle that offers luxury and comfort. Positioning has been done as – A vehicle that offers the luxury of a car and the thrill of an SUV. Companies perform best when they choose their target market(s) carefully and prepare tailored marketing programs. 3. Offerings & Brands:- Companies address needs by putting forth a value proposition, a set of benefits that they offer to customers to satisfy their needs. The intangible value proposition is made physical by an offering, which can be a combination of products, services, information and experiences. A Brand is an offering from a known source. Ex:- Mc. Donald’s Domino’s 4. Value & Satisfaction:- The offer will only be successful if it delivers value and satisfaction to the target buyers. Value increases with quality and service and decreases with price, although other factors can also play an important role in our perceptions of value. ‘Satisfaction’ reflects a person’s judgments of a product’s perceived performance in relationship to expectations.’ 4. Marketing Channels:- To reach a target market, the marketer uses three kinds of marketing channels:a. Communication Channel:- Deliver and receive messages from target buyers and include Newspapers, Magazines, radio, T.V, mail, poster etc. b. Distribution Channel:- To display, sell or deliver the physical product or service(s) to the buyer or user. It include distributors, wholesalers, retailers and agents. c. Service Channel:- To carry out transactions with potential buyers. It include, warehouses, transportation companies, banks and insurance companies that facilitate transactions. The challenge for the marketer is to select the best mix of communication, distribution and service channels for their offerings. 6. Supply Chain:- The supply chain is a longer channel stretching from raw materials to components to final products that are carried to final buyers. Ex:- Supply chain for women’s purses starts with procurement of raw materials and moves through training, cutting, manufacturing and the marketing channels to bring products to customers. 7. Competition:- Competition includes all the actual and potential rival offerings and substitutes a buyer might consider. Ex:- Steel for a car manufacturer. 8. Marketing Environment:- Marketing Environment consists of the Task Environment and the Broad Environment. The ‘Task Environment’ includes company, suppliers, distributors, dealers and target customers, who are engaged in producing, distributing and promoting the offerings. The ‘Broad Environment’ consists of six components:- Demographic environment, Economic environment, Physical environment, Technological environment, Political- Legal environment, and SocialCultural environment. Marketers must pay close attention to the trends and developments in these environment and make timely adjustments to their marketing strategies. The New Marketing Realities:- Marketplace is continuously undergoing change. Hence, marketers must attend and respond to a number of significant developments happening. These are:1. Major Societal Forces:- The marketplace today is radically different as a result of major, and sometimes interlinking, societal forces that have created new behaviors, new opportunities and new challenges:a. Network Information Technology:- The digital revolution has created an information Age, which promises to lead to more accurate levels of production, more targeted communications and more relevant pricing. b. Globalization:- Easier for companies to market in other countries and easier for consumers to buy products and services from marketers in other countries. c. Deregulation:- Resulted in greater competition and growth opportunities. d. Privatization:- Many countries have gone for privatization of public companies to increase their efficiency. Ex:- British airways and British Telecom in U.K. e. Heightened Competition:- Brand manufacturers are facing intense competition from domestic and foreign brands, resulting in rising promotion costs and shrinking profit margins. Also the powerful retailer’s effect. f. Industry Convergence:- Industry boundaries are blurring at an incredible rates as companies are recognizing that now opportunities lie at the intersection of two or more industries. Ex:- Dell, HP – MP3 players to mobile to plasma TVs and camcorders. g. Consumer Resistance:- A 2004 Yankelovich study found record levels of marketing resistance from consumers. A majority of those surveyed reported negative opinions about marketing and advertising, stating that they avoid products that they feel is overmarketed. h. Retail Transformation:- Small retailers are succumbing to the growing power of giant retailers, direct- mail firms, e-commerce, TV direct to customer ads, Home shopping T.V etc. i. Disintermediation:- The amazing success of the dot-com(s) has created disintermediation in the delivery of products and services by intervening between the traditional flow of goods. In response, many traditional companies engaged in reinter mediation and became ‘ Brick- and – Click’ retailers, adding online services to their existing offerings. The societal forces that spawned this information Age have resulted in many new consumer and company capabilities. 2. New consumer Capabilities:- Customers today are becoming less brand loyal and more price and quality sensitive in their search for value. Let us consider what consumers have today that they didn’t have yesterday:a. A substantial increase in buying power:b. A greater variety of available goods and services:c. A greater amount of information about particularly anything:d. Greater ease in interacting and placing and receiving orders:e. An ability to compare notes on products and services:f. An amplified voice to influence peer and public opinion:- 3. New Company Capabilities:- New forces also have combined to generate a new set of capabilities for today’s companies:a. Internet as a powerful information and sales channel. b. Advanced Market Research activities. Speedy and effective internal communication among employees. d. Target marketing and two-way communication are easier. e. Companies can reach the customers even on the move. f. Firms can produce individually differentiated goods. Ex:- BMW’s technology now allows buyers to design their own models from among 350 variations, with 500 options, 90 exterior colors and 170 trims. The company claims that 80% of the cars bought by individuals in Europe and up to 30% bought in USA are built to order. g. More facilities to Managers regarding purchasing, recruiting, training and internal and external communications. c.