* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
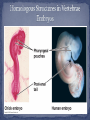
Theory of Evolution: Change in living organisms over many successive generations. #1 http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/prehistoric-world/prehistoric-time-line/ COMMON ANCESTOR: an organism from the past in which present organisms have evolved from PRESENT PAST #2 Fossil: Preserved remains or evidence of an ancient organism. #2 The lower the layer is, the older the fossil is. The higher the layer is, the younger the fossil is. #3 Homologous Structures: organisms with similar structure, but different function. #4 Analogous Structures: Different structure, similar function. These organisms DID NOT inherit their structural adaptations from a common ancestor. #5 Vestigial Structures: a structure that is no longer used by an organism, but is found in closely related species. (Ex. Human appendix and tail bone, penguin wings, whale hip bone). #5 #7 Comparative Embryology: the study of early embryo development #8 Comparative Biochemistry: comparing the DNA or amino acid sequence of organisms 9 10 13 Charles Darwin: The founder of the theory Natural Selection and author of “Origin of Species” It is not the strongest of the species that survives, nor the most intelligent that survives. It is the one that is the most adaptable to change. -Charles Darwin, Origin of Species Adaptations (structural and behavioral): inherited characteristics that increases an organisms chance of survival and opportunity to reproduce in it’s niche. Natural Selection: a process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully #9 1. Overproduction – Each species produces more offspring than can survive. 2. Genetic Variation – Individuals in the population have different traits. (ex. Different fur color, size of claws, length of tail). #9 3. Struggle to Survive – The natural environment can not support all organisms. This can lead to competition of food, shelter & mates. #9 4. Reproduction: The organisms that are well adapted to their environment reproduce and pass the favorable traits to their offspring. Those who survive & reproduce are considered “the fittest”. - Charles Darwin from Origin of Species “Light” colored pepper moth “Dark” colored pepper moth The Peppered Moth is a species commonly found in the countryside of Britain. There are two versions of the peppered moth. The peppered moth lived in an environment where trees had light colored bark. Which kind of peppered moth was more favorable to survive? Why? Coal burned during the early decades of the industrial revolution and produced soot that blanketed the countryside of the industrial areas of Britain. Naturalists noticed a change in the peppered moth population... Before Industrial Revolution After Industrial Revolution #10 Some species have evolved physical adaptations that allow them to blend with their environments. Camouflage allows organisms to become invisible to predators. As a result, more of the camouflaged individuals survive and reproduce. #10 One species evolved to resemble another species. Harmful species Harmless species #10 Species of bacteria that originally were killed by penicillin and other antibiotics have developed drug resistance. For almost every antibiotic, at least one species of resistant bacteria exists. One unintended consequence of the continued development of antibiotics is that some diseases, which were once thought to be contained, such as TB, have reemerged in more harmful forms. Genetic Change! Nucleotides or genes of DNA/RNA can change randomly (mutations). This can lead to a new variation of an organism, this may or may not give the organism an advantage to survive. A group of similar organisms that can successfully breed AND produce fertile offspring. Mules are infertile!!!