* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download macroevolution involves evolution at the large scale as species
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive isolation wikipedia , lookup
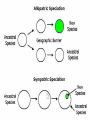
› A group of organisms that interbreed with each other and share the same gene pool. › A group of organisms that produce fertile offspring. *Simplified: A species is a group of organisms that can have children. Also their children can have children. Reproductive barriers can be PREZYGOTIC or POSTZYGOTIC. Prezygotic isolating mechanisms prevent reproduction and make fertilization unlikely geographic isolation Gamete isolation temporal isolation behavioral isolation mechanical isolation Geographic Temporal Isolation Isolation Organisms can not mate because Organisms can not mate because they reproduce in different seasons they are or different times separated by of day. geographic barriers. Mechanical Behavioral Isolation Isolation Organisms don’t Organisms can not mate mate because because their they have genitalia is different mating unsuitable for one rituals. another. Gamete Isolation Organisms can not mate because their sperm and egg will not fuse. Postzygotic Isolating Mechanisms take place once organisms have mated. Zygote mortality Hybrid Sterility Hybrid Inviability Hybrid Sterility A hybrid offspring is produced, but is sterile. Hybrid Inviability The offspring survives, but is weak and sickly. Zygote Mortality Fertilization occurs, but the zygote does not survive. ALLOPATRIC SPECIATION SYMPATRIC SPECIATION ADAPTIVE RADIATION In ALLOPATRIC SPECIATION, an ancestral population is geographically isolated, resulting in the evolution of separate species. Populations begin to diverge when gene flow between them is restricted and variations accumulate until the populations are reproductively isolated. In SYMPATRIC SPECIATION, an ancestral population is isolated, resulting in the evolution of separate species. Sympatric speciation involves speciation without a geographic barrier. Adaptive radiation involves the evolution of several new species from an ancestral species. Adaptive radiation occurs as natural selection drives members of the ancestral species to adapt to several different environments. Evolution through Natural Selection is not random. Although mutations and Genetic Drift can not be predicted and are random themselves, Natural Selection acting upon these changes is not random at all…….the best suited for their environment are still the ones most likely to survive and reproduce. How the actual “Evolution” takes place is up for some debate. Convergent Evolution…..Unrelated species growing more and more alike due to adapting to their surroundings….Analogous Structures is an example of Convergent Evolution Divergent Evolution ……When closely related species grow less and less alike due to adapting to their surroundings….ie) Darwin's Finches Coevolution ….When two or more species evolve in response to changes in the other. Extinction ….The elimination of a species on Earth….happens when a species is unable to adapt to its surroundings