* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 3C and Gender (9)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
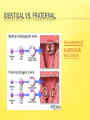
Chapter 3 NATURE VS. NURTURE NATURE VS. NURTURE Nature – genes Nurture – environment Our biological make-up and our experiences combine to make us who we are. NATURE VS. NURTURE … It’s complicating … CELLS, CHROMOSOMES, DNA, GENES •Cells in the human body have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total) •Half from your mother half from your father •Chromosomes include DNA •DNA includes genes •Genes are the building blocks for our physical development. •Humane Genome project suggests that every other human on this planet is close to being your twin sharing 99.9% of your DNA. We tend to focus on the .1% that makes us different. TWIN STUDIES Behavior geneticists use twin and adoption studies to learn the influences of genes and environment. Identical Twins Single fertilized egg that splits into two Genetically identical Fraternal Twins Develop from two separate eggs No more similar than a brother and sister IDENTICAL VS. FRATERNAL An example of a twins study and cancer TWIN AND ADOPTION STUDIES Can indicate the heritability of a trait. Heritability - The extent to which differences among people are attributable to genes. Does NOT mean that we can imply a certain trait is ___ % inherited. TWINS REARED APART Twin studies may be complicated by the fact that twins typically grow up in the same environment. So detecting if results are due to genes or environment may be difficult. Adoption studies can shed light on this issue. Video: Value in Adoption Studies Video: Gerry and Mark ADOPTION STUDIES You can also see the interaction between nature and nurture when studying adopted children. Adoptee’s personality traits bear more similarities to that of the biological parents. However, studies do show that the adoptive family environment can plan impact the adoptee’s attitudes, values, manners, faith and politics. EVOLUTIONARY PSYCHOLOGISTS Evolutionary Psychologists - Study the behaviors, emotions, and thinking that have allowed us to survive. NATURAL SELECTION CHARLES DARWIN Natural Selection: The principle that among the range of inherited trait variations, those that lead to increased reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to future generations. Ex- giraffes necks, white rabbits living in polar regions. Applied to humans- Fear developed in humans as a positive gene to be passed down- those too daring died . NATURAL SELECTION EXAMPLES Ex- Food preferences Q What food color is considered least desirable and Why? Ex-Intelligence -Those that deemed leopards nice to pet rather than dangerous did not pass on genes. Ex- Why do women prefer more muscular men. Ex- Why do men think about sex more than women? Re: bottom of p. 104 Ex. Men prefer youthful look..waists roughly one third of hips. Q. Can environment influence tastes? NATURE VS. NURTURE John Locke’s blank slate theory- everybody is born clean then socialization, experience writes on that blank slate and you become who you are. Nature Vs. Nurture Examples of how nature vs. nature ideology has influenced brutal dictatorships or moral atrocities. Social Darwinism in US (Mexican War and state sterilization programs) NATURE VS NURTURE Ex. China- “On a white sheet of paper can be printed the most beautiful words” - Mao Zedong Ex. Cambodia- “ Only the new born baby is spotless” - Pol Pot Stephen Pinker Video-Video Tools Kit TEMPERAMENT Temperament – a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity. (emotional excitability) Identical twins have more similar temperaments than fraternal twins. This is evidence that our temperament is biologically rooted. (so there may be a biological basis to our personality) ACTIVITY – STRIKING SIMILARITIES Pair up with a neighbor that you do not know well at all. Discuss these topics take note in the ways that you are similar… Politics Music Religion Clothes Jobs held Job goals Sports Hobbies Favorite subject Subjects you dislike Favorite foods Food Climate preferences Automobile preferences Sleeping habits Reading tastes Talents What bugs you? Chewing gum brand? Toothpaste brand Coffee brand Favorite magazines Pets owned Family members TV programs Personality traits Vacation spots Handedness GENDER The biological and social characteristics to which people define male or female. Overall, males and females are very similar genetically – but we cannot ignore some observable differences that are influenced by biological factors and culture. Women can do anything except.mp4 Gender Identity – one’s sense of being male or female. Video Gender Identity- Is the nature vs. nurture issue dead. Start at 1:00 GENDER DIFFERENCES: GENDER DIFFERENCES: The Myers text mentions that… WOMEN Posses more body fat Enter puberty earlier Express emotions more Are more likely to be offered helped On average 5” shorter Are more concerned with “making connections” and building relationships More open to spirituality Are usually the one both sexes turn to to share worries and hurts Hold phone conversations longer when talking to the same sex (avg. 7.2 min vs. males 4.6 min.) GENDER DIFFERENCES: The Myers text mentions that… MEN Admit to being more aggressive Are more interesting in fighting and hunting Perceived as more dominant Use communication to find solutions rather then build relationships Place less emphasis on religion Are more skeptical Believe their friendships with women are more intimate than friendships with men. Difference between men and women - YouTube GENDER ROLES Gender Roles – a set of expectations for males and females. Gender Roles in the Media by (Isabel S Leone) – YouTube Gender Roles in Disney Movies – YouTube Gender Roles-Interviews with Kids - YouTube Activity – Divide into groups of males and females… make a list of gender roles for your gender and for the opposite gender. ACTIVITY: GENDER ROLES IN THE HOME: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. When you go out, who drives? Who fills out the tax forms? Who writes “thank you” notes for gifts received? Who is more likely to ask “where are my shoes?” When the car needs repair, who takes it to the garage? Who does the laundry? Who dusts and vacuums? Who know where to find the thermometer? Who knows where to find a wrench? When guests are over for dinner who makes the drinks? Who waters the house plants? Who mows the lawn? When you go on a trip, who packs the suitcase? When you go on a trip, who packs the car? HOW DO WE LEARN GENDER? Gender Schema Theory – Children learn from their cultures a concept of what it means to be male and female and they adjust their behavior accordingly. Through language, dress, toys, and songs children begin to shape their schema (mental view for gender. Gender stereotypes in children's movies – YouTube Killing Us Softly 4: Advertising's Image of Women GENDER CONT. Gender Typing – the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role. Ex Baby X studies where 20-24 yr olds where told a 3 month old baby was male (1/3rd ), female (1/3rd ) or not told (1/3rd ). Psychologists analyzed: A) How they were talked to B) whether they were held which toy they played with football, doll or bellring 9 month old baby X’s were given a jack in the box and subjects explained the infants emotional reactions. Subjects interpreted the reactions as fear or anger (based on what they thought the baby’s gender was. C)