* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
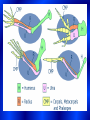
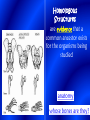
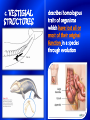
In your notes, compare the two pictures. List at least three similarities and at least three differences The change of a species over time…. Millions of years Changes in structure, function and behavior Theory: An idea which is supported by extensive, repeated experiments, but not proven as law. Why isn’t evolution a law? Limited access to the past Present day species developed (evolved) from earlier distinctly DIFFERENT species. The “evolution” of Evolutionary Theories 1.) Lamarck’s Theory: Stated that structures appear because they are needed, Called the theory of Use & Disuse ex. Longer necks in giraffes Weismann DISPROVED the theory that stated that acquired traits can be passed on to the next generation. Charles Darwin “The Father of Evolution” HOW DID DARWIN START? GALAPAGOS ISLANDS 80 80 80 GR EE NL AN D 70 70 70 60 60 50 60 50 E NORTH 40 AMERICA A 30 T 20 PACI FI C 30 L O P 50 ASI A A OCEAN N T 20 20 IC AFRI CA 10 I NDI AN O SOUTH 10 20 EQUATOR OCEAN E 10 A AMERICA TROPICOF CAPRICORN 30 TROPICOF CANCER 10 OCEAN 40 30 C 20 R 40 EQUATOR 10 U E PACIFIC TROPICOF CANCER 10 70 60 50 40 80 D AN NL EE GR 10 N 20 20 10 20 TROPOFCAPRICORN AUSTRALIA 30 30 40 40 50 50 60 60 70 80 70 80 30 30 30 40 40 50 50 60 60 70 70 80 80 30 40 40 50 50 60 60 70 70 80 ANTARCTICA80 30 30 40 40 50 50 60 60 70 70 80 80 1859 wrote book titled “Origin of the Species” Key Concepts 1. Species present now were not created in present forms instead they evolved from ancestral species 2. Natural Selection: causes evolution States that only those organisms containing the best variations can survive and reproduce in a given environment Adaptations • Inherited trait • Improves an organisms chance of survival Ex: Camouflage Individuals who survive are the ones best adapted to exist in their environment Formation of a new species due to favorable adaptations gradually accumulating, while unfavorable adaptations gradually disappear Any organisms which can: 1. Interbreed 2. Produce fertile offspring 3. Under natural conditions Darwin observed 13 species of finches on the Galápagos Islands that were similar except for differences in body size, beak shape, and eating habits. Noticed that all finches were similar to 1 finch he saw on the South American coast Darwin reasoned that the Galápagos finches must have had to compete for food. Finches with certain beak shapes that let them eat food survived longer & reproduced more than finches without those beak shapes A person has been arrested on the charge that he robbed $50,000 from the First City National Bank last night. What must the district attorney do to prove that this man is the robber? Forms of Evidence Is the sum total of all the fossils discovered and undiscovered and their placement in sedimentary rock layers A. Fossils are the mineralized or otherwise preserved remains or traces (such as footprints) of animals, plants, and other organisms is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of organisms. Structure and form A. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES When body parts look similar in different species but do not perform the same function. An example is the forelimb structure shared by cats and whales. Homologous Structures are evidence that a common ancestor exists for the organisms being studied anatomy whose bones are they? B. Analogous Structures Structures that are different but serve the same or similar purposes An example is the torpedo body shape of porpoises and sharks c. VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES describes homologous traits of organisms which have lost all or most of their original function in a species through evolution study of comparative developmental anatomy is the study of differences in chemical components among species Examples: Hemoglobin, DNA, Chromosomes IS THE STUDY OF DIFFERENCES IN CELL STRUCTURE, COMPOSTION AND FUNCTION