* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
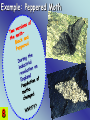
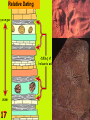
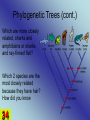
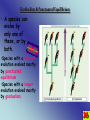
1 Age of Earth 2 Natural Selection 3 What if the environment changes? The organisms that are most suited will survive, the others will die. This is a very slow process….does not occur over night…many generations must past before any change in the population can be seen. 4 5 6 7 Example: Peppered Moth 8 9 Decent with modifications These changes increase a species’ fitness in their environment. 10 History • James Hutton -1785-Propsed that he Earth is millions of years old. • Thomas Malthus -1798populations outgrew food supplies, causing competition and a struggle for one species to survive against another • Jean-Baptiste Lamark inheritance of acquired characteristics 11 History Continued •Lylle -1833-plant and animal species had arisen, developed variations, and then became extinct over time •Alfred Russel Wallace -1858-idea of competition for resources as the main force in natural selection •Charles Darwin -1859- Publishes “On the Origin of Species” 12 Charles Darwin 13 14 Humans select and breed for certain traits. Examples: The largest hog, the cow that gives the most milk, or fastest horse. 15 Evidence for Change Over Time Fossil Record – Fossils that show how the same organism looked millions of years ago. – Use rock layers – Isotope dating 16 Relative Dating 17 18 19 20 Stages of development from an embryo 21 Vestigial organs – Organs or structures that do not seem to be used by the organism any longer. – They are usually reduced in size. 22 23 Speciation • is the evolution of a new species – occurs when interbreeding happens, or when the production of fertile offspring is prevented – natural barriers form and cause the breakup of populations to form smaller populations – Examples: Volcanoes, sea-level changes, and earthquakes 24 Speciation Mechanisms 25 • Behavioral Isolation – Populations are capable of interbreeding, but have different courtship rituals or other type of behavior. • Geographic Isolation – Separated by bodies of water or mountains. • Temporal Isolation – Reproduction takes place at different times of the year •Overtime they can change so much that they become unable to breed as they adapt to their environment. 26 Changes in allele frequency within a population 27 3 Types of Evolution 1) Divergent 2) Convergent 3) Co-Evolution Divergent Evolution Red Fox 29 Kit Fox Convergent Evolution 30 Coevolution 31 Evolution is the change in a species over time. 32 Phylogenetic Trees •Shows how closely organisms are related •Are whales more closely related to camels or humans? •Are snakes more closely related to birds or camels? 33 Phylogenetic Trees (cont.) Which are more closely related, sharks and amphibians or sharks and ray-finned fish? Which 2 species are the most closely related because they have hair? How did you know 34 Rates of Evolution 1.Gradualism 2.Punctuated Equilibrium 35 Gradualism & Punctuated Equilibrium • A species can evolve by only one of these, or by both. •Species with a shorter evolution evolved mostly by punctuated equilibrium •Species with a longer evolution evolved mostly by gradualism. 36 Gradualism •Very gradually, over a long time.... •Small variations that fit an organism slightly better to its environment are selected for •Change is slow, constant, and consistent. Punctuated equilibrium 37 •change comes in spurts. •period of very little change, and then one or a few huge changes occur •often through mutations in the genes of a few individuals. Resistance in Bacteria due to Evolution 38 Read page p403. Two main sources of genetic variation 1.Mutations 2.Genetic Shuffling 40 EOCT- It is important that you are able to explain how the concepts of genetics provide the basis for explaining natural selection and evolution. This will help you answer questions like this: What is the end result of natural selection? A increased number of offspring of a given phenotype that survive B changes in the frequency of alleles in a population C fossil formation through extinction D environmental changes of a habitat 41 Although the Arctic fox and the kit fox are closely related, they look very different because the individuals A acquired traits during their lifetimes that contributed to survival B with traits most suited to their environments reproduced most successfully C migrated long distances to environments that most suited their traits D passed on to their offspring acquired behaviors that were helpful 42 Fossils of Archeopteryx show that this animal had feathers, like a bird. It also had a bony tail, teeth, and claws on its wings, like a reptile. This fossil is evidence that supports the idea that A birds and reptiles have a common ancestor B birds have changed very little over 150 million years C reptile species are more advanced than bird species D reptiles are warm-blooded like birds 43 Horses and tapirs have a common ancestor, but now look very different. Horses now are grassland animals adapted for grazing on grass and shrubs. Tapirs are jungle animals that live in dense forests and eat fruit, leaves and aquatic vegetation. Which of the following led to the development of such differences in the two species? A selective breeding B convergent evolution C DNA hybridization D natural selection 44