* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telecommunication
Optical sound wikipedia , lookup
Digitization wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
History of smart antennas wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Digital television wikipedia , lookup
Hyperbolic navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Radio navigation wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
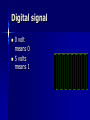
Telecommunication How It works What It is? Telecommunication, devices and systems that transmit electronic or optical signals across long distances. such as a telephone system. enables people to send and receive personal messages . key medium for delivering news, data, information, and entertainment. Way of sending Message Point-to-point : One sender to a single receiver such as telephone conversation; Point-to multi point : one sender to many receiver such as television, It often called Broadcast; How the signals sent? Telecommunications devices convert different types of information, such as sound and video, into electronic or optical signals. Electronic signals travel along a medium such as copper wire or are carried over the air as radio waves. Optical signals travel along optical fiber cable; the device on the receiving end converts the signal back into an understandable message, such as words and pictures on a computer screen. Types of signal Analog signal Digital signal Optical signal analog or digital refers to the method used to convert information into an electrical signal Analog signal An analog signal is any continuously variable signal in an analog sound recording, the variation in pressure of a sound striking a microphone creates a corresponding variation in the current passing through it. An increase in the volume of the sound causes the fluctuation of the current to increase Digital signal 0 volt means 0 5 volts means 1 Optical signal Pulse beam of laser light LED (Light Emitting Diode) send signal Fiber optic receiver Receive fiber optic signals Transmission medium Cable Fiber-optic Micro-wave Satellite Coaxial cable Developed in 1936 Made of copper wire Expensive Fiber Optics Message are digitally coded into pulses of light TAT 9 fiber optic cable can carry more than 75,000 telephone conversation at a time Microwave relay Relay from station to station Needs a clear line of sight between sending and receiving station Average distance between stations 40km As many as 600 telephone conversations can be transmitted over one microwave relay channel. Satellite communication Started at 1969 with series of satellites Orbit 35,880km above the earth Powered by solar energy Use micro wave for transmission can relay up to 33,000 calls simultaneously as well as several television channels. Way of transmission Simplex: One way communication Half Duplex: communications in both directions, but only one direction at a time Duplex: communication in both directions simultaneously Applications Telegraph Fax Telephone Radio Television Global Positioning System Voice Over IP Computer network Telephone & cellular Communication Global Positioning System space-based radionavigation system consisting of 24 satellites and ground support. accurate information about their position, time, anywhere in the world and in all weather conditions. How GPS Works GPS satellites fly in circular orbits at an altitude of 20,100 km (12,500 mi) and with a period of 12 hours point their solar panels toward the sun and their antennas toward the earth Send the signals to the receiver From that signal receiver calculate its position on earth Application of GPS Military equipment such as fighters, bombers, tankers, helicopters, ships, submarines, tanks, jeeps, and soldiers Airplane and ships use it for route navigation used to route and monitor delivery vans and emergency vehicles car navigation system Because the GPS user does not need to communicate with the satellite, GPS can serve an unlimited number of users. Inventor In 1837 Samuel Morse invented the first workable telegraph Alexander Graham Bell invented telephone in 1876 Marconi invented Radio in 1895