* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
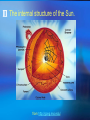
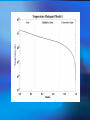
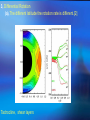
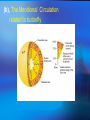
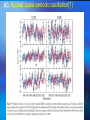
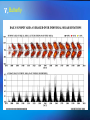
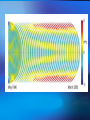
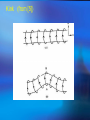
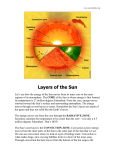
The Internal Rotation of the Sun Presented by Changyi Tan 11,03,2005 Ⅰ How to observe the interior of the Sun? 1, The method — Helioseismology Why is Helioseismology? (opaque or optical thickness) 2, The instrumentations for Helioseismology Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) Ⅱ How Helioseismology works? Basically, observe the surface sound waves of the Sun. People can get the coupled multi-modes spherical harmonic oscillation signals, and separate them to some normal mode harmonic wave. There are two kinds of sound waves — p mode and f mode. f mode is used to analyze the surface wave, it propagates on the surface of the Sun —Photosphere p mode wave is used to detect the interior of the Sun. The parameter of p mode wave is l. The restoring force is pressure gradient . from http://gong.nso.edu/. Ⅲ The internal structure of the Sun. from http://gong.nso.edu/. We concentrate on the Convection Zone. The parameters of Convection Zone: From 0.8 R~ 1 R Cool temperature~ 106 K More opaque High magnetic strength 103~104 Gauss High density~? But the density at the top of Convection Zone is very low ~ 0.0000002 gm/cm³ Ⅳ Dynamo of the convention Zone: 1, Magnetic fields: The topology of the magnetic fields is very complicated. Related to the poroidal field and toroidal field. These relate to the sunspots , CMEs, flares and so on. The magnetic pressure and tension should be stronger than them in the atmosphere. But the gas pressure should also be stronger, so β not necessarily be small. 2, Convection: Cool Temperature➱ Electrons reconbine with other particles (Ions) and the photons can be easily absorbed. This decreases the radiative conductivity and increases the temperature gradient. Where this occurs a volume of material moved upward will be warmer than its surroundings and will continue to rise further. These convective motions carry heat quite rapidly to the surface. The fluid expands and cools as it rises. At the visible surface the temperature has dropped to 5,700 K . The convective motions themselves are visible at the surface as ➱ granules and supergranules. 3, Differential Rotation (a),The different latitude the rotation rate is different.[2] Tachocline, shear layers (b), The Meridional Circulation related to butterfly (c), Appear quasi-periodic oscillation[1] Ⅴ,Butterfly From [2] ☆Physics Due to the differential rotation, the weak poroidal field will produce a strong toroidal field below surface when solar minimum. Kinks in toroidal field rise to form sunspots at low latitude. The leading polarities of south and north of the equator are due to the Coriolis Force when toroidal field rises. At the sun activity minimum, the leading polarity will reverse. Because the supergranular eddy diffusion. From [5] Kink (from [5]) ( From [5] ) Ⅵ The rotation at the deep interior—like a rigid body References: 1, Michael J. Thompson et al. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2003. 41:599-643 2, R. Howe The Internal Rotation of The Sun, 2003 3, Michael Stix The Sun. 2002 4, Peter A. Gilman, Mark S. Miesch, ApJ, 611:568-574, 2004 August 10 5, E.R. Priest, Solar Physics and MHD, 1981 Thanks a lot.