* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History 2311 Western Civilization to 1715 day three slides
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
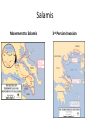
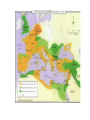
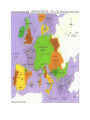
History 2311 Western Civilization to 1715 Slide Set 2 Central Texas College Fort Knox, Kentucky Bruce A. McKain Greek Society Bronze Age The Mycenaeans • Credited with the development of Bronze. • Forerunner of what we would know as Greek Society. The Bronze Age Implements Greek Democracy • Representative form of government started with ancient Athens. • The idea of a Republic was first discussed and practiced in Ancient Greece. Iliad and Odyssey • Stories by the Greek Poet Homer, who was a slave and illiterate. • Iliad – Story of Trojan War. • Odyssey – Story of the voyage of Odysseus. Homer The Polis Athens • The Greek work for the CityState, the primary governmental system of the ancient Greek world. Sparta The Greek Gods • • • • Zeus Supreme deity of the Greeks, At first was a stormgod and wielded a thunderbolt. The All-Father who populated the heavens and earth with his promiscuous liaisons. Grand Dispenser of Justice. Jupiter and Jove were his Latin names. # 4 of the Ancient Wonders The Greek Gods cont. • Ares - God of War. • Son of Zeus and Hera. • Delighted in slaughter and looting, but also a coward. • Had an adulterous affair with Aphrodite. • Latin name Mars. The Greek Gods cont. • Aphrodite –Goddess of Love and Beauty. • Born either of sea foam or was a daughter of Zeus. • Hephaestus was her husband. • Ares was her lover. • Eros was her son. • Latin name Venus. Greek Gods cont. • Apollo – God of Light and Truth, of Intelligence, of Healing, and of the arts. • Son of Zeus. • Also called Phoebus Apollo. • Latin name also Apollo. Greek Gods cont. • Artemis – Goddess of Chastity, the virgin huntress. • Twin sister of Apollo, daughter of Zeus. • Presided over childbirth, associated with the moon. • Latin name Diana. Greek Gods cont. • Athena – Virgin Goddess of Wisdom. • Sprang fully armed from the head of Zeus, after he swallowed the Titaness Metis. • Goddess of the arts, and guardian of Athens. • Also known as Pallas Athens • Latin name Minerva Greek Gods cont. • Demeter – Goddess of vegetation and fertility. • Zeus’s full sister. • Had various lovers including Zeus their daughter Persephone, who was taken by Hades. Her grief caused the earth to grow barren, return of her daughter for six months of the year allows earth to become fruitful. • Latin name Ceres. Greek Gods cont. • Eros – God of Erotic Attraction • Son of Aphrodite. • Latin name Cupid. Greek Gods cont. • Hades – Lord of the Underworld. • Brother of Zeus. • Latin names Dis and Pluto. Greek Gods cont. • Poseidon – Lord of the Seas and God of Horses. • Brother of Zeus. • Latin name Neptune. Greek Gods cont. • Pan – God of the flocks. • Son of Hermes. • Played the pipes and pursued various nymphs, all of whom rejected him for his ugliness. • Latin name Sylvanus and Faunus. The Greeks (cont.) • Modern Identification with Greek Society – Art – Politics – Sense of History – Curiosity – Education The Greeks (cont.) • Modern Identification with Greek Society – – – – Politics Sense of History Curiosity Education Persian Invasions • Marathon (490 B.C.) • Salamis (480 B.C.) • Greek Rivalry – Peloponnesian Wars 460-445, 431-404 B.C. – Invasion of Sicily – Colonization of the Mediterranean Marathon Persian Wars Plains of Marathon Marathon Initial Situation Greek Victory Salamis Movement to Salamis 3rd Persian Invasion Salamis The Battle Greeks Victorious Peloponnesian Wars Athens Sparta Peloponnesian Wars Philip of Macedon • Father of Alexander the Great. • Trained his son for a military life from an early age. • Fought the Persians and started toward a united Greece. • Died through betrayal. Alexander the Great • Spread Greek social order around the known world. • Married a number of times to cement alliances. • Died of fever/ alcohol poisoning/ poison? • Returned to Macedon for burial. Alexander’s Successors Alexander Seleucids – Syria and Mesopotamia Alexander’s Successors Ptolemis - Egypt Antigonids – Macedon and Asia Minor- later split into two kingdoms. The Romans • The Republic - Expansion 264-133 B.C. – Advantages of Italy • • • • large fertile plains mountain ranges do not impede communication protected on three sides by water protected to the north by Alps • Greek colonies firmly established in the south by 600 B.C. Etruscans • • • • Controlled area north of Latium by 700 B.C. Seized Rome by shortly after 600 B.C. City of Rome founded by Romulus Etruscan Society – Farmers, Miners,Metalworkers, walled cities,believed in an afterlife. – Women enjoyed relatively high status Romulus and Remus Latin Overthrow of the Etruscans • Setup of the Roman Republic – Patricians - land owners perhaps 10% of the population, held full citizenship – Plebeians - trade, laborers, small farmers, & debtors about 75% of the population, no right to hold office – Slaves Romans Continued • Terms – imperium – dictator – SPQR – Centuriate Assembly – Praetor – Tribunes Romans Continued • By 3rd century B.C. Rome controlled all of Italy • Conflicts with Carthage (Punic Wars) 264241,218-202, &149-146 B.C. – Results • Destruction of Carthage • Expansion eastward to control Macedon, Greece, Egypt, and most of Asia Minor by 133 B.C. Punic Wars Hannibal Hannibal’s Route of Invasion Punic Wars Battle of Cannae 215 B.C. Battle of Zama The Empire • Julius Caesar gain control in 45 B.C., assassinated in 44 B.C. • Octavian Augustus becomes first Roman Emperor (27 B.C. - 14 A.D.) • Pax Romana - two centuries of peace and prosperity • After 180 A.D. civil war weakens the empire The Empire Julius Caesar Octavian Augustus Added to the mix Mark Antony Cleopatra Judaism and Christianity The Hebrews Roman rule of the Jews Christianity as a Jewish movement Separation initiated by Paul - Spread belief throughout the empire • Romans persecuted Christians • • • • – Roman Circus – Underground movement Judaism and Christianity The Hebrews Roman rule of the Jews Christianity as a Jewish movement Separation initiated by Paul - Spread belief throughout the empire • Romans persecuted Christians • • • • – Roman Circus – Underground movement Saint Paul Saint Peter • First Bishop of Rome. • First Pope. • Martyred in Rome for his faith. The Great Persecutor - Nero Coliseum Coliseum Christianity Continued • Nero - the great persecutor • Persecution ended by Constantine in A.D. 312 • Made official religion of Rome in 380 A.D. by Theodosius • Bishop of Rome = Pope in west • Emperor of Constantinople leader of church in east • Augustine of Hippo First Christian Emperors Constantine Theodosius The Early Middle Ages • • • • • • • 500-1000 A.D. Medieval Breakdown of Roman Civilization Franks and Charlemagne The Northmen Feudal Europe Civilization of the Early Middle Ages Breakdown of Roman Civilization • The Germans – – – – – Goths Visigoths Vandals Ostrogoths Anglo-Saxons • The Huns • Barbarian Invasions • Terms – autarkic : self sufficient – vernaculars: local languages derived from Latin – barbarian : someone from outside Rome The Franks • Pepin • Clovis founder of Frankish Power – c. 496 converted to orthodox Catholic – split kingdom among heirs – by 7th century diluted power. – hereditary offices – Pepin III (the short) King of Franks r. 751-768 A.D. – Supported the Pope and gave Vatican City to Pope after taking it from Lombards Frankish Kings Pepin III Charlemagne Charlemagne 742-814 • Completed destruction of Lombards • r. 768-814 • provinces were called “marks” or “marches” • Crowned Emperor of Rome Christmas day 800 A.D. by Pope Leo III • Also known as Charles the Great • Territory included 300 counties The Northmen “Vikings” Scandinavia Sea going vessels Raided up Thames, Seine and Loire • Booty • Polygamy • • • • • Normandy granted as permanent settlement to Rolf (Rollo) c. 860 c.931 byFrankish King. • Duke William conquers England in 1066. Vikings Viking Ships