* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 14-Life History Lecture #1
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology in the United States wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Phanerozoic wikipedia , lookup
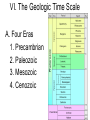
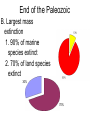
The History of Life Chapter 14 How the Earth Was Made: The Birth of the Earth Video I. Paleontologists A. Scientists who study ancient life 1. Kinds of organisms 2. Ancient climate 3. Geography II. Early History of Earth A.Very hot B. Volcanoes spewing lava and gases C. Little oxygen in the atmosphere but lots of CO2, nitrogen and water vapor II. Early History of Earth Earth Cools -lava cools (forms lands) -rains for millions of years (forms oceans -3.8 bya III. Fossils A. Sedimentary rocks contain fossilsclues to the past B. Oldest rocks 3.9 BILLION years old. III. Fossils C. The Fossilization process http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/ dinosaurs/dinofossils/Fossiltypes.html III. Fossils D. Mold (empty space) E. Casts (minerals fill a space left by decayed organism) F. Trace fossils (indirect G. Petrified (hardened/permineralized) H. Amber preserved (quickly trapped in sap & hardened) I. Frozen (preserved in ice) V. The Age of a Fossil A. Relative Dating 1. Determined by dating the rocks in the layer above and below the fossil a. Newspaper example 2. An estimate of age V. The Age of a Fossil B. Radiometric Dating 1. Determination of how many of the original atoms are left in the rock. a. Atoms decay at a steady rate 2. Half-life- Time needed for ½ the atoms to decay a. If the fossil’s half-life is 2 million years, when ½ of its atoms are gone it will be 2 million years old. V. The Age of a Fossil 3. Scientists use potassium-40 to date the oldest rocks and carbon-14 to date younger fossils a. Draw example on board 4. Errors can occur if the rock has been heated (atoms are lost or gained). VI. The Geologic Time Scale A. Four Eras 1. Precambrian 2. Paleozoic 3. Mesozoic 4. Cenozoic VII. Life in the Precambrian (4600-543 MYA) A. Earth’s formation B. Prokaryotes 1. Cynobacteria-like 2. Stromatolites C. 1.8 BYA eukaryotes evolve D. 87% of Earth’s history 1.(January-October) VIII. The Paleozoic Era 543 MYA – 245 MYA A. Cambrian explosion of life! 1. Worms, sea stars, arthropods, fishes 2. 400 MYA, ferns & early seed plants 3.Amphibians, reptiles End of the Paleozoic B. Largest mass extinction 1. 90% of marine species extinct 2. 70% of land species extinct 30% 70% IX. Mesozoic 245 MYA – 66 MYA A. Triassic period 1. Mammals (small) 2. Dinosaurs 3. Fern forest B. Jurassic period 1. Dinosaurs 2. Modern birds evolved from birds of this period End of the Mesozoic C. Cretaceous Period 1. New Mammals 2. Flowering Plants D. Mass extinction of the dinosaurs 1. 66% of all living species extinct 2. Evidence of meteorite collision (Mexico) E. Pangaea broke apart gendre Jfslkdj feo 66% died 34% survived End of the Mesozoic See “Owen’s Dinosaur Video” gendre Jfslkdj feo X. The Cenozoic Era 66 MYA – present A. Mammals flourish B. 30 MYAprimates C. 200,000 years ago, modern humans