* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light and the electron
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
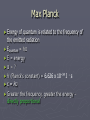
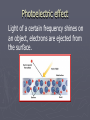
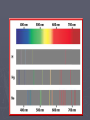
Light and the electron Quest continues to discover the structure of atom and how electrons are arranged within atoms. Wave Nature of Light ► Electromagnetic radiation – form of energy exhibiting wave-like behavior ► Ex. Visible light Wavelength (λ) ► Distance between adjacent peaks in a wave. Measured in meters. Speed of light (c) ► Light travels at 186,000 mi/s ► 3.0 x 108 m/s ► c = 3.00 x 108 m/s Frequency (Ʋ) ► Number of peaks which pass a point per second. ► Ʋ = 1/s (Hz) Wavelength vs. Frequency Putting it together ►c = λƲ ► 3.00 x 108 m/s = λƲ ► Pg. 121 practice problems 1-4 Electromagetic radiation (light) To microwave Particle Nature of Light ► Wave nature of light didn’t explain many important aspects – Why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at given temp.? ► Quantum concept – heated objects emitting different frequencies of light. Energy emitted corresponds to certain Ʋ & λ ► Quantum- minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom Max Planck ► Energy of quantum is related to the frequency of the emitted radiation ► Equantum = hƲ ► E = energy ►Ʋ = ? ► h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10–34 J · s ► c = λƲ ► Greater the frequency, greater the energy – directly proportional Albert Einstein ► Proposed that electromagnetic radiation has both wavelike and particle-like natures. ► Extended upon Planck’s equation – photoelectric effect ► Pg. 124 practice problems 5,6 Photoelectric effect Light of a certain frequency shines on an object, electrons are ejected from the surface. Atomic Emission Spectra – light produced in glowing neon signs ► Pass energy through tube filled with gas ► Causes electrons to absorb energy & become excited ► As unstable, excited electrons lose energy and spiral towards the nucleus they give off energy that corresponds with certain frequencies of light ► When emitted light is passed through a prism→ atomic emission spectra ► Each atom’s atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Pg. 126 Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Hydrogen spectrum