* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atom - SCHOOLinSITES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
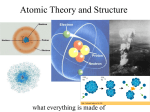
Atomic Structure What are atoms?? The structure of an atom Matter has mass and takes up space Atoms are basic building blocks of matter, and cannot be chemically subdivided by ordinary means The word atom is derived from the Greek word atom which means indivisible The Greeks concluded that matter could be broken down into particles to small to be seen. These particles were called atoms Atoms are composed of three type of particles: protons, neutrons, and electron •Protons and neutrons are responsible for most of the atomic mass •The mass of an electron is very small •Both the protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus. •Protons have a postive (+) charge •Neutrons have no charge -they are neutral. •Electrons reside in orbitals around the nucleus. They have a negative charge (-). Sum it up: Protons – positive charge – mass of 1 – located in the nucleus Neutrons – neutral – mass of 1 – located in nucleus Electrons – negative charge – mass of 0 – located in region outside of the nucleus •Electrons are found in clouds that surround the nucleus of an atom. •Because electrons move so quickly, it is impossible to see where they are at a specific moment in time. •After years of experimentation, scientists discovered specific areas where electrons are likely to be found. These shells change depending on how many electrons an element has. • The higher the atomic number, the more shells and electrons an atom will have. ORBITAL BASICS Let's cover some basics of atomic orbitals. 1. A shell is sometimes called an orbital or energy level. 2. Shells are areas that surround the center of an atom. 3. The center of the atom is called the nucleus. 4. Electrons live in something called shells. 5. Each of those shells has a name. There are a couple of ways that atomic orbitals are named. You may have heard of the SPDF system before. Chemists also use letters to name the orbitals around a nucleus. They use the letters "k,l,m,n,o,p, and q". The "k" shell is the one closest to the nucleus and "q" is the farthest away. Not all shells hold the same number of electrons. For the first eighteen elements, there are some easy rules. The k-shell only holds two electrons. The l-shell only holds eight electrons. The m-shell only holds eight electrons (for the first eighteen elements). The maximum number of electrons you will find in any shell is 32. Important Definitions Atoms, atomic structure, chemical bonding, etc. atom The smallest indivisible particle of matter that can have an independent existence. atomic number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight The sum of the weights of an atom's protons an neutrons, the atomic weight differs between isotopes of the same element. neutron An uncharged subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom. The large (mass approximately equal to 1 atomic mass unit), electrically neutral particle that may occur in the atomic nucleus. electron A subatomic particle with a negative charge. Electrons circle the atom’s nucleus in regions of space known as orbitals. element A substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number; cannot be broken down in ordinary chemical reactions. proton A subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom that carries a positive charge. The positively charged (+1) subatomic particle located in the nucleus and having a mass slightly less than that of a neutron. Electron differ by the number of protons in their atoms. molecules Units of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. The combination of atoms by chemical bonds with the component atoms in definite proportions, such as water (two H to one O). matter Anything that has mass and occupies space. ionic bond A chemical bond in which atoms of opposite charge are held together by electrostatic attraction. isotonic Term applied to two solutions with equal solute concentrations. isotopes Atoms with the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons; indicated by adding the mass number to the element's name, e.g., carbon 12 or 12C. nucleus (atom) An atom's core; contains protons and one or more neutrons (except hydrogen, which has no neutrons). radioactive decay The spontaneous decay of an atom to an atom of a different elements by emission of a particle from its nucleus (alpha and beta decay) or by electron capture. covalent bond A chemical bond created by the sharing of electrons between atoms. ionic bond A chemical bond in which atoms of opposite charge are held together by electrostatic attraction. isotopes Atoms with the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons; indicated by adding the mass number to the element's name, e.g., carbon 12 or 12C. Review Questions •Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron •The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 •An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; b) H; c) O; d) Ne; e) N •The chemical bond between water molecules is a ___ bond. a) ionic; b) polar covalent; c) nonpolar covalent; d) hydrogen •A solution with a pH of 7 has ___ times more H ions than a solutrion of pH 9. a) 2; b) 100; c) 1000; d) 9; e) 90 •The type of chemical bond formed when electrons are shared between atoms is a ___ bond. a) ionic; b) covalent; c) hydrogen •The type of chemical bond formed when oppositely charged particles are attrached to each other is a ___ bond. a) ionic; b) covalent; c) hydrogen •Electrons occupy volumes of space known as ___. a) nuclei; b) periods; c) wavelengths; d) orbitals •Carbon has an atomic number of 6. This means it has ___. a) six protons; b) six neutrons; c) six protons plus six neutrons; d) six neutrons and six electrons •Each of the isotopes of hydrogen has ___ proton(s). a) 3; b) 1; c) 2; d) 92; e) 1/2 •A molecule is ___. a) a mixture of various components that can vary; b) a combination of many atoms that will have different ratios; c) a combination of one or more atoms that will have a fixed ratio of its components; d) more important in a chemistry class than in a biology class