* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radioactivity and the Four Forces
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
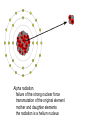
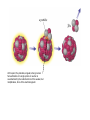
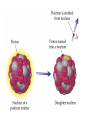
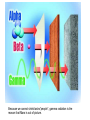
Radioactivity and the Four Forces Chapter 9, Section 1, Page 258 – 262 Monroe 12/01/08 Chapter 9, Section 1, Page 258 – 262 An atom is made up of three things. 1 A proton i. The number of protons is the ATOMIC NUMBER ii. Protons are made up of quarks iii. Protons have a positive one charge (+1), exactly A Neutron i. The number of neutrons is determined by subtracting the atomic number (see above) from the atomic mass (higher number), which follows the “-“ symbol of atoms ii. Neutrons are also made up of quarks iii. Neutrons have a charge of exactly “0”. They are neutral iv. The number of neutrons, plus the number of protons, equals the atomic mass number. An Electron i. An almost massless particle ii. Charge of exactly negative one (-1) The Nucleus of an atom has a huge collection of positive particles in it. Why does it not blow itself apart (since similar charges repel, and all the protons have the same charge)? The answer is the STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE. Four Forces of Nature Gravity ~ weakest of all. Almost nothing is known about it. It is probably carried by a particle called a graviton. Weak Nuclear force ~ keeps atoms from changing elements. Electromagnetic ~ combination of electricity and magnetism. It is carried by the interaction of the electrical/magnetic fields. Strong Nuclear ~ holds the atom together. This is the strongest of all of the forces, and is the one broken with nuclear reactions. http://aether.lbl.gov/www/tour/elements/stellar/strong/strong.h tml Alpha radiation failure of the strong nuclear force transmutation of the original element mother and daughter elements the radiation is a helium nucleus At this point, the probable, singular, strong nuclear force attraction of a single proton or neutron is overwhelmed by the collective force of the weaker, but multiplicative, force of the electromagnetic. Beta radiation, Failure of the weak nuclear force. Neutrons become protons, so electrons must be “made” so that law of conservation of charge is maintained. Beta radiation is electrons. Gamma radiation is very, very energetic electromagnetic waves (light and photons). Because we cannot shield astro”people”, gamma radiation is the reason that Mars is out of picture. Kinda how a geiger counter works Demonstration of a “mousetrap” nuclear demonstration http://www.energyforeducators.org/snavigation/nuclear.sh tml