* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The atom - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
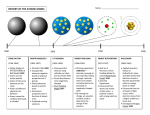
The Atom The History of a model The structure of the matter and the study of atoms really begins with Greek philosophers. They believed: Matter was made up of some material with structure All matter was formed from 4 basic elements 1. Air 3. Water 2. Fire 4. Earth Greek philosopher Democritus Matter was made up of atoms-from the word “atomos” which means indestructible. Atoms were very tiny particles Between atoms was empty space, he called the void. There are different kinds of atoms depending upon the type of matter From Democritus' time, around 400 BC, to 1700 AD not much happened. This time was called the Dark Ages and only the Alchemists were doing much and what they did didn't directly improve upon atomic theory Age of Enlightenment A revolution in scientific study came about and atomic theory advanced rapidly. In 1782 Lavoisier discovered the Law of Conservation of Matter. Joseph Proust discovered that H2O is always 11% hydrogen and 89% oxygen. (Explanation… ) Proust also found that many compounds also had consistent compositions by mass and had therefore discovered the Law of Definite Proportions John Dalton 1. 2. 3. 4. Dalton was the first to actually propose an atomic theory based on many experiments. His was the first workable atomic theory. It stated that: All matter was made up of atoms. Atoms are indestructible. Each element has its own atom and that different elements had different types of atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical. JJ Thomson discovered that elements had a negatively charged particle, and since atoms were neutral, there must be an opposite positive charge. He had discovered electrons. He proposed a new atomic theory that included the charges. His was the Raisin Bun/Plum Pudding model. Crooke’s Tube: Crooke’s Tube: Millikan Calculated the charge on an electron Oil drop experiment (1909) In 1886, it was discovered that the Crooke's Tube also emitted positive particles. Ernest Rutherford 1. 2. 3. 4. Due to the discovery of radiation Rutherford was able to discover that atoms were mostly empty space with a massive positive but tiny nucleus. He proposed a new updated planetary model where: Electrons orbited a nucleus like planets around the sun. The nucleus was tiny but massive. The nucleus is positively charged. Most of the atom is empty space. Rutherford was credited with discovering the nucleus and the proton. The number of protons in an atom is the atom's atomic number. The atomic number is identified by the symbol Z. Gold Foil Experiment Rutherford atom In 1910 JJ Thomson discovered that even atoms from the same element varied in mass. He called atoms from the same element with varying masses isotopes. The average of all the known isotopes of an element give the element its average atomic mass. Elements on the periodic table have decimals in their masses for this reason (and because they are all based on Carbon-12) Chadwick In 1930 Chadwick discovered the last subatomic particle; the neutron. Neils Bohr worked with Rutherford agreed with Rutherford's model but could not explain the physics of the model—why didn't the electron's spin into the nucleus? Bohr began studies with electromagnetic spectra of elements. electromagnetic radiation, E.R., has two important properties. 1. wavelength 2. frequency The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. Gamma Rays are the most energetic, radio waves are the least where as visible light fits in the middle. Bohr Ran electricity through gaseous versions of elements, thus an electromagnetic spectrum was produced-unique to each element. Believed that these spectra coincided with energy levels of e-. He could never predict any elemental spectrums beyond hydrogen though. Excited (electrified) electrons gain energy and jump up to a higher energy level or orbit. When they give up this exact amount of energy they return to their normal or ground state. e- can skip over many energy levels if given enough energy and they can skip many on their way back too. Modern Model - Charge Cloud Model Today's model uses predicted (calculated) locations for electrons. These possible locations are represented by clouds, the darker the clouds, the higher the “probable” location of an electron. Energy levels can only hold a certain number of electrons a. 1st energy level holds 2 e b. 2nd energy level holds 8 e c. 3rd energy level holds 18 e d. and so on. The maximum number of outer electrons is 8 The Octet Rule The outer electrons are called valence electrons and are the electrons involved in chemical reactions.