* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical Science 1 Chapter 18 – Properties of Atoms & the
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
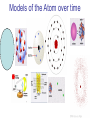
Physical Science Chapter 18 – Properties of Atoms & the Periodic Table The Elements: Forged in Stars The Origin of the Elements Chemical Symbols • Abbreviations for chemicals • Punctuation is KEY – – – – Capital Letters Subscript Superscript Spacing • Elements – ALWAYS Start with a capital letter – Symbols can be 1,2 or 3 letters – First letter is capitalized and 2nd & 3rd are lowercase • Atom- smallest piece of matter that has the properties of the element • CO doesn’t equal Co – CO = Carbon monoxide – Co = Cobalt Atomic number Always the smaller of the 2 # Always a whole # (no decimals) = number p+ Atomic mass Always the BIGGER of the 2 # Usually a decimal = # p+ & n The subatomic particles p+ = positive charge n = no charge e- = negative charge nucleus nucleus cloud Electrons have such a small mass compared to protons and neutrons we say electrons have no mass – but really they do. p+ = 1 amu amu – atomic mass unit n = 1 amu 1/12 of a Carbon -12 e- = 0 amu QUARKS Murray Gell-Mann found the name "quark" in the book "Finnegan's Wake" by James Joyce. The line "Three quarks for Muster Mark..." Gell-Mann received the 1969 Nobel Prize for his work in classifying elementary particles. Quark Symbol Spin Charge Up U 1/2 +2/3 Down D 1/2 -1/3 Charm C 1/2 +2/3 Strange S 1/2 -1/3 Top T 1/2 +2/3 Bottom B 1/2 -1/3 Finding the Quark Quarks: Inside the Atom Fermilab – National Particle Accelerator Lab Chicago IL To Find a Quark- accelerate charged particles to high speeds and cause them to collide with protons, which breaks the proton apart EXTRA CREDIT: Find out what a neutrino is & why it’s important to SD Can you figure out which cork stands for which quark? Atomic Models Models- used to help you understand something too large or too small to see Democritus – indivisible atom 450 BC Dalton- atoms are just spheres John Thomson – Plum Pudding model 1904 Discovered the electron 1897 – cathode ray tubePlum Pudding model- atoms had small negatively charged particles- electrons- embedded throughout a positively charged sphereINCORRECT BECAUSE- electrons are in clouds AROUND the nucleus, not within the nucleus. Also- did not distinguish between protons and neutrons. Models of the Atom over time Models of Atoms Ernest Rutherford – Rutherford model 1911 -Gold Foil experiment – positive nucleus (protons) -Almost all the mass of an atom was in the central atomic nucleus surround by electrons. INCORRECT BECAUSE- did not distinguish between protons and neutrons. Chadwick – discovered the neutron 1932 Niels Bohr – Bohr model 1913 - Electrons traveled in fixed orbits around the nucleus. The nucleus contained protons and neutrons. INCORRECT BECAUSE- electrons are not in fixed orbits but in a region around the nucleus- just occur more frequently in certain places. Electron Cloud Model- Current Model • Electron cloud model – Protons and Neutrons in the nucleus – Electrons in an electron cloud- the area around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are most likely to be. Very large compared to the nucleus