* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download City Networks: Learning through Patnerships
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
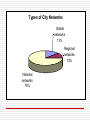
City Networks: Learning through Patnerships Zaragoza, Water Tribune 2008 Mila Freire The World Bank Outline Cities in Development – shifting paradigms Urbanization: from burden to opportunity The role of public policy – easying the process The challenges of servicing fast growing cities Cities and global goods – climate change City Networks Rapid growth in number and themes Sector issues, policy concerns Reaching the less able; sharing the fruits of knowledge Cities in Development Old paradigm Too rapid urbanization; too large cities; Increasing slums and poverty Discourage migration to cities New paradigm Economic growth and change in structure happens with concentration of people in towns Density is needed for productivity growth The challenge: how to ease urbanization process, while minimizing congestion costs City population expected to double in 30 years Climate change – the new urgent agenda Richer countries have higher urbanization and density rates 1 .8 Korea Japan Germany India Brazil South Africa China .4 .6 USA Norway Botswana .2 More rapid in the beginning Slower at higher levels of development Egypt Ethiopia Belize 0 Agglomeration Index Richer countries are denser GDP per capita grows with urbanization Non-linear relation 0 10 20 30 GDP per capita (thousands, PPP, 2000 constant US$) 40 Economic growth brings change Secondary sector increases its share in GDP; tertiary sector even more. Dispersed activities (i.e. agricultura) are replaced by more concentrated activities – manufacturing Services become a predominant sector Change is common in developped and developing countries Cities: engines of growth and service providers Within the uneveness of development some basic rules to help urbanization process Basic services need to be provided to everyone regardless whether in lagging or leading regions Lack of services (access to water, education, health) should not be the determinant for migration; but differences in productivity and income. Provision of water - part of the poverty-alleviation and part of the ammenity and business climate agenda As urbanization continues, investment in connectivity (urban transport) is required Targetted policies to promote inclusion (slums or informality) become the main policies. Again, availability of water and sanitation is the most effecive way to improve well-being at lower income levels, Preparing for the future: Cities expansion: sprawl? Density? Angel projects a trippling of built land for a doubling of urban population? Accurate of not, makes one think. Increased demand for land? Consequences on need for infrastructure, including water? Is water availability a variable in the way our cities are and will be growing? Is water being priced correctly? Lessons from Los Angeles or Phoenix Water disputes in West California. The big challenge: A billion in slums Sustainable Cities Cities contribute for 60-70% of C02 emmissions The relation of C02 (per capita) grows at first but then declines as consumers become more aware of th need to be energy efficient Industrialzed cities have initiated very important initiatives to curb influence of cities in CO2 emissions: Urban transport Building codes Encouragement to density (against sprawl) Adaptation: the challenge for cities in poored countries Arid cities – lack of water Coastal cities – possible flooding and loss of assets The challenge: knowledge and governance Urban vulnerability to climate change DIRECT IMPACTS Sea level rise Flooding and landslides Heat waves Water scarcity Decreasing water quality Worsening air quality Ground ozone formation Djibouti-Ville flooded in April 2004 Urban vulnerability to climate change INDIRECT IMPACTS Environmental refugees Djibouti, October 2004 Frequency, intensity of natural disasters Accelerated urbanization Environmental refugees Increased energy demand for heating or cooling Epidemics, worsening public health Availability and pricing of foodstuff 2. City Networks City networks emerge from the need and “joy” to share knowlege, experiences and successes. Can be national, regional and global. At present one has more than 20 global city networks More than 30 Regional networks More than 100 National Netowrks With webb pages, publication and regular stream of information. Probably thousand of twin-cities arrangements, adhoc meetings and exchange programs. Excludes networks focused on specific sectors Types of City Networks Global networks 13% Regional networks 12% National networks 75% Global Networks Are organized by themes Eclei, C-40 for environment CA for urban upgrading and city development strategy UCLG to represent a whole range of matters of concern to municipalities, probably the most representative of the global networks Have increasing political voice Often associated with UN Financed by bilateral and multilateral donors Technically important Sector City Networks GHG abatement initiatives ICLEI “Cities for Climate Change” program C40 cities partnership Clinton Foundation World Economic Forum Carbon financing, carbon trading markets DOE “Clean Cities” EU incentives system for local governments Regional Networks Important to share issues typical of each region Special important in Europe including Eurocities Latin America Asia Africa has a continental progrqam (MDP) UCLG has chapters in each Region Country Networks Particular active in Asia (37) Philipines (4), Indonesia (5), Japan (9), India, Australia (3), South Korea Latin America (16) Brazil (3), Argentina (3), Mexico (2), El Salvador, Chile (2), Bolivia Europe and Central Asia (21) Bulgaria (3), Poland (2) South Africa has two active associations Most African countries have municipal associations Very important role played in the Rwanda reconciliation process Europe (24) North America; USA (3), Mexico (1), Canada (1) Africa Country networks (cont.) National networks are particularly important in matters of decentralization, tax policy and policy reform Brazil municipal associations were fundamental to give municipalities full power as federative entity during 1988 constitutional reform Honduras and Philipines associations have major role in discussing revenue share, and progressive decentralization of responsibilities Water-city Networks Water city networks were probably the first networks to be created in the world Water rights and negotiations have been among the first documents to be found How to use, allocate and solve dispute water uses have illustrated and facilitate the exchanges accross cities At present, most of the global, regional and country networks have chapters focused on water issues. And thousands of cities, regions and NGOs have their own associations dealing with water and watr management. EUKN, Eurocities, Urbact, and other networks are associated The major challenge for most of the networks – from a development view point is whether local knowledge can be leveraged and shared especially with poorer municipalities and local governments. Thanks