* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download H 2 -receptor antagonists
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drugs used in treatment of peptic ulcer
Dr.Iman
Acid-peptic disease
A group of disorders involving erosion or ulceration of the mucosal lining of the gastrointestinal
tract; includes:
- GERD
-gastric and duodenal ulcers (peptic ulcer)
-non ulcer dyspepsia, and
-stress-related gastritis,
- Pathologic hypersecretoryZollinger Ellison syndrome which is a rare genetic condition with ↑
level of gastrin secreted by tumors in pancreas or duodenum
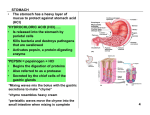
-PU occurs when there is imbalance between the damaging effects of gastric acid and pepsin,
and the defense mechanism which protects the gastric and duodenal mucosa from these
substances
Defense mechanisms include:
Mucous, bicarbonate, PGs keep good blood flow, stimulate bicarbonate and mucous production
and protect against injury (cytoprotective)
.
Peptic Ulcers
Common disease,incidence rate: 10%~12%.
Causes of peptic ulcer: the pathology is not completely understood
-↑ Gastric acid and pepsin secretion.
-↓ Mucosal resistance to acid e.g. mucus and bicarbonate.
-Role of Helicobacter pylori → ↑ gastrin, ↑ HCl.
-NSAIDs, steroids.
-Smoking, alcohol, stress, e.g. burn, head injury
Aim of Rx:
-Neutralize HCl.
-↓ HCl secretion.&
- Enhances mucosal defense system with cytoprotective or
-antimicrobial agents to eradicate the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which is detectable in over
80% of patients with duodenal ulcers..
Antacid
mechanisms:
-Reduce gastric acidity by neutralizing HCl, they are weak bases react with HCl → water and
salts.
-Pepsin is inactive at pH greater than 4, antacids ↓ pepsin activity.
-Stimulation of PG synthesis ( cytoprotective).
-Reduction of H-pylori colonization
-Antacids vary in their chemical composition, acid neutralizing capacity, sodium content, price,
palatability, solubility and side effects.
-Used 1 hour, then 3 hours after meal.
-Foods in stomach will delay emptying, allowing more time for action .While rapid gastric emptying
limited pH elevation in stomach.
Therapeutic uses:
-Relieve pain in peptic ulcer and esophagitis.
-Promote healing of duodenal ulcer Whenused regularly in the large doses needed to significantly
raise the stomach pH, but this benefit in gastric ulcer is less clear.
-Calcium carbonate used to Rx osteoporosis.
-Rx of esophageal reflux.
Individual antacids:
Magnesium hydroxide : react quickly with HCl, cause diarrhea. Another salt, magnesium
trisilicate, is an insoluble powder that reacts slowly with the gastric juice, forming magnesium
chloride and colloidal silica. This agent has a prolonged antacid effect, and it also adsorbs pepsin.
Aluminum hydroxide:which produces constipation so combined with magnesium hydroxide to
normalize bowel function
-It binds phosphate → hypophosphatemia and hypophosphaturia. This effect has been used in
treating patients with chronic renal failure
-Sufficient aluminum absorption → encephalopathy in patients with renal failure.
• -( both are not absorbed ,neutralize the acid &adsorb pepsin )
• Calcium carbonate: may cause rebound acid hypersecretion, and prolonged use with Ca+2
containing food → hypercalcaemia and alkalosis.
• Sodium bicarbonate: relieves pain within minutes,
– Not recommended for long-term use because it absorbed and → metabolic alkalosis.
– NaHCo3 liberates Co2 → belching and flatulence.
– Excess sodium intake may be undesirable in cardiac, renal diseases and hypertension.
• Dimeticone: added to antacid mixture to reduce flatulence.
Alginic acid + antacid (Gaviscon): ↓ reflux of HCl → symptomatic improvement
Aluminum, magnesium – containing antacids:
-May interfere with absorption of drugs by binding with them, or altering GIT pH or transit time
therefore reduce biological activity and availability of iron, digoxin, warfarin and some NSAIDs.
-Antacids more efficiently neutralize acid in stomach, relief pain, but short lasting.
Gastric antisecretory drugs
HCl secretion in under the control of: histamine, Ach, gastrin.
+ +
The final pathway is proton pump, H /K ATPase.
Inhibition of histamine, Ach action, ATPase have been developed.
H2-receptor antagonists:
Mechanism:
-Competitively block the binding of histamine to H2 receptors → ↓ cAMP→ ↓ HCl secretion →
promote healing and prevent recurrence.
-They also inhibit Ach and gastrin-mediated acid secretion.
-Used in Rx of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
-Tolerance can occur due to down regulation of receptors.
• The four drugs cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, and nizatidine potently inhibit (greater than 90
per-cent) basal, food-stimulated, and nocturnal secretion of gastric acid after a single
dose.
• Suppress nocturnal acid secretion effectively so given as single dose in evening for 8 weeks
→ healing ulcer.
• its utility is limited by its adverse effect profile ,drug–drug interactions & tolerance.
• The use of these agents has decreased with the advent of PPIs
Cimetidine:
Is the prototype of H2-blockers.
Rapidly absorbed T1/2 = 2 hours, given 400mg × 2, or 800mg at bed time.
Kinetics:
Orally given,IM,IV widely distributed even in milkand cross the placenta, excreted in urine, ↓ the
dose in hepatic and renal failure.
30% slowly inactivated by liver enzymes, 70% excreted unchanged in urine
Adverse effects:
Few with short term Rx.
-Headache, dizziness, constipation or diarrhea, muscular pain.
-Bradycardia and cardiac conduction defect.
-Weak antiandrogeniceffect → gynaecomastia and sexual dysfunction in males and galactorrhea,
↓ sperm count.
-In elderly → CNS disturbances as confusion, hallucination also occurs after I.V. injection.
-Inhibit cytochrome P450 → ↓ metabolism of several drugs as warfarin, valium, phenytoin,
quinidine, carbamazepine, theophylline, Imipramine, lidocaine, propranolol.
Ranitidine:
Longer duration of action than cimetidine.
5-10 fold more potent.
Minimal side effects, no antiandrogenic or prolactin stimulating effect.
Not affect mixed-function oxygenase system in the liver, therefore not affect concentration of
other drugs.
50% metabolized and 50% excreted unchanged.
Famotidine:
Similar to ranitidine in action.
20 – 50 times potent than cimetidine.
T1/2 = 3 hours, 25% metabolized and 75% excreted in urine.
Nizatidine:
T1/2 = 1 hour, 10% metabolized and the other 90% excreted unchanged in urine, similar to
ranitidine in action and potency.
Eliminated principally by the kidney.
st
Because little 1 – pass metabolism occurs, its bioavailability is nearly 100%.
No I.V. preparation is available.
Notes:
st
-Except Famotidine, all these agents inhibits gastric 1 – pass metabolism of ethanol.
-Ketoconazol needs acidic media for absorption so, it will not efficiently absorbed with H2
antagonists.
-No benefit from combining of antacid and H2 antagonists.
-Combination of H2-antagonist and PPI → inhibition of the efficacy of the later.
Therapeutic uses
•
•. Peptic ulcer, recurrence is common after stop Rx, this can be prevented by eradication ofpylori.
Z.E.S., hiatus hernia.
•To prevent heart burn (Gastroesophageal reflux).
- Acute stress ulcers: These drugs are given as an intravenous infusion to prevent and manage
acute stress ulcers associated with high-risk patients in intensive care units.
However, because tolerance may occur with these agents in this setting, PPIs have gained favor
for this indication
+
+
Inhibitors of H /K -ATPase proton pump (PPI):
+
+
-Omeprazole: is the first of a class of drugs that bind to of H /K -ATPase enzyme system of
+
parietal cell → suppress of H ions to gastric lumen.
-Lansoprazole,dexlansoprazole ,rabeprazole, pantoprazole and esomeprazole
Action: all are prodrugs with an acid-resistant enteric coat to protect them from premature
activation by gastric acid. The coating is removed in alkaline duodenum, and the prodrug- a weak
base, is absorbed and transported to parietal cell canaliculus, where it converted to active form,
+ +
forming covalent bond with H /K -ATPase – cycteine residue. It takes about 18 hours for
enzymes to resynthesized.
They inhibit basal and stimulated HCl secretion over 24 hours.
A single 20mg Omeprazole ↓ HCl secretion over 24 hours.
Uses:
Superior to H2 antagonists in ↓ HCl secretion and healing of peptic ulcer and erosive esophagitis.
H pylori treatment
Preferred in Rx of Zollinger – Ellison syndrome.
Rx of GERD-gastro-esophageal reflux disease.
↓ Bleeding from ulcer caused by aspirin and other NSAIDs, also used with antimicrobial regimen
against H-pylori
-If an H2-receptor antagonist is needed, it should be taken well after the PPI. H2 antagonists
reduce the activity of the proton pump, and PPIs require active pumps to be effective.
Kinetics:
Delayed – release formulation and effective orally.
Pantoprazole is also available as I.V. injection.
Metabolites are excreted in urine and feces.
An oral product containing omeprazole combined with sodium bicarbonate for faster absorption
Adverse effects:
Well tolerated.
-Omeprazole inhibit cytochrome P450 – 2C family → ↓ metabolism of warfarin, diazepam,
carbamazepine, phenytoin → enhance the action of these drugs, the inhibition is less than
cimetidine.
- Omeprazole and esomeprazole may decrease the effectiveness of clopidogrel because they
inhibit CYP2C19 and prevent the conversion of clopidogrel to its active metabolite-------→a
possible increased risk of cardiovascular events.
- Elevated gastric pH may also impair the absorption of calcium
carbonate. Calcium citrateis an effective option for calcium supplementation in patients on acid
suppressive therapy
-PPIs may increase the risk of fractures, particularly if the duration of use is 1 year or greater
-With long term use → ↑ risk of gastric carcinoid tumors due to prolonged hypochlorhydria and
secondary hypergastrinemia (↑ gastrin secretion → stimulate growth of gastric epithelium).
Other cause of tumor that hypochlorhydria → ↑ colonization of stomach bacteria with convert
ingested nitrates into carcinogenic nitrosamines.
- Diarrhea and Clostridium difficilecolitis may occur in community patients receiving PPIs.
-PPI and H2 antagonists ↓ absorption of Vit. B12 because acid is required for its absorption
Antimuscarinic agents:
Stimulation of muscarinic receptors → ↑ GIT motility and secretory activity.
AntimuscarinicDicyclomine used as adjunct in the management of peptic ulcer and Z.E.
syndrome.
Cardiac arrhythmias and urinary retention limit its use.
Used in refractory ulcers or with nocturnal pain.
Used + H2 antagonist.
Octerotide:
Synthetic somatostatin analog.
Inhibits secretion of several peptide hormones and gastric and pancreatic secretion.
Effective in Rx of Z.E. syndrome.
Lower portal pressures and ↓ risk of variceal hemorrhage in liver disease and portal hypertension.
Limited use due to I.V. administration.
•
•
Mucosal protective agents (cytoprotective compounds):
Mechanism: enhance mucosal protection, prevent mucosal injury. ↓ inflammation, ulcer bleeding.
Sucralfate:
-A complex salt of sucrose sulphate and aluminum hydroxide binds to positively charged groups
in proteins of both normal and necrotic mucosa.
-The result is a viscous paste which adheres to ulcer base,protect them from acid & pepsin
Also it binds to and inactivates pepsin and bile acids.
-Stimulates PG release, mucus, bicarbonate output.
-Requires an acidic pH for activation, therefore not used with H2antagonist ,PPIs or antacids.
-It interferes with absorption of Co-administrated ciprofloxacin, theophylline, digoxin, phenytoin
and amitriptyline by binding with them.
- its use is limited due to the need for multiple daily dosing and drug–drug interactions
Bismuth Chelate (colloidal bismuth):
Effectively heal peptic ulcers.
Antimicrobial effect, ↑ PGs synthesis.
Inhibit pepsin, ↑ mucus secretion, interact with glycoproteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to coat
and protect ulcer crater.
Misoprostol:
Synthetic analog of PGE1, as well as lansoprazole → prevent gastric ulcer induced by NSAIDs.
Less effective than PPI on H2 antagonist.
Used in patients taking NSAIDs and at high risk of NSAIDs induced ulcer e.g. elderly or with ulcer
complication.
Cause uterine contraction → contraindicated in pregnancy, vaginal spotting, and dysmenorrhoea.
Dose related diarrhea, nausea, are most common.
Antimicrobial agents:
To eradicate H-pylori associated with peptic ulcer disease → rapid healing and low recurrence
rate.
-Endoscopic biopsy of gastric mucosa is needed ,serology and urea breath tests .
-80 – 90% successful eradication of H-pylori achieved by:
- triple therapy → PPI + clarithromycin and metronidazole{if patient allergic to amoxicillin} or
amoxicillin → 2 weeks.
-Or quadruple therapy → bismuth subsalicylate and metronidazole + tetracycline + H2 antagonist
or PPI for 2 weeks.
Heart burn not associated with H-pylori; therefore need no Rx with antibiotics.