* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MEASLES
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
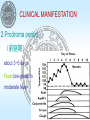
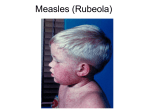
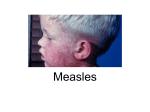
MEASLES (RUBEOLA) Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children’s Hospital MEASLES(麻疹) SUMMARY 1.Measles is an acute infectious disease 2.caused by the measles virus. 3. symptoms and signs such as fever, sneezing, cough, conjunctivitis(结膜炎), koplik spots(科氏 斑) and rashes MEASLES(麻疹) ETIOLOGY 1.be of paramyxoviridae(副粘病毒属) 2.only one serum type 3.the habit and resistance 4.can be from secretions(分泌物), urine,blood MEASLES(麻疹) 1.Measles is an RNA virus 2. be found in nasopharyngeal (鼻咽 部的)secretions,blood,and urine. 3. can remain active for at least 34 hr at room temperature. MEASLES(麻疹) EPIDEMICOLDGIC FEATURE Before widely using Measles virus’s attenuated(减毒的) vaccine,Measles epidemiced once per 2~4 years.But now this epidemic disappears and the adult patients gradully increase. MEASLES(麻疹) 1. epidemic throughout the world 2. In the past,epidemiced in the spring , 2~4 yr intervals ,new groups of susceptible(易感 者) children 3. be rarely subclinical 4. the age of peak incidence was 5~10yr 5. Individuals born before 1957 are considered to be immune from natural infection. MEASLES(麻疹) Infectious resourse: Patient,only Measles is very contagious(传染的);approximately 90% of susceptible family contacts acquire the disease. Maximal dissemination of virus occurs by droplet spray during the prodromal period (前驱期). Transmission to susceptible contacts often occurs prior to diagnosis of the original case MEASLES(麻疹) 1. Infants acquire immunity transplacentally (经胎盘) from mothers who have had measles or measlesimmunization. 2. This immunity is usually complete for the first 4~6mo of life and disappears at a variable rate. 3. Although maternal antibody levels are generally undetectable in the infant by the usual tests performed after 9 mo of age, some protection persists, which may interfere with immunization MEASLES(麻疹) 1. infants of mothers with measles vaccine- induced immunity lose passive antibody at a younger age than infants of mothers who had measles infection. 2. Infants of mothers who are susceptible to measles have no measles immunity and may contract the disease with the mother before or after delivery. MEASLES(麻疹) Infectivity ① People are easily affected ② Covert(隐性) infection is rare ③ <8M infant, >8M people ④ Immunocompetence(免疫力) is forever MEASLES(麻疹) PATHOGENESIS Two virus toxemic(毒血的) symptoms 1.Invade the mucosal cells 2.Virus blood symptom MEASLES(麻疹) 1. 1.The essential lesion(损害) is found in the skin, in the mucous membrances of the nasopharynx,bronchi, and intestinal tract,and in the conjunctivae. 2. Serous exudate(渗出) and proliferation of mononuclear cells and a few polymorphonuclear cells occur around the capillaries. MEASLES(麻疹) 3. Hyperplasia(肿大) of lymphoid tissue usually occurs,perticularly in the appendix,where multinucleated giant cells(多 核巨细胞) of up to 100 uM in diameter(Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells) may be found. MEASLES(麻疹) Koplik spots consist of serous exudate and proliferation of endothelial cells similar to those in the skin lesion. A general inflammatory reaction of the buccal and pharyngeal mucosa extends into the lymphoid tissue and the tracheobronchial mucous membrane. Interstitial pneumonitis resulting from measles virus takes the form of Hech giant cell pneumonia.Bronchopneumonia may be due to secondary bacterial infection. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Typical measles 1.Incubation period(潜伏期) 6~18 days,ordinally 10~14 days,even to 21~28 days; low fever,uncomfortable MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION The patient may transmit the virus by the 9th-19th day after exposure and occasionally as early as the 7th day, before the illness can be diagnosed. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION 2.Prodroma period (前驱期) about 3~5 days. Fever,low-grade to moderate fever MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION URI a dry cough,coryza,anconjunctivitis. These symptoms nearly always precede the appearance of Koplik spots ,the pathognomonic sign of measles,by 2-3 days. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Koplik spots they are grayish white dots, usually as small as grains of sand, that have slight,reddish areolae,occasionally they are hemorrhagic(出血的).They tend to occur opposite the lower molars but may spread irregularly over the rest of the buccal mucosa.Rarely they are found within the midportion of the lower lip,on the palate,and on the lacrimal caruncle(泪埠). MEASLES(麻疹) Koplik spots appear and disappear rapidly, usually within 12-18 hr.As they fade a red,spotty discoloration of the mucosa may remain. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Others The conjunctival inflammation and photophobia(畏光) may suggest measles before Koplik spots appear.In particular,a transverse line of conjunctival inflammation,sharply demarcated(以为划界的) along the eyelid margin,may be of diagnostic assistance in the prodromal stage.As the entire conjunctiva becomes involved,the line disappear. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION 3.Rash period: about 3~5 days. The turn usually starts as faint macules on the upper lateral parts of the neck,behind the ears,along the hairline,and on the posterior parts of the cheek.The individual lesions become increasingly maculopapular as the rash spreads rapidly over the entire face,neck,upper arms,and upper part of the chest within approximately the first 24 hr. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION ① During the succeeding 24 hr it spreads over the back,abdomen,entire arm,and thighs. ② As it finally reaches the feet on the 2nd-3rd day,it begins to fade on the face.The rash fades downward in the same sequence in which it appeared. ③ The severity of the disease is directly related to the extent and confluence of the rash.In mild measles the rash tends not to be confluent,and in very mild cases there are few. MEASLES(麻疹) MEASLES(麻疹) MEASLES(麻疹) MEASLES(麻疹) colour and shape The rash is often slightly hemorrhagic,in severe cases with a confluent rash,they are maculopapular(斑丘疹).As the rash fades ,branny desquamation(糠麸状脱屑) and brownish discoloration(棕色色素沉着) occur and then disappear within 7-10 days. MEASLES(麻疹) Symptoms accompany The temperature rises abruptly as the rash appears and often reaches 40oC(104oF) or higher.In uncomplicated cases,as the rash appears on the legs and feet the symptoms subside rapidly within about 2 days usually with an abrupt drop in temperature to normal. MEASLES(麻疹) ① Patients up to this point may appear desperatately ill,but within 24 hr after the temperature drops,they appear essential well. ② Lymph nodes at the angle of the jaw and in the posterior cervical(颈的) region are usually enlarged. MEASLES(麻疹) ③ Otitis media(中耳炎),bronchopneumonia, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea(腹 泻) and vomitting are more common in infants and small children than in older children. MEASLES(麻疹) CLINICAL MANIFESTATION 4.Recover period: 3~5 days after the onset of rashes 1) Rashes fade from face,completely gone within 6 days 2)branny desquamation, brownish discoloration 3) Fever falls MEASLES(麻疹) LABORATORY FINDINGS 1. Tolal leukocyte counts 2. Multinucleated giant cells 3. Measles IgM antibody 4. Tissue culture 5. Measles antigen MEASLES(麻疹) COMPLICATIONS AND SEQUELAE (并发症和后遗症) 1.Respiratory complications ①Bacterial superinfections ②Pneumonia,bronchotitis,bronchospasm(支 气管痉挛), croup(哮吼) MEASLES(麻疹) 2.Cerebral complications ①Encephalitis(大脑炎) ②Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis(SSPE)(亚 急性硬化性全脑炎) MEASLES(麻疹) 3.Other complications: ① Black measles ② Thrombocytopenia(血小板减少症),appendicitis(阑 尾炎),keratitis(角膜炎), myocarditis(心肌炎) ③ Reactivation or progression of TB(tuberculosis) ④ Premature delivery or stillbirth (死产) ⑤ Mild liver function test elevation MEASLES(麻疹) DIAGNOSIS 1. Exposure to measles 10~14 days previously 2. Prodroma of fever,cough,conjunctivitis and coryza(鼻炎) 3. Koplik sports 4. Maculopapular rash 5. Leukopenia MEASLES(麻疹) TREATMENT,PROGNOSIS and PREVENTION Recovery generally occurs 7~10 days after onset of symptoms 1.Therapy: ①Eye care,cough relief,fever reduction ②Second bacterial infections:antimicrobial ③Ribavirin ④Vitamin A MEASLES(麻疹) 2.Active vaccination ①First time is after 8M ②Revaccination upon entrance into primary or second school 3.Patient should be isolated 5 days from rashes 4.Exposed individuals: ①Vaccination within 72 hours ②immune globulin within 6 days MEASLES(麻疹) 5.Morbidity and mortality rates(致病率与死亡率) are substantial because malnutrition(营养不良) and secondary infections 6.Suspected cases should be diagnosed promptly and reported to local health department. MEASLES(麻疹) 课后练习 1.何为麻疹早期与恢复期诊断标志 2.麻疹病人该隔离多长时间,何时传染性最强 3.麻疹的鉴别诊断 4.Koplik spot, 5.SSPE MEASLES(麻疹) 参考文献 尼尔逊儿科学 儿科学,人民卫生出版社,薛辛东主编 Paediatrics,北京大学医学出版社 MEASLES(麻疹) MEASLES(麻疹)