* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Salmonellosis PowerPoint
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
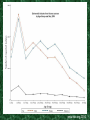
Chapter 28: Infectious Diseases Lesson: 1&3 Target Audience: Parents of Children Ages 1-4 Authors: Ashley Campbell Lauren Heatherly Janet Liebman Rakel Sanchez • An infectious disease • An infection caused by a bacteria called Salmonella United States= 40,000 reported cases yearly - Actual number of infections may exceed one million Approximately 600 persons die annually People of all ages can catch salmonella Infants and young children are at a greater risk due to their underdeveloped immune systems www.cdc.org,2004 Unwashed hands Raw poultry, eggs, and unpasteurized milk/cheese products Cross-contamination Fecal-oral transmission Animal feces Contact with infected animals Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Stomach pain Headache Fever Onset 12-72 hours after infection Usually lasts 4 to 7 days - most recover without treatment - fluid intake to avoid dehydration Severe infections may require hospitalization/antibiotics - May spread from the intestines to the blood stream, and then on to other body sites, which can cause death unless treated with antibiotic • Laboratory tests identify Salmonella in the stools of the infected person • Once Salmonella has been identified, further testing can determine the specific type, then antibiotics are given No vaccine Don’t eat raw or undercooked food Cross-contamination of foods should be avoided Do not prepare food or pour water if you are infected with the bacteria Avoid direct/indirect contact between reptiles and infants Wash hands, kitchen surfaces, and utensils with soap and water after they have come in contact with raw meat or poultry Wash hands after contact with animal feces Avoid direct/indirect contact between reptiles and infants • Active immunity- your body develops to protect you from disease - Some last a lifetime - Some only last a short period of time • Passive immunity- the temporary immunity that an infant acquires from its mother 1. Explain to children what germs are and where they are found 2. How to properly wash their hands 3. When to wash their hands • Salmonellosis is an infectious disease • Infants and young children are at the highest risk • Most commonly spread by unwashed hands, cross-contamination, and infected animals • Remember the six steps of proper hand washing