* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The RESPIRATORY System
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
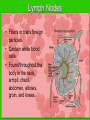
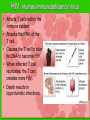
The IMMUNE System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Learning Log • Why do we need the immune system? • How often is it used? Functions of the Immune System • Provide immunity to the body by protecting against disease. • Identify and kill pathogens and tumor cells. • Produces white blood cells and antibodies. • Filters out organisms that cause disease. Structures of the Immune System Tonsils • Lymphoid tissue located on either side of the throat. • Destroy harmful organisms that enter the body through the mouth. Lymph Nodes • Filters or traps foreign particles. • Contain white blood cells. • Found throughout the body in the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen, elbows, groin, and knees. White Blood Cells • Protect against infection and disease. • Produced in the bone marrow and move to other parts of the body until they’re needed to fight infection. • Not released into the bloodstream until they’re needed. Diseases and Disorders • Human immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) • Lupus • Mononucleosis AIDS • • • • • • • Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Contagious disease comprising the immune system. Caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Capable of becoming multi drug-resistant. AIDS is the final stage of the HIV infection. Average incubation period for AIDS development is 10 years from point of infection. Characterized by opportunistic infections. There is no cure. HIV Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Affects T cells within the immune system. • Attacks the RNA of the T cell. • Causes the T cell to alter its DNA to become HIV. • When infected T cell replicates, the T cell creates more HIV. • Death results in opportunistic infections. How AIDS & HIV Affect the Body • Video Lupus • Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disorder affecting many organ systems. • Body’s defenses are turned against itself and immune cells attack healthy tissues. • Signs & Symptoms – Fever – Weight loss – Sensitivity to sunlight Mononucleosis • Also known as the kissing disease. • Infectious inflammatory disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. • Most commonly affects young adults between the ages of 15 and 25.