* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Need for a Stronger Public Health Communication and
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
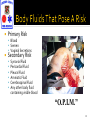
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Bloodborne Pathogens & TB Annual refresher Training Program 2011 1 OSHA requirement…. Refresher training must cover topics listed in the standard to the extent needed and must emphasize new information or procedures Comp. Dir., pg. 61 2 Discuss common citations and current exposure statistics Review some infection control concepts. Review updated information on infectious diseases Discuss basic safety protection measures to keep you safe Explain what to do and what will happen if you get an exposure. 3 Failure to update Exposure Control Pan annually Failure to have a sharps injury log Failure to have an Exposure Control Plan Failure to use engineering /work practice controls. Failure to document consideration and implementation of safety medical devices to reduce exposure risk Failure to have vaccine declination forms Failure to offer training at no cost and during work hours. Failure to offer hepatitis B vaccine to at risk employees and post-exposure follow up. Failure to have an implementation schedule for the Exposure Control Plan. Failure to discard sharps into sharps containers as close as possible to site of use. OSHA Jan. 2010 4 National AIDS – NA Hepatitis B – 3,022 Hepatitis C – 652 Syphilis – 12,833 TB – 11,540 WNV- 663 Virginia AIDS – 698 Hepatitis B – 130 Hepatitis C – 8 Syphilis –789 TB – 292 WNV- 0 CDC, 4/2010 5 AIDS – 184 (117 living) Hepatitis B – 37 Hepatitis C – 53 Syphilis – 7 TB – 15 WNV- 0 Lyme – 203 (Not BBP) 6 Measles cases – 74 Mumps – 1,991 Pertussis (whooping cough) – 16,858 Chickenpox – 20,480 August 19, 2010 8 Ryan White Notification Law - is back! Now listed under Part G 9 “Remains current with the latest information and scientific knowledge pertaining to bloodborne pathogens” LCFR Exposure Control Plan has been revised. Found on the LCFR website. Paragraph ©(1)(iv), CPL 2-2.69, OSHA 10 A disease is an illness caused by a microorganism, also known as a pathogen. An infection is the growth of an organism in a host. A communicable disease is an infectious organism that can pass readily from person to person. Therefore, all diseases are infectious, but not all diseases are communicable. 11 Virulence Dose Organism Mode of Entry Host Resistance 12 13 Primary Risk Blood Semen Vaginal Secretions Secondary Risk Synovial Fluid Pericardial Fluid Pleural Fluid Amniotic Fluid Cerebrospinal Fluid Any other body fluid containing visible blood “O.P.I.M.” 14 Tears, sweat, urine, stool, vomitus, nasal secretions, and sputum do not pose a risk unless they contain visible blood! 15 NOT AN EXPOSURE Blood on intact skin Vomit on your face Urine on your skin Patient coughs in the ambulance. AN EXPOSURE Blood on broken skin Vomit (with visible blood in it) in your eyes Blood coughed in eyes and/or mouth while suctioning 16 17 18 0.4% CDC, September, 2008 19 Offers protection via “immunologic memory” There is NO formal requirement or recommendation for a booster CDC, 1992,1997, June 29, 2001 20 If titer was never performed, DO NOT go back and do one Titer would be done if an exposure occurs Once you have a positive titer, you never have to titer test again even if an exposure occurs •CDC, 1997, June 29, 2001 21 Incident rate continues to decline Rate in US- 1.3% •September, 2008 22 Contamination of multi-use vials Reuse of syringes Needle-sharing use by HCWs Miriam Alter, MD, HIC, May 2010 23 15% - 20% of acute infections Sexual exposure 24 Risk for contracting HCV from a contaminated sharps injury Down to 1.5% 25 If you are exposed to a hepatitis C positive patient, you should have a blood test in 4- 6 weeks HCV-RNA (blood test) Cost - $65.00 26 If only slight liver abnormalities, treatment may not be needed Mayo Clinic, 2009 27 There is no recommendation for the routine screening of healthcare workers Hepatitis C is not efficiently transmitted occupationally • AJIC, 1999, Vol.. 27 (1):54-55 • CDC, 1998, CDC, 6/29/01 28 HCV testing of the source patient HCV testing of the employee (ALT, if patient positive HCV-RNA 4-6 weeks) • CDC, June 29, 2001 29 30 1978 - December 2006 57 documented cases ▪ 0 in fire/EMS personnel ▪ 24 Nurses ▪ 18 Lab Techs ▪ 49 were sharps related exposures •HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report 31 OSHA states that “an employers failure to use rapid HIV testing when testing is required by paragraph (f) (3)(ii)(A) would usually be considered a violation of that provision” OSHA Letter, July 21, 2006 32 California Illinois Iowa Louisiana Maine Maryland New Hampshire New Mexico North Carolina North Dakota Rhode Island Virginia 33 If source patient is negative with rapid testing = no further testing of health-care worker Use of rapid testing will prevent staff from being placed on toxic drugs for even a short period of time •CDC, May , 1998, CDC June 29, 2001, September 2005 34 35 Follow target populations Immigrant screening Active involvement in global efforts 36 75% of cases California New York Illinois Texas Florida Georgia New Jersey 37 Foreign Born Children Inmates HIV Positive Homeless CDC, MMWR, November 4, 2005 38 The Commonwealth of Virginia identified 245 confirmed cases of active TB disease. Correction facilities poses as a large risk to employees, inmates and surrounding communities 21 TB cases in Loudoun County 39 With drug treatment 10% become noninfectious 2 days after start of drugs 14 days 100% become non-infectious • CDC, MMWR, Nov. 4, 2005 40 HIPPA permits disclosure of TB information within health care community. 41 Mask patient with a surgical mask EMS risk is low Dr. Jensen, CDC personal communication with K. West, Jan. 25, 2006 42 TB Initial and annual OSHA 1910.134 Exemption for fit testing N95- Emergency Escape 43 QuantiFERON (QFT-Gold) Blood test for latent TB infection This test is being performed during County physicals CDC, December 16, 2005 44 OSHA 1996 Enforcement Directive still in effect Writing a new one OSHA enforcement – CDC 2005 TB Guidelines 45 46 Airborne virus transmitted by droplet contact Respiratory tract infection caused by the influenza virus. Fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, muscle aches, extreme fatigue are common. (Clear up in 1 to 2 weeks) 20,000 deaths nationwide and more than 100,000 hospitalizations, annually. The elderly and people with chronic health problems are much more likely 47 EMS to receive vaccine as – High Risk “Direct patient care” Signed Declination form must be kept on file if vaccination declined. 48 For healthy persons ages 5 - 49 49 Incubation period: 2-8 days No rapid human to human cases 50 Human Cases Fever, cough, sore throat Muscle aches Eye infections Bloody diarrhea Pneumonia (antibiotics not effective) Respiratory Distress, 4-13 days after onset 51 Virus deep in the lungs Not spread via coughing or sneezing Droplet transmission – not airborne CDC, March 2006 52 Surgical mask on the patient Droplet transmission CDC, pandemicflu.gov DHHS 53 Planning Family Work ▪ Pandemicflu.gov Participate in annual flu vaccine program During patient care, travel history on patient assessment Should be done on anyone with trouble breathing 54 In production Tested against Avian Flu in humans Not effective in 50% Requires a higher dose 55 FDA – Monitor for signs of behavioral changes ▪ Delirium ▪ Hallucinations ▪ Other psychotic behavior FDA, November, 2006 56 If you have signs or symptoms stay home Do not come to work and get others sick 57 58 Continue to rise in the U.S. Post exposure follow up if source is HIV positive or Hepatitis C positive Low risk 59 California New York Texas Florida 60 Update plan to eliminate syphilis by 2015 61 62 Communicable – Mosquito to person Blood transfusion organ donation In utero Sharps injury “Incubation” = 3 – 14 days Infectious – not transmitted person to person 63 Cases have moved westward Highest Cases Colorado Texas Nebraska Illinois 64 65 Methicillin-resistant staphaureus (MRSA) Caused more than 94,000 life-threatening infections and nearly 19,000 deaths in 2005 Most associated with healthcare settings Most frequent among people with weakened immune systems 66 Clusters among athletes, military recruits, children, prisoners May live on surfaces contaminated with body fluids containing MRSA Treated with antibiotic and/or having your doctor drain the infection 67 Skin-to-skin contact Crowded conditions Poor hygiene Sharing of Personal Items 68 69 70 Vaccine – Menactra 11 -17 year old High School College freshmen entering dorm living Military recruits Microbiologists working with N. meningitides CDC, MMWR, May 27, 2005 71 Close contacts/household members Child-care contacts Persons in direct contact with patient oral secretions Kissing Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation Endotracheal intubation/tube management Prolonged contact – flight lasting > 8 hours CDC, MMWR, May 27, 2006 72 73 CDC Guidelines Work Restrictions Immunizations/Vaccinations Post exposure 74 CDC defines: Health care personnel All paid and unpaid persons working in health care settings who have the potential for exposure to infectious materials, including body substances, contaminated medical supplies and equipment, contaminated environmental surfaces or contaminated air 75 MMR Tdap Chickenpox vaccine Flu Vaccine Hepatitis B vaccine 76 100 Health Care Workers infected Immunity History of physician diagnosis Receipt of at least 1 dose of mumps vaccine Positive mumps IgG 77 Within 3 feet of infected person No surgical mask used 78 2 doses needed for coverage 1 dose = 80% protection CDC, 2006 79 Must exclude from work 13th -26th day Vaccine cannot be used post exposure 80 Standard Precautions No procedure changes-just change in name 81 BSI – aka Standard Precautions Good hand washing NRB or Surgical mask on the patient Protective eyewear N-95 respirator for care provider 82 83 Hand washing after touching blood/body fluids/contaminated objects after glove removal Provide 15 sec. of friction ▪ DO NOT squeeze the site to express blood 84 No antibacterial soap Alcohol based foam or gel No artificial nails or extensions • CDC, October,2002 85 Practical and feasible Gloves must be used when there is reasonable anticipation of contact with contaminated surfaces or when performing vascular access procedures, direct contact with patient mucous membranes or non- intact skin 86 CDC Avoiding latex remains the cornerstone for eliminating latex sensitivity- 1997 8% -12% health care workers have latex related health problems- April 2003 87 Mask Use - Eye Protection For procedures that may generate splash/splatter of blood/body fluids 88 Surgical mask Filters what goes out Respirator Filters what comes in Never put a respirator on a patient 89 Genie™ safety Lancets Baxa Multi-dose vial adapters Filter Straws Micro Pin Blunt cannula 90 If Source patient tests Positive HIV antibody Hepatitis C antibody Hepatitis B titer if not on file as a positive 91 When there is exposure to blood as the result of a human bite The source is the patient bitten The biter is monitored and treated as needed 92 Wash site with soap and water Seek medical attention if needed Contact dispatch and advise them to have the ICO to contact you Advise receiving facility of exposure incident 93 Hospital grade EPA disinfectant Bleach solutions Change every 24 hours 1:100 for general areas or patient contact items 94 Per OSHA, the medical facility must either clean the equipment or bag for pick up and safe handling/transport OSHA Letter October 4, 2000 95 Passed by Congress March, 2000 Requires OSHA update the bloodborne pathogens standard Requires employee input to evaluation and selection of devices 96 2001 – 50% fewer injuries than in 1993 Phlebotomy – 70% decrease IV cath – 55% decrease EpiNet 2003 There continues to be a decline on sharp injuries Not in Loudoun County!!! 97 HIV = 0.3 % Remember! A glove cleans the needle as it punctures it – by 50%! HBV = 6 - 30% HCV = 1.8% 98 Reminder – Glass is considered a sharp ▪ Glass blood tubes ▪ Capillary tubes These should not be used 99 Now all contaminated sharps injuries must be listed on the OSHA 300 log Splash/splatter events with blood/OPIM must be recorded Sharps are the #1 way personnel are exposed January 18, 2001 100 Employee name Brand of device used Where incident happened How incident happened Does NOT go to OSHA Note: If you get a sharp injury, you must complete Sharp Injury Description Form – 101 102 Don’t Panic…did you really get exposed? Clean the site with soap and water as soon as possible. Contact LCFR – ECC and have the Infection Control Officer notified as soon as possible. Notify the receiving health care facility of the exposure. Do not provide your personal insurance information 103 The ICO will discuss your exposure with you and provide you with additional instructions. Follow-up procedures may be required. All information pertaining to your exposure incident will be keep confidential. 104 If the source patient is identified and tested, there is no need to draw bloods on employee. If source patient tests are positive, then follow up will be done. 105 All exposure forms, procedures to follow and Exposure Control plan can be found on the County web site: www.Loudoun.gov 106 Link from Home page to Infection Control Procedures and Forms 107 Complete the “Good Samaritan Handout” at scene. If unable to locate form, provide the Infection Control Officer the following: Good Samaritan’s name Contact information Unit # the patient was transported by Incident # and Patient # Name of facility patient was transported to 108 Designated Infection Control Officer – Deputy Chief Jose Salazar Back up Infection Control Officers – Battalion Chief Tim Menzenwerth Captain Mike Mahoney Captain Daniel Neal 109 Bed Bugs While not a BB or AB pathogen, there has been a rising concern… 110 No evidence that bed bugs are involved in the transmission of any disease agent. Proper cleaning/disinfection as done after any call must be followed. If presence of bed bugs is confirmed, follow additional steps… 111 Clothing: Wash clothes in hot water, Dry at high setting Soak delicate clothes in warm water with lots of detergent for several hours before rinsing. Wool items, shoes and many other items can be placed in hot dryer for 30 minutes 112 Equipment/Bags Loosely placed in a large sealable plastic bag. Place bag in direct sunlight for several hours. Temperature in bag must reach 120 F. Thermometer should be used to insure proper temperature is reached. 113 Clean out vehicle of any debris Vacuum patient area to include bench, seats, action area, and compartments Mop/clean floors with hot water 114 115 116 Discussed common citations and current exposure statistics Reviewed some infection control concepts. Reviewed updated information on infectious diseases. Discussed basic safety protection measures to keep you safe Explained what to do and what will happen if you get an exposure. Provided information about bed bugs. 117 118