* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Diseases
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
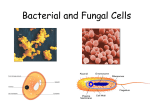
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Infectious Diseases Four categories Viral Bacterial Fungal Parasitic Some infections can be prevented by immunization 2 Infectious Diseases Many have incubation period Symptoms Fever, nausea, and vomiting Malaise Cough and rash Anorexia 3 Infectious Diseases Treatment Varies but may consist of good nutrition Rest Non-aspirin antipyretics 4 Viral Diseases Usually treated symptomatically Invade host and can lay dormant Reactivated by certain triggers: stress, illness, trauma 5 Viral Diseases Common viral diseases Measles Rubeola: Koplik’s spots Rubella: “German measles” Mumps: inflammation of parotid glands 6 Viral Diseases Varicella - “chickenpox” or herpes zoster Poliomyelitis - polio virus; immunization has reduced threat of disease Influenza: “flu” Common cold: rhinovirus 7 Viral Diseases Mononucleosis - “kissing disease” from Epstein-Barr virus Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 8 Bacterial Diseases Pathogens such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, haemophilus, clostridium Symptoms Fever, cough, headache, difficulty breathing, and sore throat Treatment based on causative agent 9 Bacterial Diseases Common bacterial diseases Pertussis - “whooping cough” Diphtheria - severe inflammation of respiratory system Tuberculosis - “consumption” 10 Bacterial Diseases Common bacterial diseases Tularemia - “Rabbit Fever” Impetigo - dermatitis caused by staphylococcus or Group A streptococcus 11 Bacterial Diseases Acute tonsillitis - infection of the palatine tonsils located on posterior wall of nasopharynx Otitis Media - acute bacterial infection of middle ear 12 Fungal Diseases Skin or mucous membranes in children Usually not severe but irritating Fungal diseases Candidiasis - thrush is an oral fungal infection 13 Fungal Diseases Fungal diseases Tinea ○ Ringworm ○ Tinea corporis (face, trunk, extremities) ○ Tinea cruris - “jock itch” ○ Tinea pedis - athlete’s foot 14 Parasitic Diseases Common where there is poor nutrition, contaminated water, low socioeconomic conditions Common parasitic diseases in United States Giardiasis - infection by protozoa Pediculosis - lice 15 Parasitic Diseases Common parasitic diseases in United States Pinworms - parasitic nematodes that infect intestines and rectum Roundworms - parasites that lodge in intestines, absorbing nutrients from host 16 Respiratory Diseases Most common childhood diseases seen by physicians Respiratory diseases Sudden Infant Death Syndrome - abrupt unexplained death of an infant under the age of one Croup - known as laryngotracheobronchitis 17 Respiratory Diseases Adenoid Hyperplasia - enlargement of pharyngeal tonsils Asthma - chronic respiratory system disease Pneumonia - inflammation of lung parenchyma 18 Digestive Diseases Children may experience serious development problems due to lack of appropriate ingestion, digestion, absorption, or elimination Fluid and electrolyte imbalance are frequently more severe in children 19 Digestive Diseases Examples Fluid imbalance Food allergies Eating disorders - major problem among children, especially adolescent females 20 Musculoskeletal Diseases Soft tissue injuries and fractures to joint and bone Legg-Calvé-Perthes – avascular necrosis of upper end of femur Ewing’s Sarcoma - malignant neoplasm occurring before age 20 21 Blood Diseases Leukemia - malignancy of blood-forming cells in bone marrow Most common disorder of blood and blood- forming organs in children 22 Neurologic Diseases Reye’s Syndrome - acute encephalopathy in children under age 15 who have had a viral infection 23 Eye and Ear Diseases Have profound effects on child’s ability to learn and develop Common diseases Strabismus - lazy or cross-eye Deafness - may be caused by genes, trauma, infections, exposure to ototoxic drugs 24 Trauma Child abuse - serious problem in United States, and it is often fatal Suicide - third leading cause of death among young people 25 Trauma Drug abuse - illicit drug, alcohol, and tobacco use among children Epidemic among adolescents Poisoning - among top five causes of accidental death under age 10 26