* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
Survey
Document related concepts
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Phage therapy wikipedia , lookup
Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
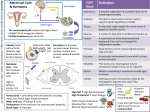
Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Viruses: • are much smaller than bacteria •consist of a genome in a protective coat •reproduce only within host cell •use enzymes and ribosomes of host to make more viruses Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Virus destroys host DNA, makes new viruses, digests cell wall Lysogenic cycle: Virus inserts DNA into host genome (becoming a dormant prophage). Generations later, virus reactivates. Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lytic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: prophage Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Lysogenic cycle: Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Animal Viruses: • are diverse in their means of infection •often have an envelope acquired from cell membrane. Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Retroviruses: • made of RNA •use reverse transcriptase to make DNA from RNA template •DNA inserts into host genome as dormant provirus. Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Emerging viruses: •existing viruses that are expanding their host territory. Chapter 18 Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Viroids: •naked RNA Prions: •infectious proteins •mad cow disease. Bacteria Plasmids: •Small rings of DNA with accessory genes Bacteria Plasmids: •Small rings of DNA with accessory genes. chromosome plasmid Bacteria Transformation: Bacteria Transformation: •Bacteria take up naked DNA Bacteria Transformation: •Bacteria take up naked DNA Bacteria Transformation: •Bacteria take up naked DNA Bacteria Transduction: Bacteria Transduction: •Phages carry bacterial DNA Bacteria Transduction: •Phages carry bacterial DNA Bacteria Transduction: •Phages carry bacterial DNA Bacteria Transduction: •Phages carry bacterial DNA Bacteria Transduction: •Phages carry bacterial DNA Bacteria Conjugation: Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria Conjugation: •Bacteria “mate” to share DNA Bacteria The F-factor gives a bacteria the ability to conjugate Bacteria The F-factor gives a bacteria the ability to conjugate. The F-plasmid carries the genes for sex pili. Bacteria Hfr cells (high frequency or recombination cells) have the F plasmid incorporated into the chromosome Bacteria Hfr cells (high frequency or recombination cells) have the F plasmid incorporated into the chromosome. The F-factor of an Hfr carries other genes along with it. Bacteria R-plasmids carry antibiotic resistance. Bacteria Transposons are “jumping genes” that can move about in the genome. .