* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Preventing Infectious Diseases
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
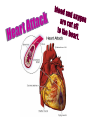
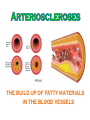
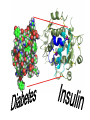
agents that invade the body and cause diseases. List and describe the 5 main pathogens. Virus – tiny; survive and replicate only inside living cells; can’t be killed (has to run its course) organisms that absorb and use the nutrients of living or dead organisms single celled; larger than bacteria Malaria: Spread by mosquito bites Feed off of other living things (Lice) What are the 4 ways infectious diseases can be spread? Describe how each of the following diseases are treated: medicine (antibiotics) are used to slow or kill the growth of bacteria. You must take all meds or it can come back! any meds. taken are to treat the symptoms; only time will cure viral disease. Usually treated with O.T.C. anti-fungal cream (athletes foot) Good hygiene is the best preventative measure; other medications require prescription prevention best, for ex. don’t share brushes, use medicated shampoo, etc. 3. What is our body’s first line of defense against disease? What is ? ~ It is the body’s second line of defense from pathogens. The inflammatory response shows that body is attacking pathogens. 5. If a pathogen gets past the physical barriers, what system kicks in to fight the disease from the inside? Your white blood cells produce antibodies that travel through the lymphatic system to fight the pathogens. What are some things you can do to stay well? Protect yourself Regular Check up Eat healthy Drink water Get enough sleep Vaccines Reduce stress Exercise Avoid contact with sick people 7. List and describe the 5 most common bacterial diseases • sore throat, fever, yellow or white specks on the throat Sinus Infection headache, thick mucous, feeling pressure in your head • Inflammationof the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord affects the digestive system, usually spread by contaminated food 8. List and describe the symptoms for the common viral diseases: headache, sore muscles, sore throat, fever, vomiting, fatigue and coughing Swine Flu scratchy sore throat, sneezing, runny nose pain and swelling of glands in the throat, possible rash fatigue, runny nose, cough, slight fever, small white dots in the mouth, rash covering the body Fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat & weakness inflammation of the liver, jaundice, fever, dark urine ~ Diseases that are caused partly by unhealthy behaviors and partly by other factors. ~ They are called this because a person’s habits, behaviors and practices largely determine whether a person develops a lifestyle disease. 10.What is the difference between controllable factors and uncontrollable factors? habits, practices or behaviors you can change, you have control of them (ex: smoking, eating habits, exercise). 11. What are cardiovascular diseases? the force of blood exerts against walls of blood vessels the build up of fatty materials in the blood vessels 13. How are cardiovascular diseases detected? 14. What are some things you can do to prevent cardiovascular diseases? 15. Can you treat Cardiovascular Diseases? ~ Yes you can treat them through diet and exercise, medicines, surgery, angioplasty, pacemakers and transplants ~ A disease caused by uncontrolled cell growth 17. What is the difference between benign tumors and malignant tumors? ~ Don’t Smoke ~ Sunscreen ~ Eat more veggies and less fat ~ Exercise and watch your weight ~ Get regular check ups ~ Diabetes is a disorder in which cells are unable to get glucose from the blood. You do not produce insulin! 22. What type of treatment is there for someone with Type 1 Diabetes? 23. Can diabetes be prevented? ~ Occasionally a pregnant woman may temporarily develop diabetes, usually near the end of her pregnancy, can cause the baby to be big.