* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
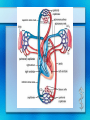
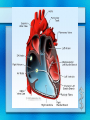
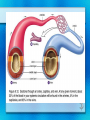
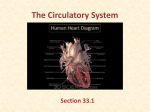
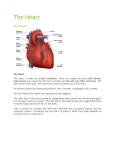
Circulatory System Chapter 37 Circulatory System • Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood Heart • Atrium – Upper Chambers that receive blood • Ventricles – Lower Chambers that pump blood out of the heart • Myocardium – Powerful heart muscles that pump blood • Valves – Flaps that prevent blood backflow Pulmonary Circulation • Involves the lungs 1. Start at the RIGHT side of the heart 2. Blood pumped from the heart to the lungs 3. At the lungs, blood release CO2 and receives O2 Systemic Circulation 1. O2 rich blood goes to the LEFT side of heart 2. Blood is pumped to the rest of the body 3. Tissues and cells of the body receive O2 and blood receives CO2 waste 4. Starts over at the RIGHT side for Pulmonary Circulation Pacemaker • Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) Located at the top of the Right Atrium 1. Impulse spread from SA Node to fibers around Atria, contracts 2. Atrioventricular Node (AV Node) picks up impulse 3. Impulse spreads to fibers around ventricles, contracts Blood Vessels • Aorta – Large artery of the heart and leads blood to body • Arteries – Carries O2 rich blood to tissues of body – Pulmonary Arteries carry deoxygenated blood to lungs to become oxygenated • Capillaries – Smallest vessels where O2 and CO2 exchange occurs at the tissues Blood Vessels • Veins – Brings de-oxygenated blood back to the heart – Valves to prevent backflow and encourage blood to return to the heart – Near skeletal muscles • Muscle Contraction encourages blood to pump back to the heart