* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acute Coronary Syndrome
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
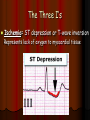
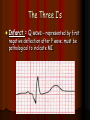
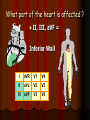
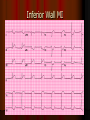
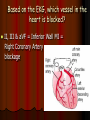
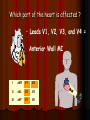
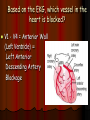
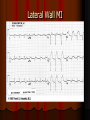
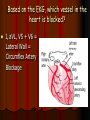
Acute Coronary Syndrome What is Acute Coronary Syndrome ? How can I look at an EKG and tell what part of the heart is affected ? What do ICU RNs need to know ? What is Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) ? Acute Coronary Syndrome is when occlusion of one or more of the coronary arteries occurs, usually following plaque rupture, resulting in decreased oxygen supply to the heart muscle. ACS is the largest cause of death in U.S. Over 1 million people will have Myocardial Infarctions this year; almost half will be fatal. Majority of mortality associated with ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI). Who is at risk for ACS? Anyone with history of CAD, HTN, ESRD, DM Blood loss due to GI Bleed, surgery, trauma Patients on dialysis with AV Fistulas (↑ myocardial O2 demands) Decreased O2 saturations (particularly in COPD) Fever, hyperthyroidism, sustained tachycardia, prolonged hypotension, hypothermia, DIC, drug use (especially cocaine) Who is at risk for ACS? Conditions that may mimic ACS include: Musculoskeletal chest pain Pericarditis (can have acute ST changes) Aortic dissection Central Nervous System Disease (may mimic MI by causing diffuse ST-T wave changes) Pancreatitis/Cholecystitis The Three I’s Ischemia= ST depression or T-wave inversion Represents lack of oxygen to myocardial tissue The Three I’s Injury = ST elevation -- represents prolonged ischemia; significant when > 1 mm above the baseline of the segment in two or more leads The Three I’s Infarct = Q wave — represented by first negative deflection after P wave; must be pathological to indicate MI What part of the heart is affected ? II, III, aVF = Inferior Wall I aVR V1 V4 II aVL V2 V5 III aVF V3 V6 Inferior Wall MI Based on the EKG, which vessel in the heart is blocked? II, III & aVF = Inferior Wall MI = Right Coronary Artery blockage Which part of the heart is affected ? • Leads V1, V2, V3, and V4 = Anterior Wall MI I aVR V1 V4 II aVL V2 V5 III aVF V3 V6 Anterior Wall MI Based on the EKG, which vessel in the heart is blocked? V1 - V4 = Anterior Wall (Left Ventricle) = Left Anterior Descending Artery Blockage What part of the heart is affected ? I, aVL, V5 and V6 Lateral wall of left ventricle I aVR V1 V4 II aVL V2 V5 III aVF V3 V6 Lateral Wall MI Based on the EKG, which vessel in the heart is blocked? I, aVL, V5 + V6 = Lateral Wall = Circumflex Artery Blockage What do ICU RNs need to know? You should do a 12-Lead EKG when: A patient who has CAD risk factors complains of Chest Pain When you are analyzing your rhythm strip on the flowsheet, and you notice that it looks different from the previous shift; OR any arrhythmias or changes in rhythm If your patient who is intubated / sedated suddenly begins to have hemodynamic changes putting stress on the heart + lungs What do ICU RNs need to know? Unexplained tachycardia Tachypnea Sudden elevation in PA catheter #’s or ICP (unexplained) Nausea and/or diaphoresis that doesn’t make sense Pallor Symptoms of sudden heart failure (pulmonary edema/crackles) Unexplained restlessness/all of a sudden needs more sedation Summary After completing an EKG, look at each of the leads for ST segment changes Remember the three I’s: Ischemia, Injury, and Infarct !! Identify the section of the heart (and vessel supplying it) affected by the blockage according to the groups of leads changing in the EKG Remember the symptoms that would prompt you to obtain an EKG!