* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 抗心绞痛药和降血脂药
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
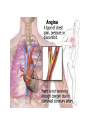
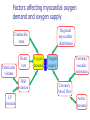
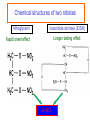
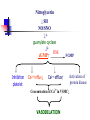
Drugs used in angina pectoris Antianginal drugs Learning Objectives By the end of this class, you can… Describe the antianginal mechanism of Nitrites, β-blockers and CCBs Clarify the vasodilatory mechanism of NO Select antianginal agents for the treatment of different types of angina pectoris Methods for treatment ■ To improve perfusion: ■ To reduce metabolic demand Factors affecting myocardial oxygen demand and oxygen supply Regional myocardial distribution Contractile state Ventricular volume Heart rate Wall tension LV pressure Oxygen Oxygen = supply demand Coronary vascular resistance > Coronary blood flow Aortic pressure Drugs classifications ▲ ▲ ▲ Organic nitrates: Nitroglycerin Calcium antagonists β-Receptor blockers Chemical structures of two nitrates Nitroglycerin Isosorbide dinitrate (IDSN) Longer lasting effect Rapid onset effect -O-NO2 Mechanism of action in VSM NO(EDRF) activate GC increase c-GMP activate cGMPdependent kinase decrease Ca induce de-phosphorylation of the myosin light chain relaxation Nitroglycerin ↓ SH NO/SNO ↓+ guanylate cyclase ↓+ PDE cGMP ↑ Inhibition platelet Ca2+ influx↓ Ca2+ efflux↑ 5’GMP Activation of protein kinase Concentration of Ca2+ in VSMC↓ VASODILATION Organic nitrates Pharmacological effects and mechanism: ■ dilate peripheral vein preload Oxygen ■ dilate peripheral artery afterload consumption ■ Dilate coronary artery perfusion of ischemic myocardium Pharmacokinetics: ■ ■ ■ ■ very low bioavailability per os Sublingual Rapid onset(2~5min) Acute adverse effects: postural hypotension, throbbing headache Tolerance : depletion of free –SH (hydrosulfuryl ) groups NITRATES TOLERANCE " Decrease in the effect of a drug when administered in a long-acting form" Develops with all nitrates Is dose-dependent Disappears in 24 h. after stopping the drug Tolerance can be avoided - Using the least effective dose - Creating discontinuous plasma levels NITRATES CONTRAINDICATIONS Previous hypersensitivity Hypotension ( < 80 mmHg) 1st trimester of pregnancy β-Receptor blockers Pharmacological effects: Oxygen consumption Myocardial contractility Heart rate Clinic use : stable and unstable angina Propranolol not for variant angina because of coronary artery contraction due to its β-receptor blocked and α receptor relatively activated. ß-ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypotension: BP < 100 mmHg Bradycardia: HR < 50 bpm Chronic bronchitis, ASTHMA Severe chronic renal insufficiency Effects of nitrates alone and with β-blockers in angina pectoris Nitrates alone βblockers Heart rate Reflex increase Decrease Combined nitrates with β-blockers Decrease Arterial pressure Decrease Decrease Decrease* End-diastolic volume Decrease Increase None decrease Contractility Reflex increase Decrease None Coronary vasospasm Decrease Increase None or Pharmacological effects of CCB ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Myocardial oxygen consumption Cardiac contractility, heart rate Peripheral vessels dilation , afterload dilate coronary artery, release its spasm Ca2+ overload apoptosis,necrosis Calcium channel blockers ▲ Clinic use : variant angina ▲ Nifedipine not for unstable angina? ▲ Reflex increase in heart rate and cardiac contractility ▲ How to control ? ▲ β-Receptor blockers Other drugs for angina ■ ■ Anti-platelet drugs: aspirin, persantin Chinese medicine: salvia miltiorrhiza, panax notoginseng -promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis Non-Pharmacologic Management Limit alcohol No high saturated fat/high cholesterol foods Maintain normal blood lipid levels Maintain blood pressure within normal range Regular exercise Optimal weight Maintain blood glucose within normal range No tobacco The Original Question from Step1-USMLE A 60 y-o woman with a history of smoking presents with the chief complaint of chest pain that occurs at night while at rest. A treadmill test is negative. A 24 hr holter recording reveals transient ST elevation and AV block (suggestive of occlusion of her right coronary artery) that are temporally associated with anginal attacks. A coronary angiography with provocative testing with acetylcholine injection reproduces her chest pain & ECG changes. Which drug will be contraindicated in her treatment? A. B. C. D. E. diltiazem isosorbide dinitrate metoprolol nitroglycerin sublingually verapamil Features & diagnosis of Variant angina Symptoms typically occur at rest, rather than on exertion (thus attacks usually occur at night). ▲ The treadmill stress test is always negative. ▲ It is associated with specific ECG changes (elevation rather than depression of the ST segment). ▲ The gold standard is coronary angiography with injection of provocative agents into the coronary artery. Depending on the local protocol, provocation testing may involve substances such as ergonovine, methylergonovine or acetylcholine. ▲ Beta blockers (both beta-1 selective and nonselective types) are contraindicated in vasospastic angina because of the concern about blocking beta-2 receptors in coronary arteries, and leaving "alpha receptors unopposed"...resulting in enhanced likelihood of vasospasm.