* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology part 1
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
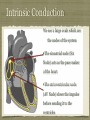
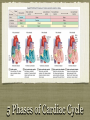
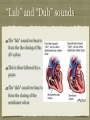
Physiology of the Heart Physiology of the heart You should understand by now that the Physiology of the Heart refers to the function of the heart You need to be familiar with the conduction system of the heart, the cardiac cycle, sounds of the heart, and cardiac out put Conduction System of the Heart Cardiac muscle is unique because it can contract spontaneously and independently even if all nervous connections to the heart are severed These contractions however, are not erratic but regular and steady in rhythm Beats per minute The atrial cells of the heart beat roughly 60 times per minute The ventricular cells of the heart beat only 20-40 times per minute Without some unifying system to control them the heart would be an uncoordinated and inefficient pump Intrinsic Conduction The Intrinsic Conduction System (Nodal System) of the heart is made of very specialized cardiac tissue that is a cross between muscle and nervous tissue Intrinsic Conduction We see 2 large ovals which are the nodes of the system •The sinoatrial node (SA Node) acts as the pace maker of the heart •The atrioventricular node (AV Node) slows the impulse before sending it to the ventricles Cardiac Cycle Two most important terms in understanding cardiac cycle are Systole and Diastole Systole is heart contraction Diastole is heart relaxation 5 Phases of Cardiac Cycle Cardiac sounds In a healthy heart you should be able to hear a steady “lub-dub” sound of contraction We have to understand that there is a sequence to the sounds lub-dub, pause, lub-dub, pause “Lub” and “Dub” sounds The “lub” sound we hear is from the the closing of the AV valves This is then followed by a pause The “dub” sound we hear is from the closing of the semilunar valves Blood flow It is important to realize that blood flows silently as long as the flow is smooth and un-interupted If the flow becomes irregular we can hear murmurs