* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 30.3 The Heart and Circulation
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
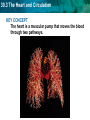
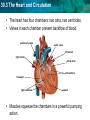
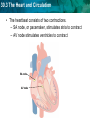
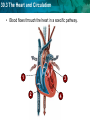
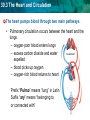
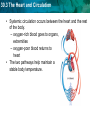
30.3 The Heart and Circulation KEY CONCEPT The heart is a muscular pump that moves the blood through two pathways. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation The tissues and structures of the heart make it an efficient pump. • Cardiac muscle tissue works continuously without tiring. NORMAL HUMAN HEART 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • The heart has four chambers: two atria, two ventricles. • Valves in each chamber prevent backflow of blood. pulmonary valve aortic valve left atrium right atrium mitral valve left ventricle tricuspid right ventricle septum • Muscles squeeze the chambers in a powerful pumping action. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • The heartbeat consists of two contractions. – SA node, or pacemaker, stimulates atria to contract – AV node stimulates ventricles to contract SA node AV node 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway. 1 3 2 4 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway. – oxygen-poor blood enters right atrium, then right ventricle – right ventricle pumps blood to lungs – oxygen-rich blood from lungs enters left atrium, then left ventricle – left ventricle pumps blood to body 30.3 The Heart and Circulation The left ventricle is the largest chamber of the heart. How is its size related to its function? • The larger volume and more muscle tissue exert enough force to propel blood throughout the body. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation The heart pumps blood through two main pathways. • Pulmonary circulation occurs between the heart and the lungs. – oxygen-poor blood enters lungs – excess carbon dioxide and water expelled – blood picks up oxygen – oxygen-rich blood returns to heart Prefix “Pulmo” means “lung” in Latin Suffix “ary” means “belonging to or connected with” 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • Systemic circulation occurs between the heart and the rest of the body. – oxygen-rich blood goes to organs, extremities – oxygen-poor blood returns to heart • The two pathways help maintain a stable body temperature.