* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beat Still My Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
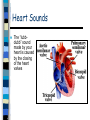
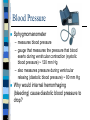
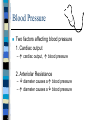
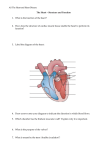
Beat Still My Heart Chapter 10 – Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure Heart Sounds The “lubbdubb” sound made by your heart is caused by the closing of the heart valves Heart Sounds When your heat pumps . . . Lubb Sound the ventricles contract, blood is forced into the arteries (aorta and pulmonary artery), the atrioventicular (AV) valves close and the lubb sounds is produced Dubb Sound The atria contract and blood is squeezed into the ventricles The semil-lunar valves close and the dubb sound is produced murmur -valves don’t close properly and blood leaks past http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/hhw/hhw_pumpi ng.html Cardiac Output Cardiac output - the amount of blood that flows from each side of the heart / minute Two Factors – stroke volume – heart rate Cardiac Output Stroke Volume – the quantity of blood pumped with each beat ~ 70ml Heart Rate – is the number of times the heart beats per minute Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = 70 beat/min x 70 ml/beat = 4900 ml/min Cardiac Output Problem: – Patrick has just finished exercising and in order for his heart to keep up with the increased oxygen demands it is pumping at 150 beats per minute. Patrick’s heart can deliver 70ml of blood per beat. What is Patrick’s cardiac output? Heart rate X Stroke volume 150 beats/min X 70ml/beat 10500ml/min or 10.5L/min Blood Pressure Sphygmomanometer – measures blood pressure – gauge that measures the pressure that blood exerts during ventricular contraction (systolic blood pressure) ~ 120 mm Hg – also measures pressure during ventricular relaxing (diastolic blood pressure) ~ 80 mm Hg Why would internal hemorrhaging (bleeding) cause diastolic blood pressure to drop? Blood Pressure Two factors affecting blood pressure 1. Cardiac output – cardiac output, blood pressure 2. Arteriolar Resistance – diameter causes a blood pressure – diameter causes a blood pressure How to measure your blood pressure: http://www.wikihow.com/Check-YourBlood-Pressure-with-aSphygmomanometer Hypertension Caused by increased resistance to blood flow which results in increased blood pressure High blood pressure can lead to weakened blood vessels Major cause is diet, but may also be hereditary Regulation of Blood Pressure Nervous system responses cause either increased outflow of blood from arteries (sympathetic NS) or decrease heart rate and stroke volume (parasympathetic NS) Response to Exercise NS stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline (epinephrine) – This stimulates the release of RBC’s – Increased RBCs = increased O2 transport – Adrenaline also increases heart rate and breathing which increases O2 transfer rate through body Thermoregulation To Do: Textbook Questions p. 335 #2, 5, 7, 10