* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pulmonary Circulation
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
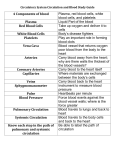
The Circulatory System The “Heart” of the Matter What You’ll Learn • How to compare arteries, veins, and capillaries • The pathway of blood through the chambers of the heart • The pulmonary and systemic circulation systems The Purpose of the Cardiovascular System • In our bodies, the cardiovascular system distributes materials (blood, oxygen, remove cell waste, and other nutrients) throughout our body. http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&source=hp&q=picture+of+a+highway&aq=1&aqi=g9gm1&aql=&oq=picture+of+a+high&gs_rfai= The Heart http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/photos/heart/#heart-angiogram_986_600x450.jpg The Heart • • • • The major organ in the cardiovascular system. (pg. 547) Made of cardiac muscle. It is a closed system. Composed of four cavities: – Left and Right ATRIA (upper chambers) – Left and Right VENTRICLES (lower chamber) http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.starsandseas.com/SAS_Images/SAS_Physiol_Images/SAS%2520cardiopics/heart_chambers.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.starsandseas.com/S AS%2520Physiology/Cardiovascular/Cardiovascular.htm&usg=__LaYV1b8fkWdIjhQFRgjVQAZ6FM=&h=510&w=588&sz=18&hl=en&start=2&um=1&itbs=1&tbnid=usQAd5D5wFvrEM:&tbnh=117&tbnw=135&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dpicture%2Bheart%2Bchambers%26 um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DX%26tbs%3Disch:1 “Pump It Up” The Pulmonary Circulatory Circulation System Systemic Circulation Coronary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation (Heart Circulation) Heart Picks up O2 Lungs Systemic Circulation (Body Circulation) Aorta Body •Blood enters the Aorta and Aorta carries blood away from the heart •O2 rich blood is pumped to all organs and tissues of body (except heart & lungs) Veins •O2 is exchanged into CO2 & waste and returns to heart through the veins Coronary Circulation (Heart Circulation) • Heart has own blood vessels that supply it with nutrients and O2 • Blockage of blood flow results in a heart attack. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Capillaries •Move blood away from heart •Ventricles connect to Aorta •Contraction of heart = blood moved from heart into arteries •Move blood into heart •Valves keep blood moving toward the heart •Near skeletal muscles, squeezing = contraction =blood from heart into arteries •Connect arteries and veins •Walls are microscopic •“Blood Shot” eyes •Waste and CO2 move into capillaries to be carried back to heart http://www.bobs-webdb.com/images/arterycs.jpg Blood Pressure • When the heart pumps blood through the cardiovascular systems, it exerts a force called blood pressure on the walls of the vessels. • arteries and lower in capillaries and veins • How it is measured: Systolic/Diastolic Pressure Why It’s Important • Plays a vital role as the transport system of the body. • Failure of the cardiovascular system: – Atherosclerosis – Hypertension • How to keep the heart healthy: – Good diet – Regular checkups – Exercise Atherosclerosis http://www.heartattacktreatmenttips.com/wpcontent/uploads/2009/09/Atherosclerosis.jpg Cardiovascular Vocabulary • Atria: Two upper chambers of the heart • Ventricle: The two lower chambers of the heart • Pulmonary Circulation: Flow of blood through the heart, to the lungs, and back to the heart • Systemic Circulation: Most extensive part of the circulatory system in which blood moves to and from all body organs and tissues, except the heart and lungs • Coronary Circulation: Flow of blood to the tissues of the heart. • Artery: Blood vessel with a thick elastic wall made from smooth muscle that moves blood away from the heart Cardiovascular Vocabulary • Vein: Blood vessel that moves blood to the heart and has valves to prevent backward movement of the blood • Capillary: Microscopic blood vessel that connects arteries and veins; nutrients, oxygen (O2), waste materials, and carbon dioxide (CO2) diffuse through its walls • Blood Pressure: force exerted on vessel walls by blood when the heart pumps through the cardiovascular system; normally 120/80 for a young adult • Atherosclerosis: Cardiovascular condition resulting from fatty deposits on arterial walls, which can clog blood vessels ad interfere with blood flow • Hypertension: Cardiovascular disorder, also caused by high blood pressure, that can cause atherosclerosis Circulation Test Questions 1. Where does the exchange of food, oxygen, and wastes occur? – a. arteries c. veins – b. capillaries d. lymph vessels 2. What are the lower chambers of the heart called? – a. Atrium c. Ventricles – b. Aorta d. Veins 3. Contrast pulmonary and systemic circulation: 1. ________________ a cardiovascular disorder resulting from fatty deposits on the arterial walls, which can clog blood vessels and interfere with blood flow. Answers to Circulation Test Questions 1. B – capillaries 2. C- ventricles 3. Pulmonary circulation transports blood through the heart and to the lungs. Systemic circulation transports blood to all parts of the body. 4. Atherosclerosis The End • Power point created by: Ms. Walsh • Chapter 20.1 Circulation