* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System - Pupils Copy
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
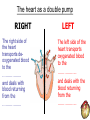
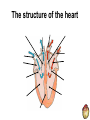
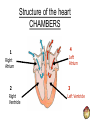
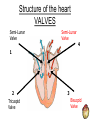
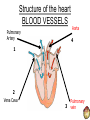
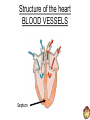
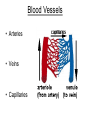
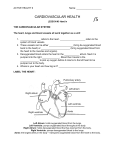
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM What does Oxygenated and Deoxygenated mean? • Oxygenated blood: • Deoxygenated blood: The heart as a double pump RIGHT The right side of the heart transports deoxygenated blood to the …………….. and deals with blood returning from the …………….. LEFT The left side of the heart transports oxygenated blood to the …………….. and deals with the blood returning from the …………….. How it Works LUNGS HEART BODY Oxygenated and Deoxygenated blood • When the blood leaves the lungs it is …………………. • The blood then visits the muscles in the body and gives the oxygen to them so they can work. • The blood is now …………………. • The …………………. blood then visits the lungs when it picks up oxygen and becomes …………………. The structure of the heart Structure of the heart CHAMBERS 1 Right Atrium 2 Right Ventricle 4 Left Atrium 3 Left Ventricle Structure of the heart VALVES Semi-Lunar Valve Semi-Lunar Valve 4 1 2 Tricuspid Valve 3 Bisucpid Valve Structure of the heart BLOOD VESSELS Pulmonary Artery Aorta 4 1 2 Vena Cava 3 Pulmonary vein Structure of the heart BLOOD VESSELS Septum Functions of the chambers • The right atrium takes deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and stores it before sending it through the tricuspid valve. • The right ventricle receives de-oxygenated blood through the tricuspid valve before pumping it up the pulmonary artery to the lungs. Functions of the chambers • The left atrium • The left ventricle Functions of the valves • The tricuspid valve stops blood flowing back into the right atrium. • The bicuspid valve • The semi lunar valves stop blood flowing back into the left and right ……………… Functions of the blood vessels • The vena cava transports de-oxygenated blood from the body to the heart. Here is gives the oxygen to the working muscles. • The pulmonary artery Functions of the blood vessels • The pulmonary vein transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. • The aorta Blood Vessels • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries Thermoregulation: Vasodilation of vessels • This is when you body temperature rises. • It is when the blood vessels expand, meaning the blood flows nearer to the surface of the skin. • It is a way of cooling you down. • It makes your skin become red after a heart raising activity. Thermoregulation: Vasoconstriction of vessels • This is when your body temperature decreases, which makes your blood vessels constrict. • This means less blood flows near the surface of your skin so less heat is lost. • It happens when you are • It happens when you are cold.