* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L-2 heart sounds
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
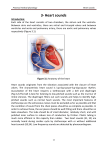
HEART SOUNDS Dr. Taj • There are four heart sounds SI, S2, S3 & S4. • Two heart sound are audible with stethoscope S1 & S2 (Lub - Dub). • S3 & S4 are not audible with stethoscope Under normal conditions because they are low frequency sounds. • Ventricular Systole is between First and second Heart sound. • Ventricular diastole is between Second and First heart sounds. First heart sound (S1) • It is produced due to the closure of Atrioventricular valves (Mitral & Tricuspid) • It occurs at the beginning of the systole and sounds like LUB • Frequency: 50-60 Htz • Time: 0.15 sec Second heart sound (S2) • It is produced due to the closure of Semilunar valves (Aortic & Pulmonary) • It occurs at the end of the systole and sounds like DUB • Frequency:80-90 Htz • Time: 0.12 sec • It is short and sharp Third heart sound (S3) • It occurs at the beginning of middle third of Diastole • Cause of third heart sound – Rush of blood from Atria to Ventricle during rapid filling phase of Cardiac Cycle. It causes vibration in the blood. • Frequency: 20-30 Htz • Time: 0.1 sec Fourth heart sound (S4) or Atrial Sound • It occurs at the last one third of Diastole (just before S1) • Cause of Fourth heart sound – Due to Atrial contraction which causes rapid flow of blood from Atria to Ventricle and vibration in the blood. • Frequency: < 20 Htz Note: • Third and Fourth heart sound are low pitched sounds therefore not audible normally with stethoscope • S3 may be heard in children and young adults but usually pathological in old age Heart valves - superior view Function of papillary muscle & Chordae tendineae AREAS OF AUSCULTATION AREAS OF AUSCULTATION The Events of the Cardiac Cycle Heart Murmurs • Murmurs are abnormal sounds produced due to (usually) abnormal flow of blood through abnormal heart valves eg.: stenosis or incompetence. WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW FROM THIS LECTURE? • Functions of A-V vales & Semilunar valves. • Functions of papillary muscles. • There are four heart sounds : S1, S2, S3, & S4. • Audible with stethoscope are only S1 & S2 (Lub / Dub) • Use of stethoscope. • Places to be auscultated on the chest for heart sounds i.e. Aortic, pulmonary, Mitral & tricuspid area. • Position of the subject while auscultation. • Recording of heart sound – Phonocardiogram. • Relationship of heart sound with ECG. • Splitting of second heart sound A2-P2. • Listening of S3 & S4 in physiological & pathological conditions • Murmurs (abnormal heart sounds). Relationship of heart sound with ECG Relationship of heart sound with ECG Splitting of second heart sound A2-P2. • Physiologic splitting of the 2nd heart sound occurs during deep inspiration when the A2 component splits from the P2 component by more than 0.2 seconds.