* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
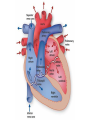
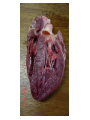
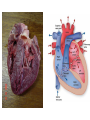
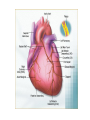
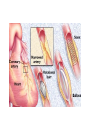
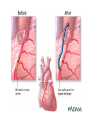
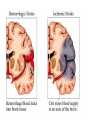
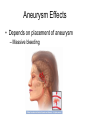
The Heart Heart Function Example • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H04d3r JCLCE Intact Heart… This shows the pig heart from the front, with the portion on the right of the picture being the left side of the heart and vice versa. The aorta is clearly visible at the top, with an atrium on either side, while the ventricles are in the bottom left. BiologyMad.com Heart Attack – Prolonged blockage of blood to an area of the heart resulting in muscle tissue damage. • Symptoms of a heart attack – Pressure in chest, fullness, squeezing pain. – Pain spreading to shoulders, neck, or arms – Lightheadedness, fainting, sweating, nausea • • • • • High blood cholesterol High blood pressure Smoking Obesity Lack of physical activity What is a stroke? • Tissue damage to area of the brain due to disruption in blood supply, depriving that area of the brain of oxygen. Causes of Strokes 1. Blockage in cerebral artery that cuts off or reduces blood supply a) blood clot b) piece of plaque becomes lodged in the artery. 2. Hemorrhage – happens suddenly. Less frequent than infarction but more damaging and more likely to cause death. Symptoms of a Stroke • Sudden – weakness or numbness of the face, arm, or leg (usually on one side of the body) – dimness or loss of vision (usually one eye) – Loss of speech or trouble talking or understanding speech – Unexplained, severe headache – Dizziness, unsteadiness, or sudden fall Stroke Risk Factors • High blood pressure • Cigarette smoking • Heart disease, diabetes, and their risk factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. • High red blood cell count (making the blood thicker and likelier to clot). • Mini-strokes – transient ischemic attacks (TIA) Effects of Stroke • Motor impairments often due to paralysis on one side of the body (side opposite to brain damage). – After about 6 weeks of rehab about 50% of patients can perform independently (many with cane or walker). • Language, learning, memory, and perception problems depend on location of the injury. Aneurysm • A blood filled, balloon-like bulge in a blood vessel. How does this happen? • The walls of blood vessels (almost exclusively arteries) are weakened and begin to bulge • What weakens the vessel walls? – Disease – Infection – Copper deficiency – Genetics Aneurysm Effects • Depends on placement of aneurysm – Massive bleeding Questions (Answer these on a sheet of loose leaf paper) • Are you currently doing anything that would put you at risk for any of these circulatory disorders? • Are you currently doing anything that would prevent these circulatory disorders? • Are you aware that you have any family history of the circulatory system disorders we went over today? • You are made the Premier of Nova Scotia for a day and your platform was entirely focussed on health care reform. You are given the power to make 2 laws that will increase overall circulatory system health in the province. What 2 laws do you make and why?