* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
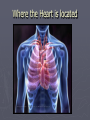
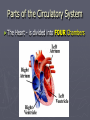
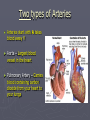
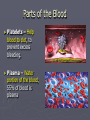
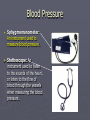
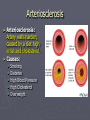
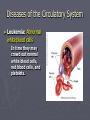
The Circulatory System Where the Heart is located Circulatory or Cardiovascular System 1. 2. 3. 4. Delivers materials (oxygen and glucose) Removes wastes (CO2 removed from lungs) Regulates body temperature (blood flow) Fights disease Delivering Removing Parts of the Circulatory System ► The Heart - is divided into FOUR Chambers Three Kinds of Blood Vessels ► Arteries – Carries blood away from the heart ► Veins – Carries blood back to the heart ► Capillaries – Delivers low-oxygen blood to veins (Smallest) Two types of Arteries ► Arteries start with A takes blood away !! ► Aorta – Largest blood vessel in the heart ► Pulmonary Artery – Carries blood containing carbon dioxide from your heart to your lungs Parts of the Blood ► Red Blood Cells – Made in bone marrow; carries oxygen, food, and rids body of CO2 and waste ► White Blood Cells – Help fight disease and infection by destroying bacteria and germs that enter the body. Made in the lymph nodes Parts of the Blood ► Platelets – Help blood to clot, to prevent excess bleeding. ► Plasma – Water portion of the blood; 55% of blood is plasma The Blood Body contains 4-6 L Consists of Water Red Blood Cells Plasma White blood cells and platelets Four Types of Blood ► Type A: 42% ► Type B: 10% ► Type AB: 3% ► Type O: 45% ► RH Factor = is the Accepts A and O Accepts B and O Accepts AB and O Universal Donor + and – of the blood Four Filters of the Blood 1. Liver 2. Kidneys 3. Lymph Nodes – located in the neck 4. Spleen – Cemetery for the red blood cells Blood Disorders Blood Pressure: (Hypertension) The force or pressure developed by the heart, which acts to pump blood through the circulatory system. Blood Pressure ► Sphygmomanometer: An instrument used to measure blood pressure. ► Stethoscope: An instrument used to listen to the sounds of the heart, or listen to the flow of blood through the vessels when measuring the blood pressure. Arteriosclerosis ► Arteriosclerosis: Artery walls harden; caused by a diet high in fat and cholesterol. ► Causes: Smoking Diabetes High Blood Pressure High Cholesterol Overweight Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System ► Stroke: Happens when a cluster of blood cells blocks blood vessels in the brain. ► Stroke Stroke is a “Brain Attack” Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System ► Prevention: Don’t Smoke Drink in moderation (21) Get cholesterol checked Exercise 30 minutes daily Consume a low fat diet ► Treatment: Medication Rehabilitation Diseases of the Circulatory System ► Leukemia: Abnormal white blood cells In time they may crowd out normal white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Diseases and Disorders of the Circulatory System ► Hemophilia: Blood does not clot properly ► Prevention: No prevention, you are born a hemophiliac ► Treatment: Transfusions of blood clotting factors.