* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
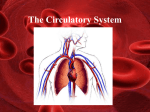
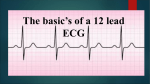
Introduction to the Heart Introduction to the Heart • The heart is a cone-shaped muscular organ located within the __________. • Its apex rests on the ____________. • Its base is at the level of the _________ rib. • The coronary arteries that nourish the myocardium arise from the _____________. • The ____________ are receiving chambers; the _________ are discharging chambers. • The muscular walls of the heart is called the _____________. • The myocardium of the ______ ventricle is much thicker than that of the _______ ventricle. • The membrane that lines the heart and forms the valve flaps is called the _______________. Introduction to the Heart • The outermost layer of the heart is the ______________. • The covering surrounding the heart is called the _____________. • The space between the ____________ and ___________ is called the pericardial ______. • The pericardial sac contains a small amount of fluid to help reduce ____________ when the heart contracts. Anatomy of the Heart 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ 4. _________________________ 5. _________________________ 6. _________________________ 7. _________________________ 8. _________________________ 9. _________________________ 10. _________________________ 11. _________________________ 12. _________________________ 13. _________________________ 14. _________________________ 15. _________________________ Flow of Blood Through the Heart A. Blood enters heart from the head and upper extremities via the _____________________. B. Blood enters heart from the lower extremities via the ________________________. C. Into the __________________ D. Across the ________________ E. Into the __________________ F. Across the ________________ G. Into the __________________ H. On its way to the ___________ I. Blood returns to the heart via the ______________________, now fully loaded with oxygen. J. Into the __________________ K. Across the ________________ L. Into the __________________ M. Across the __________________ N. Into the __________________ O. From here, blood is distributed through the body through ___________ and ___________. P. Blood returns to vena cava by way of _______________. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ 4. _________________________ 5. _________________________ 6. _________________________ 7. _________________________ 8. _________________________ 9. _________________________ 10. _________________________ 11. _________________________ 12. _________________________ 13. _________________________ 14. _________________________ 15. _________________________ A Microscopic Look at Heart Muscle Listening to Heart Sounds The Conduction System: The Nerves of the Heart How to Read an ECG How to Read an ECG • A recording of the electrical activity of the heart is called an _____________. • The period when the atria are depolarizing (getting ready to contract) is called the ___________. • The period when the ventricles are depolarizing (getting ready to contract) is called the ____________. • The period when the ventricles are repolarizing is called the ____________. How to Read an ECG • An abnormally slow heartbeat (slower than 60 beats per minute in a non-athlete) is called ______________. • An abnormally rapid heartbeat (faster than 100 beats permit at rest) is called _______________. • A condition in which the heart is uncoordinated and useless as a pump is called ______________. • Transient chest pain, resulting from ischemia of the myocardium, is called______________. Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation Fetal Circulation Identify: Umbilical cord Umbilical arteries Umbilical vein Foramen ovale Ductus arteriosus Anatomy of Blood Vessels Anatomy of Blood Vessels • Tunica intima • Tunica media • Tunica externa o Single layer of endothelium o Bulky middle coat, containing smooth muscle and elastin o Provides a smooth surface to decrease resistance to blood flow o The only tunic of capillaries o Also called the adventitia o The only tunic that plays an active role in blood pressure regulation o Supporting, protective coat