* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jeopardy for Blood and Circulation
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
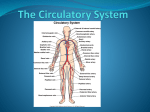
Jeopardy for Blood and Circulation Anatomy and Physiology Review Blood 100 – Where are blood cells made in adults? Bone marrow of flat bones 200 – Give two functions of blood Carry oxygen, nutrients, hormones to cells, carry waste like carbon dioxide and toxins away, etc. 300 – What % of blood is white blood cells? 1% 400 – Who could the A and B blood types each donate to and receive from & what blood types would each make anti-bodies to? A could donate to A and AB, B could donate to B and AB, A can receive from A and O, B can receive from B and O, A makes anti-bodies to B and AB, B makes anti-bodies to A and AB 500 – What hormone stimulates red blood cell production, what organ produces it? Erythropoeiten , kidney Heart Anatomy 100 – Chamber that pumps to whole body Left ventricle 200 – Valves between the ventricles and aorta or pulmonary trunk Semilunars 300 – Name of the left AV valve Bicuspid or Mitral Valve 400 – Name of the heart muscle and serous membrane over the heart? Myocardium, pericardium 500 – When the ventricles are relaxing which vessels are open/closed? The AV’s are open, SL are closed Heart Conductivity 100 – Pacemaker of the Heart Sinoatrial Node 200 – Where the electrical wave begins in the ventricles. AV bundle 300 – Where the impulse pauses before going into the ventricles. AV node 400 – What does the QRS wave represent? The depolarization of the ventricles (sodium is flowing into the cardiact muscle cells) 500 – Trace the path of electricity thru the ventricles AV bundle, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers CO./BP 100: What does stress hormones do to blood pressure? Increase it (bind to receptors causing vasoconstriction and increasing heart rate) 200: What is the top blood pressure number called? Systolic (pressure when ventricles are contracting) 300: Name two things that effect blood pressure and how? (cold – increase, nicotine – increase, alcohol, decrease, exercise – increase, etc.) see pwrpt. & coloring 400: Name two major control factors of blood pressure? Heart rate and vasoconstriction & body position 500: Describe baroreceptor reflex You stand up and your blood pressure drops because the blood pools at the feet – the pressure receptors (baroreceptors) in the carotid arteries sense low pressure to the brain and cause you to pass out – however, your brain is already increasing heart rate and constricting blood vessels to increase the pressure – if corrected quick enough you just get dizzy and then it goes away Blood Vessels 100: Define Arteries vs. Veins Arteries take blood away from the heart, veins bring blood back to the heart 200: Name two structural differences between arteries and veins Arteries have thicker smooth muscle (tunica media), a smaller lumen, and no valves 300: What is a blood vessel with only tunica intima called? capillary 400: Name 3 parts of blood vessels and what type of tissue each is made of: Tunica intima (epithelium), tunica media (smooth muscle), tunica externa (connective) 500: From heart back to heart- name vessel types starting with arteries Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, heart Arteries and Veins: 100: Name the arteries that go to the lungs pulmonary 200: Name the arteries that feed the kidney renal 300: Name the arteries going to the head and name the arteries going to the heart (myocardium) Carotid, coronary 400: Name the arteries that split off the abdominal aorta and go toward human leg iliac 500: Trace the arteries from aorta to elbow on the right side of the body Brachiocephalic, rt. Subclavian, rt. Axillary, rt. brachial Cardiac Cycle: 100: What makes the heart sounds? Closing of the AV valves then closing of the SL valves 200: How do you tell if there is a heart murmur? After the lub and before the dub you hear a little sound as some blood squirts into the atrium 300: What is it called when ventricles are contracted? Ventricular systole 400: When ventricles contract what closes? The AV valves 500: When ventricles are relaxing which valves are open/closed? AV are open, SL are closed Potpourri 1 100: 3 Things that describe cardiac muscle cells. Cylindrical and branched, intercalated discs, striated 200: Why can blood leave capillaries and not arteries? Just a single layer of epithelium which are permeable to the things that can leave 300: What is the highest percent of blood made out of? Plasma which is mostly water 400: What is the inside lining of the heart called and made of? Endocardium – epithelium 500: What are two things produced by platelets? Serotonin and thromboplastin Pot. 2 100: What organ monitors blood pressure through blood volume? kidneys 200: What is the purpose of lymphocytes? Specific immunity – T cells kill foreign cells, B cells make antibodies to clump foreign cells 300:What are two ways that help the blood return from the feet to the heart? Skeletal muscle movement, breathing, valves 400: Why can’t you see the atria repolarizing on an EKG? It happens the same time the ventricles are depolarizing so you can’t see it 500: What is the final step of blood clotting? Lots of little fibrinogen molecules are linked together to form bigger ropes called fibrin to plug the hole Blood Cells: 100: What blood cell is most numerous? Red blood cell 200: What blood cell is the first response? neutrophil 300: What is the purpose of neutrophils and monocytes? Phagocytes (endocytose junk and bacteria) 400: What is the purpose of basophils? Release histamine which causes inflammation 500: What are the two types of lympocytes and how are they specific? T cells kill infected cells that have a specific marker, B cells make antibodies that match a specific marker protein on a bacteria or virus Final Jeopardy! What are the arteries that feed the liver, stomach, and 2 intestines? Hepatic – liver Gastric – stomach Intestine – superior and inferior mesenteric