* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
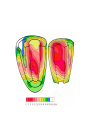
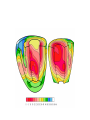
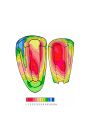
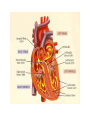
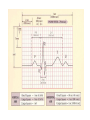
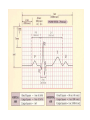
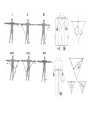
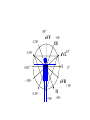
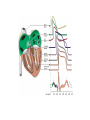
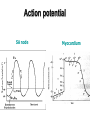
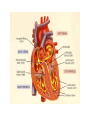
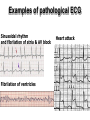
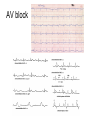
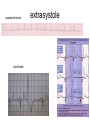
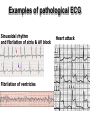
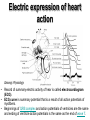
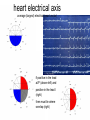
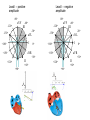
heart muscle smooth muscle excitation contraction coupling striated muscle Description of curves P = Impulse spread through atria PQ = neutral (isoelectric) line after depolarisation of all atria myocardium QRST = ventricle complex Q = negative oscillation – beginning of ventricle depolarisation in septum R = continue of depolarisation wave through the ventricle S = negative oscillation – activation of last part of ventricle myocardium in left ventricle base ST = neutral (isoelectric) line after ventricle depolarisation (plató phase in action potential) T = repolarisation from epicardium to endocardium According to the amplitude, lower or upper case is used > 5 mm - Q, R, S < 5 mm - q, r, s -90o -120o aVF -60o III -30o -150o aVL I +180o +150o aVR II +120o +90o +60o 0o +30o Action potential SA node Myocardium Examples of pathological ECG Sinusoidal rhythm and fibrilation of atria & AV block Fibrilation of ventricles Heart attack AV block 1. Blokáda levého raménka Tawarova (BLRT) (synonymum: LBBB - left bundle branch block) According to the QRS interval -complet block - QRS > 0,12s -incomplet - QRS < 0,11s Incidence: heart attack (congenital LBBB extremely rare. aortal stenosis or diphteria) Blokáda pravého raménka Tawarova (BPRT) (RBBB - right bundle branch block) Incidence: RBBB heart attack, chronic cor pulmonale, atrium septal defect. incomplete RBBB normal in cyclist and boaters (volume load to right ventricle). supraventricular ventricular extrasystole reentry ECG leads R On the right arm, avoiding bony prominences – RED L In the same location that RA was placed, but on the left arm this time – YELLOW G On the right leg, avoiding bony prominences – BLACK (ground) LL In the same location that G was placed, but on the left leg this time – GREEN V1 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 & 5) just to the right of the sternum (breastbone). V2 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 & 5) just to the left of the sternum. V3 Between leads V2 and V4. V4 In the fifth intercostal space (between ribs 5 & 6) in the mid-clavicular line (the imaginary line that extends down from the midpoint of the clavicle (collarbone). V5 Between leads V4 and V6 V6 Horizontally even with V4 and V5 in the midaxillary line. (The midaxillary line is the imaginary line that extends down from the middle of the patient's armpit.) Leads and electrodes Limb Thoracic Evaluation of the ECG • Pulse: regular, irregular • Rhythm: sinusoidal or other (nodal = from AV node) • Frequency: Normal 60-90 pulses/min • Heart electrical axis inclination: normal (the same way), to left (outside), to right (inside) just generally from limb leads I and III. Exactly by using Einthoven’s triangle. • Description of waves, their duration and intervals. Frequency • Heard frequency = 72 pulses/min, = pulse interval 0.83 s • During relaxation the frequency changes based of the respiration (RESPIRATION ARYTMIA) = inspiration - increased frequency, expiration – decreased frequency. • Bradycardia = fysiological = deep long-term inspiration, deep forward bend and knee band = reflex changes of vagal tonus. • Tachycardia = fysiological = swallow (decrease of vagal tonus), change of position from lying or sitting to standing (ORTOSTATIC REACTION). Examples of pathological ECG Sinusoidal rhythm and fibrilation of atria & AV block Fibrilation of ventricles Heart attack reentry Electric expression of heart action Ganong: Physiology • Record of summary electric activity of hear is called electrocardiogram (ECG). • ECG curve is summary potential that is a result of all action potentials of myofibers. • Beginnings of QRS complex and action potentials of ventricles are the same and ending of ventricle action potentials is the same as the end of wave T. heart electrical axis average (largest) electrical heart vector) if positive in the lead aVF (above left) and positive in the lead I (right) then must lie where overlap (right) Lead I – positive amplitude Lead I – negative amplitude -90o -120o aVF -90o -60o -120o III -30o -150o aVL I +180o +150o 0o aVR aVF -60o III -30o -150o aVL I +180o +150o aVR +30o II +120o +60o +90o 0o +30o II +120o +60o +90o Heart electrical axis inclination • Each myocyte produce dipole during action potential - vector with specific dimension and direction. • Cell vector head from depolarised to polarised part, i.e. in direction of action potential spread. • If the cell is completely depolarised (plató phase) or polarised (resting phase), vector is neutral. • Electrical heart vector is a summary of all cell’s vectors in one time point Normal value is -30° až +105° Shift of the axis to right above 105 ° = hypertrophy of RV or long and slim Shift of the axis to left below -30° = hypertrophy of LV or obese people