* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
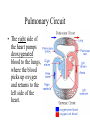
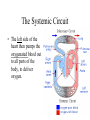
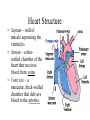
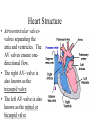
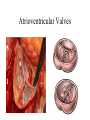
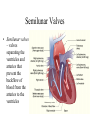
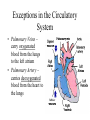
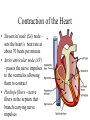
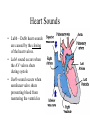
The Circulatory System By: D. Reis The Circulatory System • The circulatory system has 4 principal functions: • Transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide • Distribution of nutrients and transport of wastes • Maintenance of body temperature • Circulation of hormones Pulmonary Circuit • The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen and returns to the left side of the heart. • The Systemic Circuit • The left side of the heart then pumps the oxygenated blood out to all parts of the body, to deliver oxygen. • The Circulatory System • If you are confused as to which way the blood flows through the heart, try this saying "When it leaves the right, it comes right back, but when it leaves the left, it's left." Heart Structure • Septum – wall of muscle separating the ventricles • Atrium – a thinwalled chamber of the heart that receives blood from veins • Ventricle – a muscular, thick-walled chamber that delivers blood to the arteries. • Heart Structure • Atrioventricular valvesvalves separating the atria and ventricles. The AV valves ensure onedirectional flow. • The right AV- valve is also known as the tricuspid valve • The left AV-valve is also known as the mitral or bicuspid valve Atrioventricular Valves Semilunar Valves • Semilunar valves – valves separating the ventricles and arteries that prevent the backflow of blood from the arteries to the ventricles • The Difference between Arteries and Veins • Arteries usually carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to tissues. • Veins usually carry de-oxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart. • THERE ARE SOME IMPORTANT EXCEPTIONS!!!! Exceptions in the Circulatory System • Pulmonary Veins – carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium • Pulmonary Artery – carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs The Right Side of the Heart • The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava (2 large veins). The right atrium pumps blood into the right ventricle . The right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs via the pulmonary artery. In the lungs the deoxygenated blood receives oxygen. The Left Side of the Heart • The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins. The left atrium pumps blood into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body via the AORTA ( the largest artery in the body) • Both ventricles pump blood out of the heart at the same time. Contraction of the Heart • Sinoatrial node (SA) node – • sets the heart’s beat rate at about 70 beats per minute • Atrioventricular node (AV) - passes the nerve impulses to the ventricles allowing them to contract • Purkinje fibers – nerve fibers in the septum that branch carrying nerve impulses Heart Sounds • Lubb – Dubb heart sounds are caused by the closing of the heart valves. • Lubb sound occurs when the AV valves shuts during systole • Dubb sound occurs when semilunar valve shuts preventing blood from reentering the ventricles Heart Murmur • Occurs when the valves do not close completely • A gurgling sound is produced from the blood rushing from the ventricles back to the atria and can be detected with the use of a stethoscope. • The heart compensates for decreased oxygen delivery by beating faster.