* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HERAT PHYSIOLOGY & CONDUTION SYSTEM
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
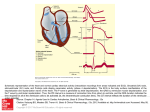
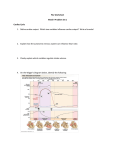
HEART PHYSIOLOGY & CONDUCTION SYSTEM Ana Ribić Mentor: A. Žmegač Horvat PHYSIOLOGY phase 1 - A-V Valves Open, Semilunar Valves Closed p wave of ECG atrial depolarization → atrial contraction → pressure increases → pressure gradient across the AV valves blood flow across the open atrioventricular (AV) valves "a-wave" ventricular end-diastolic volume (EDV) ventricular preload phase 2 - All Valves Closed QRS complex → ventricular depolarization first heart sound (S1) ventricular pressure rises "isovolumetric" contraction phase 3 - Aortic and Pulmonic Valves Open; AV Valves Remain Closed initial and rapid ejection of blood into the aorta and pulmonary arteries from the left and right ventricles total energy of blood ventricular maximal outflow pressure blood continues to flow into atria phase 4 - Aortic and Pulmonic Valves Open; AV Valves Remain Closed after the QRS ventricular repolarization T-wave ventricular pressure falls slightly left atrial and right atrial pressures gradually rise phase 5 - All Valves Closed aortic and pulmonic valves abruptly close second heart sound (S2) isovolumetric relaxation dicrotic wave end-systolic volume LAP continues to rise http://www.google.hr/imgres?imgurl=http://www.stethographics.com/heart/i mages/s123.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.stethographics.com/main/physiology _hs_introduction.html&h=312&w=545&sz=55&tbnid=_Rg21HUd1Y5qXM:&t bnh=76&tbnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dheart%2Bsound&hl=hr&usg=_ _K4rsx1G_XCRY8TFdItVW4Fi9rBw=&ei=dYSeS8m_A4ee_gb0_qn7CQ&sa= X&oi=image_result&resnum=5&ct=image&ved=0CBkQ9QEwBA phase 6 - A-V Valves Open intraventricular pressures fall below their respective atrial pressures ventricular filling third heart sound (S3) phase 7 - A-V Valves Open ventricles continue to fill with blood and expand → intraventricular pressures rise aortic pressure and pulmonary arterial pressures continue to fall CONDUCTION SYSTEM 1. Sinoatrial node (SA node) -sends the electrical impulse that triggers each heartbeat - upper area of the right atrium 2. Atrioventricular node (AV node) sends an impulse through the nerve network to the ventricles 3. Common AV bundle 4. Right & left bundle branches nerve fibers that send impulses that cause the cardiac muscle tissue to contract ELECTROCARDIOGRAM e-lek-tro-KAR-de-o-gram - EKG/ECG painless test that records the heart's electrical activity signal causes the heart to contract and pump blood and creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an electrocardiogram signal causes the heartbeat each heartbeat has two basic parts: diastole and atrial and ventricular systole P wave - represents the wave of depolarization that spreads from the SA node throughout the atria P-R interval -represents the time between the onset of atrial depolarization and the onset of ventricular depolarization QRS complex - ventricular depolarization ST segment - time at which the ventricle is depolarized and corresponds to the plateau phase of the ventricular action potential T wave - represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization Q-T interval - represents the time of both ventricular depolarization and repolarization An EKG shows: how fast your heart is beating whether the rhythm of your heartbeat is steady or irregular the strength and timing of electrical signals as they pass through each part of your heart This test is used to detect and evaluate many heart problems, such as heart attack, arrhythmia and heart failure http://video.google.co m/videoplay?docid=5 7014962196875995 81&ei=NGeS_T5C4rk2gLfoeH0D A&q=heart+conductio n+system&hl=hr# http://www.cvphysiology.com http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov http://www.wisegeek.com metacafe.com