* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System: - Hinsdale Township High School
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
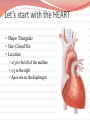
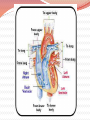
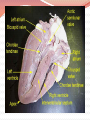
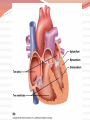
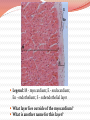
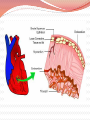
Cardiovascular Structure Why do we need a CV system? The heart pumps blood and blood vessels transport blood, so that Oxygen reaches all cells of the body Carbon dioxide reaches the lungs to be exhaled What other vital components are carried through the blood vessels (in the blood)? Nutrients Hormones WBC’s Blood flows through 60,000 miles of vessels! CV system continued What happens when the blood vessels of your extremities & body surface— Vasodilate? (widen) Blood travels to these areas, releasing heat Vasoconstrict? (narrow) Blood travels to the core, conserving heat Therefore: CV system is also important for temperature regulation Summary Structures of the CV System Heart Blood Vessels Arteries, arterioles Veins, venules Capillaries Functions of the CV System Transport Temperature regulation Let’s start with the HEART Shape: Triangular Size: Closed Fist Location: 2/3 to the left of the midline 1/3 to the right Apex sits on the diaphragm X & 0 are two common areas where heart sounds are checked Chambers of the Heart Two upper chambers– atria (pl.) Right atrium Left atrium Receive blood Two lower chambers- ventricles Right ventricle Left ventricle Pump blood Based on the functions of the atria vs. the ventricles, how do you think their structures differ? Because ventricles pump blood and atria simply receive it, ventricles must have THICK MUSCULAR walls. Heart Structure: Layers Inner lining: endocardium. Wall of the heart: myocardium (cardiac muscle tissue) Outer lining: epicardium Same as the visceral pericardium Legend: M - myocardium; E - endocardium; En - endothelium; S - subendothelial layer What layer lies outside of the myocardium? What is another name for this layer? Pericardium: Outer Sac surrounding the heart, composed of two layers Visceral pericardium (layer closest to the heart, also called the epicardium) Parietal pericardium (outermost layer) Lubrication b/w layers reduces friction