* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
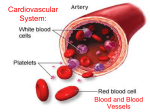
1 Conduction System 2 ECG 3 Cardiac Cycle 4 Cardiac Output 5 Blood Vessels 6 Blood Pressure 7 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $100 $100 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 8 The heart contains this special type of muscle tissue. 9 What is a cardiac muscle tissue? 10 The normal range for heart rate. 11 What is 60-100 bpm? 12 Area of tissue known as “The Pacemaker” of the heart. 13 What is the Sinoatrial (SA) node? 14 The SA node causes the contraction of these two heart chambers. 15 What are the atria? 16 List the five components of the conduction system in order. 17 What are the SA node, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers? 18 The letters ECG stand for this. 19 What is ElectroCardioGram? 20 In an ECG, the P wave represents. 21 What is atrial contraction? 22 In an ECG, the QRS wave represents. 23 What is ventricular contraction and atrial relaxation? 24 Draw a typical ECG and label the waves with the correct letters. 25 26 If a person’s ECG is abnormal and it is found that her own intrinsic conduction system is not working properly this type of medical device my be attached to her heart. 27 What is pacemaker? 28 Name given to the phase of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles contract. 29 What is systole? 30 Name given to the phase of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles relax. 31 What is diastole? 32 Causes the first heart sound – “Lub” 33 What is closure of the AV valves? 34 35 Causes the second heart sound – “Dub” 36 What is closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves? 37 Abnormal or unusual heart sounds caused by turbulent blood flow in the heart are called this. 38 What are heart murmurs? 39 The two factors that determine cardiac output. 40 What are heart rate and stroke volume? (CO=HRxSV) 41 Term used to describe the amount of blood pumped by a ventricle with each beat. 42 What is the stroke volume? 43 This is a person’s cardiac output if his stroke volume is 70ml/beat and his heart rate is 60beats/min. 44 What is 4,200ml/min? 45 If the heart pumps 5250 ml/min. What amount returns to the heart every min.? 46 What is 5250 ml/min.? 47 The total volume of blood in the human body (approximately). 48 What is approximately 5 liters? 49 Type of blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. 50 What is an artery? 51 Type of blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart. 52 What is a vein? 53 Name of blood vessels capable of exchanging materials with body cells. 54 What are capillaries? 55 Structures found in veins that help them to return blood to the heart against gravity. 56 What are valves? 57 58 Type of blood vessel that has a thick muscle layer and elastic tissue. 59 What is an artery? 60 A person’s highest blood pressure occurs during this phase of the cardiac cycle. 61 What is systole or ventricular contraction? 62 Type of blood vessel in which blood pressure is highest. 63 What is the aorta or the major arteries? 64 Type of blood vessel in which blood pressure is the lowest. 65 What are the major veins or the vena cavae? 66 The two factors that determine blood pressure. 67 What are cardiac output and peripheral resistance? (BP=COxPR) 68 The blood in veins is often at such low pressures that it can’t move against gravity to return to the heart. Name a mechanism that helps venous blood return to the heart. 69 What is the muscular pump? 70