* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
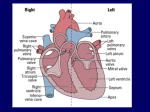
The Heart Anatomy Histology Electrical Properties Cardiac Cycle Grab Bag $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 FINAL ROUND Anatomy: $100 Question The heart is located here: a. inside the pericardial cavity b. in the mediastinum, which is located in the pericardial cavity c. in the mediastinum, which is located in the thoracic cavity d. in the thoracic cavity, which is located in the mediastinum ANSWER BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $100 Answer The heart is located here: a. inside the pericardial cavity b. in the mediastinum, which is located in the pericardial cavity c. in the mediastinum, which is located in the thoracic cavity d. in the thoracic cavity, which is located in the mediastinum BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $200 Question This statement about the epicardium is true: a. is also known as the parietal pericardium b. is a layer of cardiac muscle c. is the visceral pericardium d. lines the heart chambers e. is the pacemaker of the heart ANSWER BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $200 Answer This statement about the epicardium is true: a. is also known as the parietal pericardium b. is a layer of cardiac muscle c. is the visceral pericardium d. lines the heart chambers e. is the pacemaker of the heart BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $300 Question Strong connective tissue strings that are attached to papillary muscles and to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves are called this: a. musculi pectinati (pectinate muscle) b. chordae tendineae c. trabeculae carneae d. the skeleton of the heart e. the interventricular septum ANSWER BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $300 Answer Strong connective tissue strings that are attached to papillary muscles and to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves are called this: a. musculi pectinati (pectinate muscle) b. chordae tendineae c. trabeculae carneae d. the skeleton of the heart e. the interventricular septum BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $400 Question Given these valves: 1. aortic semilunar valve 2. bicuspid (mitral) valve 3. pulmonary semilunar valve 4. tricuspid valve Arrange them in the order in which an erythrocyte would pass through them after returning to the heart from the left arm. a. 1,2,3,4 c. 4,3,2,1 b. 2,3,1,4 d. 3,1,2,4 ANSWER BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $400 Answer Given these valves: 1. aortic semilunar valve 2. bicuspid (mitral) valve 3. pulmonary semilunar valve 4. tricuspid valve Arrange them in the order in which an erythrocyte would pass through them after returning to the heart from the left arm. a. 1,2,3,4 c. 4,3,2,1 b. 2,3,1,4 d. 3,1,2,4 BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $500 Question A blood clot in the anterior interventricular artery would cause a myocardial infarction in this area: a. left atrium and posterior left ventricle b. anterior walls of the left and right ventricles, and interventricular septum c. posterior walls of the left and right ventricles d. lateral walls of the right atrium and ANSWER right ventricle BACK TO GAME Anatomy: $500 Answer A blood clot in the anterior interventricular artery would cause a myocardial infarction in this area: a. left atrium and posterior left ventricle b. anterior walls of the left and right ventricles, and interventricular septum c. posterior walls of the left and right ventricles d. lateral walls of the right atrium and right ventricle BACK TO GAME Histology: $100 Question This statement describes the skeleton of the heart: a. electrically insulates the atria from the ventricles b. is composed of bones and cartilage c. is the location of the pacemaker d. is composed of calcified cardiac ANSWER muscle BACK TO GAME Histology: $100 Answer This statement describes the skeleton of the heart: a. electrically insulates the atria from the ventricles b. is composed of bones and cartilage c. is the location of the pacemaker d. is composed of calcified cardiac muscle BACK TO GAME Histology: $200 Question This structure is NOT present in cardiac muscle cells: a. desmosomes b. gap junctions c. smooth sarcoplasmic reticulum d. terminal cisternae e. transverse (T) tubules ANSWER BACK TO GAME Histology: $200 Answer This structure is NOT present in cardiac muscle cells: a. desmosomes b. gap junctions c. smooth sarcoplasmic reticulum d. terminal cisternae e. transverse (T) tubules BACK TO GAME Histology: $300 Question Intercalated discs include these structures: a. gap junctions, desmosomes, interdigitating folds b. gap junctions, tight junctions, ttubules c. gap junctions, desmosomes, ttubules d. sarcoplasmic reticulum, interdigitating folds ANSWER BACK TO GAME Histology: $300 Answer Intercalated discs include these structures: a. gap junctions, desmosomes, interdigitating folds b. gap junctions, tight junctions, ttubules c. gap junctions, desmosomes, ttubules d. sarcoplasmic reticulum, interdigitating folds BACK TO GAME Histology: $400 Question Damage to cells of the AV bundle would prevent the cardiac impulse from reaching this: a. SA node b. atria c. AV node d. ventricles ANSWER BACK TO GAME Histology: $400 Answer Damage to cells of the AV bundle would prevent the cardiac impulse from reaching this: a. SA node b. atria c. AV node d. ventricles BACK TO GAME Histology: $500 Question Given these structures of the conduction system of the heart: 1. atrioventricular bundle 2. AV node 3. bundle branches 4. Purkinje fibers 5. SA node Choose the arrangement that lists the structures in the order an action potential passes through them. a. 2,5,1,3,4 b. 2,5,3,1,4 c. 5,2,1,3,4 ANSWER d. 2,5,4,1,3 BACK TO GAME Histology: $500 Answer Given these structures of the conduction system of the heart: 1. atrioventricular bundle 2. AV node 3. bundle branches 4. Purkinje fibers 5. SA node Choose the arrangement that lists the structures in the order an action potential passes through them. a. 2,5,1,3,4 c. 5,2,1,3,4 b. 2,5,3,1,4 d. 2,5,4,1,3 BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $100 Question The resting membrane potential (RMP) depends upon this: a. low permeability to Na b. high permeability to K c. low permeability to Ca d. all of these e. none of these ANSWER BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $100 Answer The resting membrane potential (RMP) depends upon this: a. low permeability to Na b. high permeability to K c. low permeability to Ca d. all of these e. none of these BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $200 Question In cardiac muscle cells rapid depolarization is caused by the opening of this: a. voltage-gated Ca2+ ion channels b. voltage-gated K+ ion channels c. voltage-gated Na+ ion channels d. b and c ANSWER BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $200 Answer In cardiac muscle cells rapid depolarization is caused by the opening of this: a. voltage-gated Ca2+ ion channels b. voltage-gated K+ ion channels c. voltage-gated Na+ ion channels d. b and c BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $300 Question This is the normal rate of spontaneous depolarization of the SA node: a. 20 - 40 per minute b. 40 - 60 per minute c. 70 - 80 per minute d. over 100 per minute ANSWER BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $300 Answer This is the normal rate of spontaneous depolarization of the SA node: a. 20 - 40 per minute b. 40 - 60 per minute c. 70 - 80 per minute d. over 100 per minute BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $400 Question In an EKG, the P wave represents this: a. depolarization of the atria b. repolarization of the atria c. depolarization of the ventricles d. repolarization of the ventricles ANSWER BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $400 Answer In an EKG, the P wave represents this: a. depolarization of the atria b. repolarization of the atria c. depolarization of the ventricles d. repolarization of the ventricles BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $500 Question This condition observed in an ECG suggests that the AV node is not conducting action potentials: a. complete lack of the P wave b. complete lack of the QRS complex c. more QRS complexes than P waves d. P waves and QRS complexes are not synchronized e. a prolonged PR interval ANSWER BACK TO GAME Electrical Properties: $500 Answer This condition observed in an ECG suggests that the AV node is not conducting action potentials: a. complete lack of the P wave b. complete lack of the QRS complex c. more QRS complexes than P waves d. P waves and QRS complexes are not synchronized e. a prolonged PR interval BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $100 Question Contraction of the atrial myocardium is called this: a. atrial systole b. atrial diastole c. ventricular systole d. ventricular diastole ANSWER BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $100 Answer Contraction of the atrial myocardium is called this: a. atrial systole b. atrial diastole c. ventricular systole d. ventricular diastole BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $200 Question During the period of ejection in the cardiac cycle, the atrioventricular valves are __________ and the semilunar valves are __________ . a. closed, closed b. closed, open c. open, closed d. open, open ANSWER BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $200 Answer During the period of ejection in the cardiac cycle, the atrioventricular valves are __________ and the semilunar valves are __________ . a. closed, closed b. closed, open c. open, closed d. open, open BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $300 Question Blood flows neither into nor out of the ventricles during this: a. the period of isovolumic contraction b. the period of isovolumic relaxation c. diastole d. systole e. both a and b ANSWER BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $300 Answer Blood flows neither into nor out of the ventricles during this: a. the period of isovolumic contraction b. the period of isovolumic relaxation c. diastole d. systole e. both a and b BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $400 Question Cardiac output is defined as this: a. blood pressure times peripheral resistance b. peripheral resistance times heart rate c. heart rate times stroke volume d. stroke volume times blood pressure e. blood pressure minus peripheral ANSWER resistance BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $400 Answer Cardiac output is defined as this: a. blood pressure times peripheral resistance b. peripheral resistance times heart rate c. heart rate times stroke volume d. stroke volume times blood pressure e. blood pressure minus peripheral resistance BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $500 Question In a person who has a damaged left ventricle due to a heart attack, they would experience this: a. left ventricle pumps less blood than the right b. blood accumulates in the pulmonary vessels c. blood accumulates in the systemic vessels d. won’t have any effect e. a and b ANSWER BACK TO GAME Cardiac Cycle: $500 Answer In a person who has a damaged left ventricle due to a heart attack, they would experience this: a. left ventricle pumps less blood than the right b. blood accumulates in the pulmonary vessels c. blood accumulates in the systemic vessels d. won’t have any effect e. a and b BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $100 Question This occurs at the same time as atrial systole: a. the ventricles are also in systole b. the atrioventricular valves are closed c. blood is being pumped into the aorta and pulmonary trunk d. blood is being pumped into the ANSWER ventricles BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $100 Answer This occurs at the same time as atrial systole: a. the ventricles are also in systole b. the atrioventricular valves are closed c. blood is being pumped into the aorta and pulmonary trunk d. blood is being pumped into the ventricles BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $200 Question This is the effect of norepinephrine on the heart: a. decreases the rate and strength of contraction b. increases the rate and strength of contraction c. decreases the amount of blood pumped per minute ANSWER d. has no effect on the heart BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $200 Answer This is the effect of norepinephrine on the heart: a. decreases the rate and strength of contraction b. increases the rate and strength of contraction c. decreases the amount of blood pumped per minute d. has no effect on the heart BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $300 Question This structure returns blood to the right atrium: a. coronary sinus b. inferior vena cava c. superior vena cava d. both b and c e. all of the above ANSWER BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $300 Answer This structure returns blood to the right atrium: a. coronary sinus b. inferior vena cava c. superior vena cava d. both b and c e. all of the above BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $400 Question A decrease in blood pH and an increase in blood carbon dioxide levels result in this: a. increased heart rate b. increased stroke volume c. increased sympathetic stimulation of the heart d. increased cardiac output e. all of the above ANSWER BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $400 Answer A decrease in blood pH and an increase in blood carbon dioxide levels result in this: a. increased heart rate b. increased stroke volume c. increased sympathetic stimulation of the heart d. increased cardiac output e. all of the above BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $500 Question Damage to this part of the brain would cause the body to have less control over cardiac activity: a. cerebral cortex b. thalamus c. basal nuclei d. medulla oblongata ANSWER BACK TO GAME Grab Bag: $500 Answer Damage to this part of the brain would cause the body to have less control over cardiac activity: a. cerebral cortex b. thalamus c. basal nuclei d. medulla oblongata BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Question All cardiac veins empty into the ______, which then empties into the ______. a. coronary sinus; left atrium b. coronary sinus; right atrium c. great cardiac vein; right atrium d. great cardiac vein; left atrium ANSWER BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Answer All cardiac veins empty into the ______, which then empties into the ______. a. coronary sinus; left atrium b. coronary sinus; right atrium c. great cardiac vein; right atrium d. great cardiac vein; left atrium BACK TO GAME