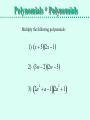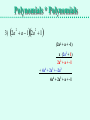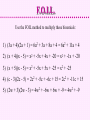* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Use the FOIL Method
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Root of unity wikipedia , lookup
Rook polynomial wikipedia , lookup
Field (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Capelli's identity wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic variety wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Horner's method wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Gröbner basis wikipedia , lookup
Cayley–Hamilton theorem wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial ring wikipedia , lookup
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial greatest common divisor wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Multiplying Polynomials Distribute and FOIL Polynomials * Polynomials Multiplying a Polynomial by another Polynomial requires more than one distributing step. Multiply: (2a + 7b)(3a + 5b) Distribute 2a(3a + 5b) and distribute 7b(3a + 5b): 6a2 + 10ab 21ab + 35b2 Then add those products, adding like terms: 6a2 + 10ab + 21ab + 35b2 = 6a2 + 31ab + 35b2 Polynomials * Polynomials An alternative is to stack the polynomials and do long multiplication. (2a + 7b)(3a + 5b) (2a + 7b) x (3a + 5b) Multiply by 5b, then by 3a: When multiplying by 3a, line up the first term under 3a. Add like terms: (2a + 7b) x (3a + 5b) 21ab + 35b2 + 6a2 + 10ab 6a2 + 31ab + 35b2 Polynomials * Polynomials Multiply the following polynomials: 1) x 52x 1 2) 3w 22w 5 3) 2a a 12a 1 2 2 Polynomials * Polynomials 1) x 52x 1 (x + 5) x (2x + -1) -x + -5 + 2x2 + 10x 2x2 + 9x + -5 2) 3w 22w 5 (3w + -2) x (2w + -5) -15w + 10 + 6w2 + -4w 6w2 + -19w + 10 Polynomials * Polynomials 3) 2a a 12a 1 2 2 (2a2 + a + -1) x (2a2 + 1) 2a2 + a + -1 + 4a4 + 2a3 + -2a2 4a4 + 2a3 + a + -1 Types of Polynomials • We have names to classify polynomials based on how many terms they have: Monomial: a polynomial with one term Binomial: a polynomial with two terms Trinomial: a polynomial with three terms F.O.I.L. There is an acronym to help us remember how to multiply two binomials without stacking them. (2x + -3)(4x + 5) F : Multiply the First term in each binomial. 2x • 4x = 8x2 O : Multiply the Outer terms in the binomials. 2x • 5 = 10x I : Multiply the Inner terms in the binomials. -3 • 4x = -12x L : Multiply the Last term in each binomial. -3 • 5 = -15 (2x + -3)(4x + 5) = 8x2 + 10x + -12x + -15 = 8x2 + -2x + -15 F.O.I.L. Use the FOIL method to multiply these binomials: 1) (3a + 4)(2a + 1) 2) (x + 4)(x - 5) 3) (x + 5)(x - 5) 4) (c - 3)(2c - 5) 5) (2w + 3)(2w - 3) F.O.I.L. Use the FOIL method to multiply these binomials: 1) (3a + 4)(2a + 1) = 6a2 + 3a + 8a + 4 = 6a2 + 11a + 4 2) (x + 4)(x - 5) = x2 + -5x + 4x + -20 = x2 + -1x + -20 3) (x + 5)(x - 5) = x2 + -5x + 5x + -25 = x2 + -25 4) (c - 3)(2c - 5) = 2c2 + -5c + -6c + 15 = 2c2 + -11c + 15 5) (2w + 3)(2w - 3) = 4w2 + -6w + 6w + -9 = 4w2 + -9