* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BITS AND PIECES III INVESTIGATION 3.4 REPRESENTING
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
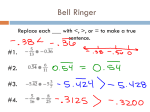
BITS AND PIECES III INVESTIGATION 3.4 REPRESENTING FRACTIONS AS DECIMALS What are terminating decimals? Terminating decimals are numbers that do not repeat when divided. When you take 1 and divide it by 2, you get 0.5. When you take 1 and divide it by 4, you get 0.25. What are repeating decimals? What are repeating decimals? Repeating decimals are numbers that repeat. When doing 1 divided by 3 the number never ends and continuously repeats 3 after 0. When doing 1 divided by 11 the number never ends and continuously repeats 09 after 0. Why do fractions like 1/2 and 1/4 also have terminating decimal forms? Why do fractions like 1/2 and 1/4 also have terminating decimal forms? Because they can make equivalent fractions with denominators of 10, 100, 1000, etc. 1/2 = 5/10; 1/4 = 25/100 1.) 2/5 = 4/10 = 0.4 2.) 3/8 = 375/1000 = 0.375 3.) 5/6 is Repeating = 0.83333...... 4.) 35/10 = 3.5 5.)8/99 is Repeating = 0.8888...... 1.) 2/5 = 4/10 = 0.4 2.) 3/8 = 375/1000 = 0.375 3.) 5/6 is Repeating = 0.83333...... 4.) 35/10 = 3.5 5.)8/99 is Repeating = 0.8888...... 1/4, 2/8, 4/16, 5/20, 6/24, 25/100 = 0.25 The decimal matches the fraction that has 10, 100, 1000, etc. as a denominator 25/100 = 0.25 35/100 21456/10000 89050/100000= 8905/10000 214560/100000= 21456/10000 1/3, 1/6, 1/9, 5/15 1. To tell whether a fraction has a terminating or repeating decimal representation, examine it in its simplest form. Fractions with terminating decimals only have 2’s and/or 5’s in the prime factorization of the denominator. Fractions with repeating decimals will have factors other than 2 or 5 in the denominator. 2. There is no repeating decimal with 10, 100, 1000, etc. as its denominator.